Layered material is used to reproduce materials that have a bottom specular surface plus a top clear coat.
Typical examples are carbon fibers panels, metallic paints, and surfaces that might have reflective specks like granite of manufactured stones.
The layered model is better explained with an illustration where we can visually show what the various parameters do.
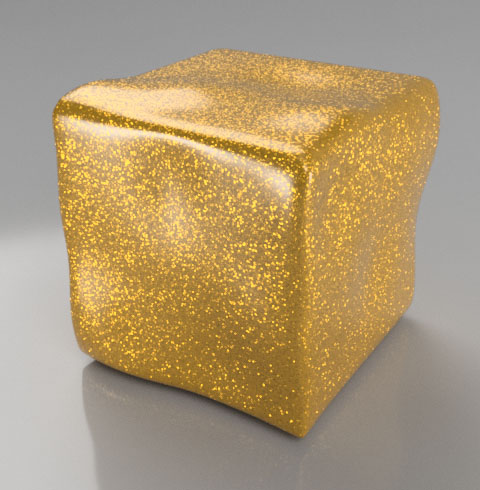 Metallic paint |
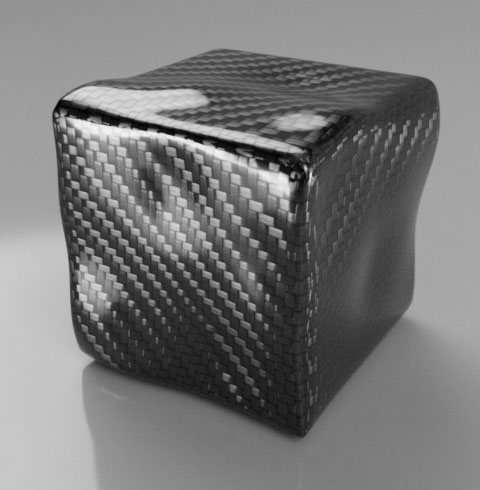 Carbon Fiber |
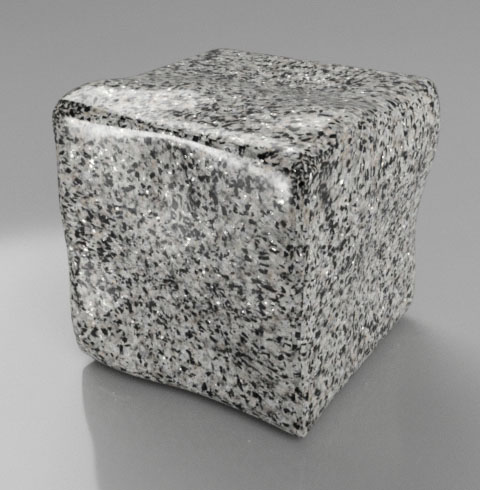 Granite |
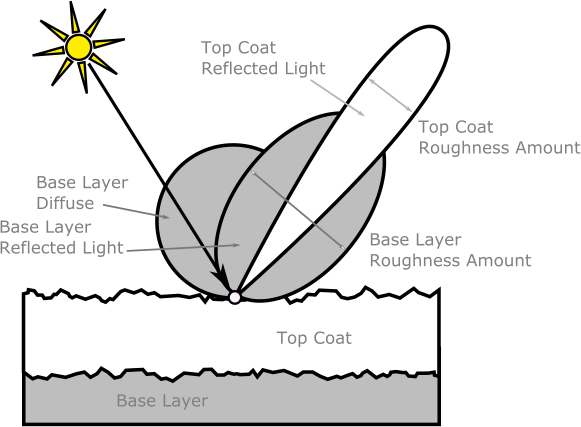
While the top coat layer is always present, Weight selects between the diffuse (0.0) or the metal (1.0) layers underneath, or blends between the two.
There are two typical uses for this lower layer mixing. Using a constant value, you can color the metallic reflections, or using a texture map, you can create highly reflective particles on a mostly diffuse surface.
Layered Material Specific Parameters
- Base Color (or Image)
- This is the color of the base layer where no highlights are present.
- Base Highlights Color
- This is the color of the metallic highlights of the base layer.
- Base Highlights Weight
- This value blends the Base Color and Base Highlights Color with 0.0 showing only the Base Color, and 1.0 showing only the Highlights Color.
- Using a middle of the range value it blends the two colors adding a Base Color hue to the Highlight Color.
- Using a black and white texture it can be used to mask areas where highlights are present from where there is only diffuse color.
-
- Metallic Paint Example
- This example shows how to simulate a typical car paint with embedded metallic flakes.
-

Pick any color you want as the base diffuse color
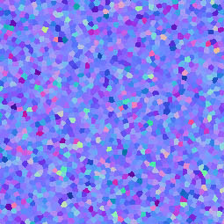
Add a random orientation normal map for the base highlights Relief Pattern

Use a Weight to blend the base color and highlights
- Top Coat is set to be glossy and slightly reflective. The result:

- Carbon Fiber Example
- With Carbon Fiber we use a texture to orient the anisotropy of the highlight layers based on the fibers direction.
-

The base diffuse color is almost black
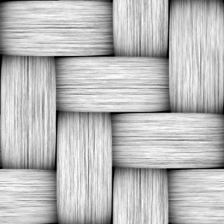
The highlights use a color texture to simulate the small fibers
The anisotropy orientation texture is used to stretch the highlight in the fibers direction
- Base Roughness is set to a high value of at least 0.75, and Anisotropy is set to a value of 0.8 or above. Top Coat is set to be glossy and slightly reflective. The result:

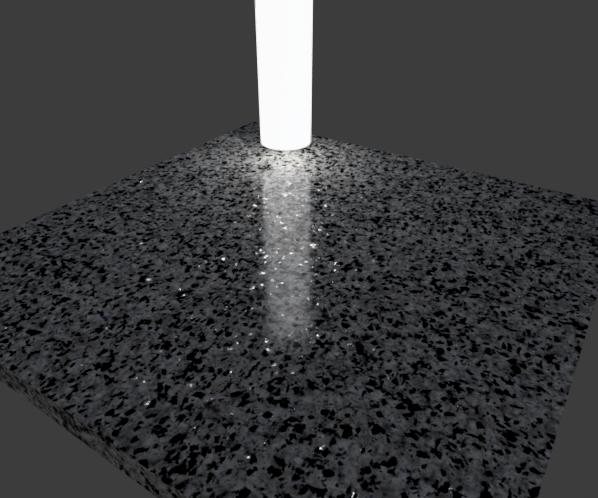
- Granite Example
- This example uses a texture to place highlights only in small areas of the surface where quartz particles strongly reflect incoming light.
-

The Base Color is a granite colored texture

The Weight is used to mask most of the surface and only show highlights in small specks
The Base Highlight Bump (normal map) is used to give the reflective highlights a random orientation

The Top Coat Color uses a texture to create non-reflective pits and random variations to the granite particles
- this is the result, plus an image showing the highlight specks: