Integration Phase 3: Loading and Unloading NavData
Now that you have some NavData for your terrain, you need to add some code to load it into your Database when you load the corresponding terrain in your game, and to remove it from your Database when it is no longer needed.
To add NavData to a Database, you must:
- Read the data from the .NavData file into memory. In this example, we use a default file opener object provided with the Autodesk Navigation SDK.
- Create an instance of the NavData class, and set it up with a pointer to the data.
- Provide the NavData object to your Database by calling its NavData::AddToDatabaseImmediate() or NavData::AddToDatabaseAsync() method.
Later on in this tutorial, when you integrate NavData generation into your level design tools, you can instead integrate the NavData into the same data loading pipeline you use for your other assets, and use NavData::LoadFromMemory() to set up your NavData instance from the memory location in which you load the NavData. See Integration Phase 6: Using the NavData Generation API.
[code from Tutorial_FirstIntegration.cpp]
#include "gwnavruntime/navdata/navdata.h" #include "gwnavruntime/kernel/SF_File.h" #include "gwnavruntime/base/fileopener.h" ... class MyGameLevel { public: ... bool Initialize(Kaim::World* world); ... void Destroy(); ... protected: Kaim::Ptr<Kaim::NavData> m_navData; ... }; bool MyGameLevel::Initialize(Kaim::World* world) { Kaim::Ptr<Kaim::File> kaimFile; Kaim::DefaultFileOpener fileOpener; // Open the NavData file. const std::string navdataFilePath = TestSystem::Instance().InputDir() + "generated/castle/castle.NavData"; kaimFile = fileOpener.OpenFile(navdataFilePath.c_str(), Kaim::OpenMode_Read); if(kaimFile == KY_NULL) return false; // Instantiate and load the NavData from the file contents. m_navData = *KY_NEW Kaim::NavData; KyResult loadingResult = KY_ERROR; loadingResult = m_navData->Load(kaimFile); // Close the NavData file. kaimFile ->Close(); kaimFile = KY_NULL; // Check that the NavData have been correctly loaded. if (KY_FAILED(loadingResult)) return false; // Add the NavData to the Database. // AddToDatabaseImmediate() forces the new NavData to be added and // stitched immediately in the current frame. In your final game, you // will probably want to use AddToDatabaseAsync(), which time-slices // the addition of the new data over multiple frames to avoid CPU peaks. m_navData->Init(world->GetDatabase(0)); m_navData->AddToDatabaseImmediate(); ... return true; } ... void MyGameLevel::Destroy() { ... m_navData->RemoveFromDatabaseImmediate(); m_navData = KY_NULL; ... } class MyGameWorld { ... public: ... MyGameLevel m_gameLevel; ... }; bool MyGameWorld::Initialize(bool doVisualDebugTutorial) { ... return m_gameLevel.Initialize(m_navWorld); } ... void MyGameWorld::Destroy() { m_gameLevel.Destroy(); ... }
Connect the Navigation Lab to your game.
You will not immediately see the NavMesh in the 3D view of the Navigation Lab. This is normal; to avoid sending potentially large amounts of data across the network, NavData is not sent from the game to the visual debugger. However, it can be very helpful to load the NavData and geometry when debugging to see the debugging data sent from the game in context.
Therefore, the Navigation Lab prompts you to provide a path that contains the NavData files loaded into the game:
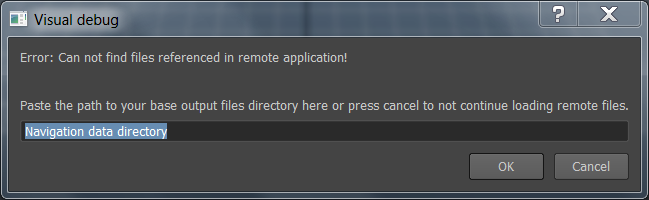
- If you want to load your NavData from your local disk, you can enter the directory name and click OK. The Navigation Lab will append the relative directory that was saved into the NavData (see Integration Phase 2: Generating your First NavData) to the path that you provide here. If it is able to find .NavData and .ClientInput files in the specified directory, it will load them automatically. See the Log window for details on the directories within which it searches for matching NavData.
- Alternatively, you can press Cancel to skip loading the NavData for now. At any time during a live debugging session, you can drag and drop your .NavData file onto the 3D view.
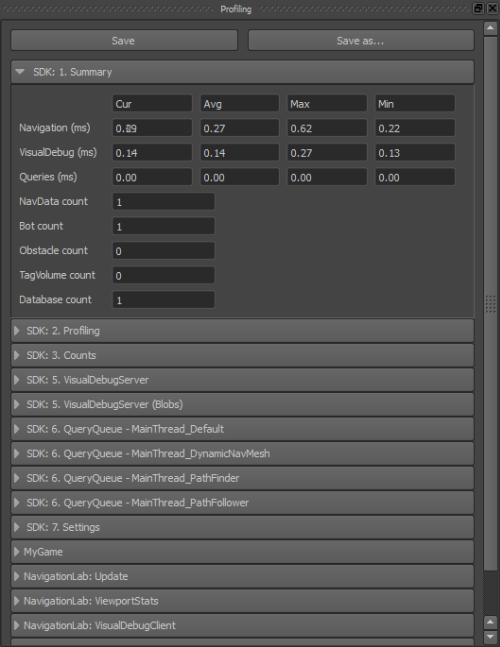
To verify that your NavData has been correctly loaded in the game, open the Profiling panel. In the Summary group, your NavData count value must be greater than 0. If you loaded your NavData into memory using the DefaultFileLoader as shown in the code example above, your Memory Footprint value will also include the size of your data.
Alternatively, you can render the NavData in your game or editor to test whether the NavData is loaded correctly. See Rendering NavData.