Repair a mesh body
Use the Repair tool to repair a mesh body to prepare it for further design and manufacturing operations in Fusion.
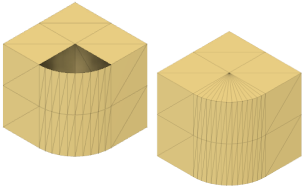
In the Design workspace, on the Mesh tab, select Prepare > Repair
 , or click the warning icon next to the mesh body in the Browser.
, or click the warning icon next to the mesh body in the Browser.The Repair dialog displays.
In the canvas, select a mesh body to repair.
In the dialog, select a Repair Type:
- Close Holes: Makes the fewest number of changes to the mesh body. Fixes flipped triangles and closes holes. (Fastest)
- Stitch and Remove: Makes the same changes as Close Holes, and also stitches triangles, removes double triangles, removes degenerated faces, and removes tiny shells. (Fast)
- Wrap: Makes the same changes as Stitch and Remove, and also wraps the surface of the mesh body. All inner structures are destroyed. (Average)
- Rebuild: Reconstructs the mesh body using one of 4 rebuild types. All inner structures are destroyed. (Slowest)
Optional: For the Rebuild repair type, select a Rebuild Type and adjust associated settings:
- Fast: Rebuilds mesh body quickly, but not accurately.
- Density: Increase or decrease the density of triangles in the mesh body.
- Preserve Sharp Edges: Rebuilds mesh body while preserving sharp edges.
- Density
- Accurate: Rebuilds mesh body as accurately as possible.
- Density
- Offset: Specify the distance to offset the repaired mesh from the original mesh body.
- Adaptive: Rebuilds the mesh using a varying mesh density, using a higher density mesh at key feature locations.
- Blocky: Rebuilds mesh body in a blocky style.
- Density
- Fast: Rebuilds mesh body quickly, but not accurately.
Check or uncheck Preview:
- Unchecked: Displays the original body in the canvas. Quick Analysis and Detailed Analysis display results before applying any repair settings.
- Checked: Displays a preview of the repaired body in the canvas. Quick Analysis and Detailed Analysis display a preview of the results using the current repair settings.
View the Quick Analysis result:
- The Check indicates there are no issues.
- The Warning indicates there are issues to repair:
- Mesh Is Closed: One or more holes or missing faces prevent the mesh body from being watertight.
- Mesh Is Oriented: One or more faces is flipped in the opposite direction from the rest of the mesh body.
- Mesh Has Positive Volume: The majority of faces are oriented in a direction that cannot produce a mesh body with positive volume.
Expand the Detailed Analysis section to view and adjust specific details of the repair:
- View the Issue Type and number of issues Before and After applying the current repair settings.
- Opacity: Adjust the opacity of the mesh body to investigate issues more easily.
- Small Shell Threshold: Specify the maximum size of small shells to repair.
- Degenerate Threshold: Specify the maximum size of degenerate edges and faces to repair.
Click OK.
The repaired mesh body displays in the canvas.
Tips
- A warning icon displays next to the mesh body in the Browser when it contains errors. Hover over the warning icon to display the specific errors, or click it to start the Repair tool.
- Mesh is not closed: One or more holes or missing faces prevent the mesh body from being watertight.
- Mesh is not oriented: One or more faces is flipped in the opposite direction from the rest of the mesh body.
- Mesh does not have positive volume: The majority of faces are oriented in a direction that cannot produce a mesh body with positive volume.
- Use the Close Holes or Stitch and Remove repair types for faster results and fewer changes to the mesh body. For more complex repairs, use the Wrap or Rebuild repair types, but keep in mind that these will take longer to compute and will make more significant changes to the mesh body.
- Use the Repair tool to fix errors in a mesh body to prepare it for further design and manufacturing operations. Errors may include holes in the mesh body or suboptimal arrangement, orientation, or intersection of faces on the mesh body.
- After a significant repair, regenerate and refine face groups on the mesh body, so that they map closely to logical geometric features.