For more information about displacement, see Displacement maps.
Note:
- Avoid using Environment textures for displacement mapping. The basic characteristics of environment mapping preclude accurate calculations when used for displacement mapping.
- During bump or displacement mapping, if an image file contains a mask channel, the mask channel is used for displacement and bump mapping. If the mask channel is absent, the luminance of the RGB is used to displace and, or bump map.
If you prefer to use the luminance information as the alpha, turn on the Alpha Is Luminance attribute (in the Color Balance section of the file texture’s Attribute Editor).
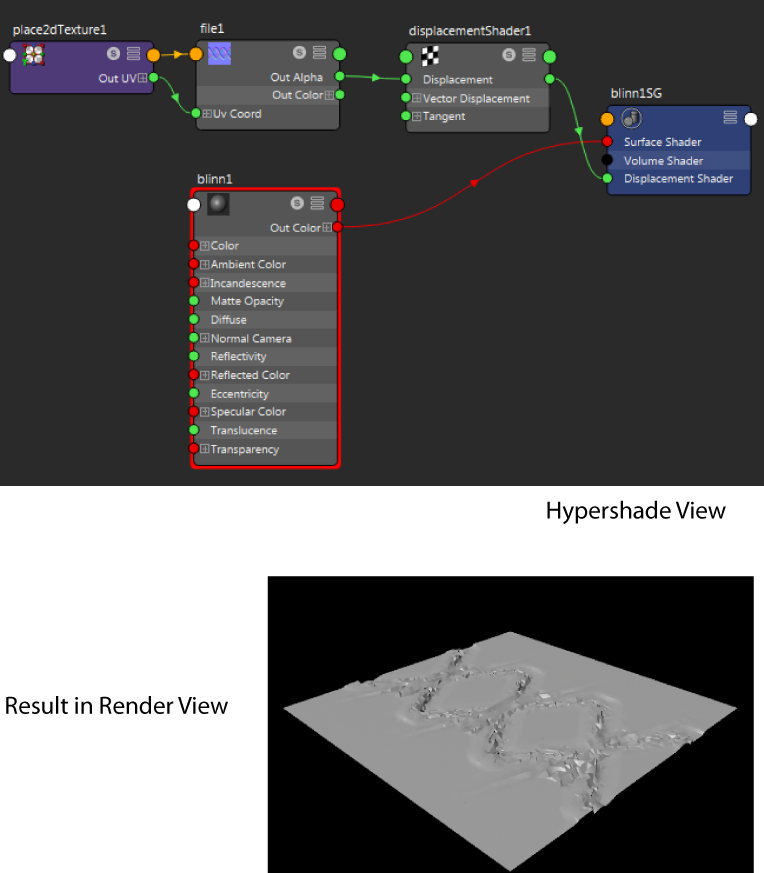
To create a displacement map
- In the Hypershade window, drag and drop the desired material, for example, a Blinn, to the work area to create it, and middle-drag the material swatch onto the object in the viewport to assign it.
- Select the shading group node. In the shading group Attribute Editor, click the map button beside the Displacement mat attribute and assign it a new file node.
- In the file tab, assign the desired image file.
- Click the Render the current frame button to see the render results.
Tip: By default, displacement map results do not display in the viewport. To preview the results, see Preview the displacement results.
You can also use Modify > Convert > Displacement to Polygons to bake the displacement into the actual polygon geometry.