Incandescent Metal Material
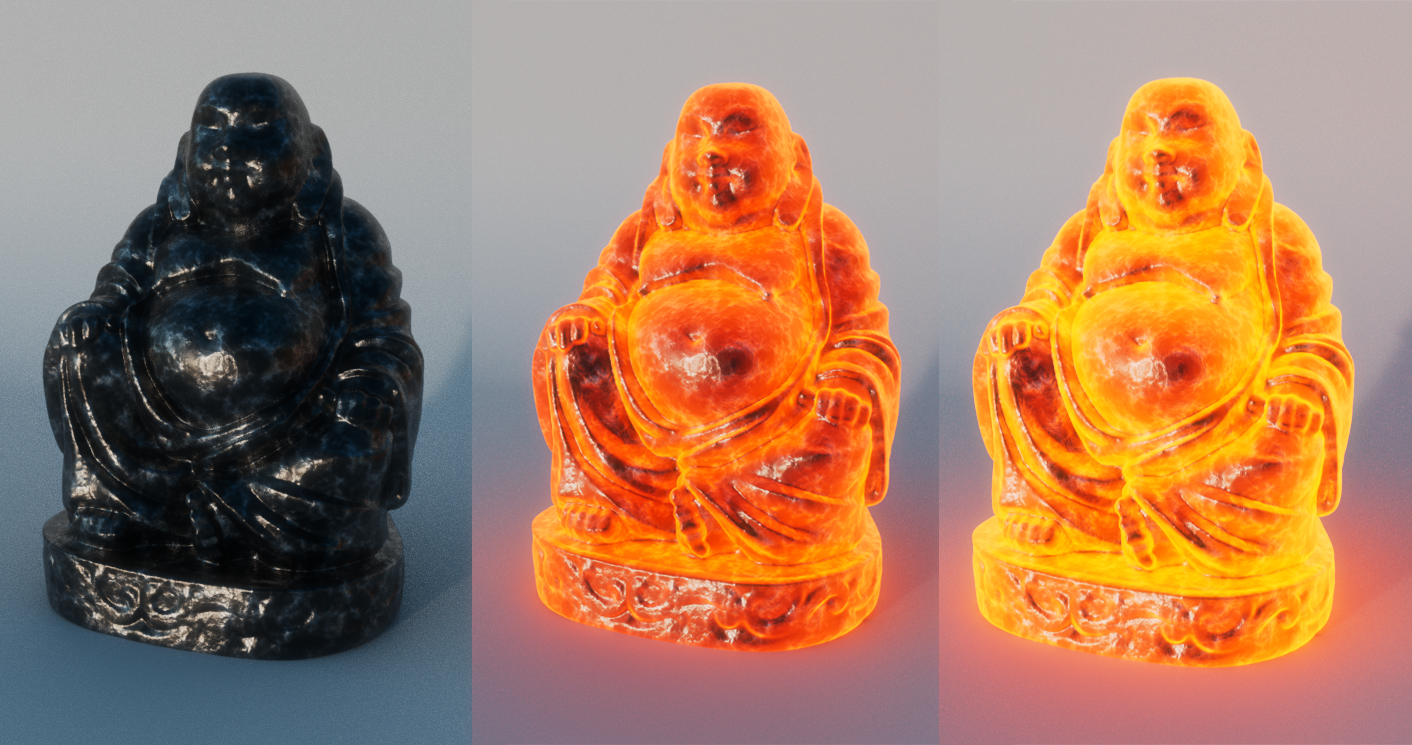

This simple tutorial demonstrates how to create an incandescent metal material. It uses a variety of shaders such as facing_ratio, range, multiply and cell_noise connected to the emission_color of the standard_surface shader. Thanks to Slava Sych for the assistance with this tutorial.
The shader used in this tutorial can be found here.
Standard Surface
Create a standard_surface shader and assign to your model.
- Increase metalness to 1
Cell Noise
Create a cell_noise shader (cell_noise1) and change the following parameters:
pattern : worley2
additive : Enabled
octaves : 4
lacunarity : 1.76
amplitude : 0.72
scale XYZ: 25 25 25 (remember that Scale values depend on the size of your model).
Range shader (range3)
Create a range shader and connect it to the base_weight of the standard_surface shader. Connect the cell_noise shader to the Input of range3 . Change the following parameters:
input_min : 0.249
output_min : 0.3
output_max : 0.7
smoothstep : Enabled
Range shader (range2)
Create another Range shader and change the following parameters:
input_min : 0.3
input_max : 0.7
output_min : 0.1
smoothstep : Enabled
Bump2D
Create a bump2D shader and change the bump_height to 0.02. Connect the range shader (range2) to bump_map in the bump2d shader, and connect the bump2d shader to normal of the standard_surface shader.
Facing Ratio
Create a facing_ratio shader and change the following parameters:
bias : 0.6
gain : 0.48
linear : Enabled
invert : Enabled
Color Correct
- Create a color_correct shader. Change the input color RGBA to: 2.9642 0.5212 0 1
Connect the facing_ratio shader and color_correct shaders to a multiply shader (multiply1).
Range Shader (range4)
Create another range shader and change the following parameters:
input_min : 0.249
input_max : 0.484
output_min : 0.7
output_max : 1
Enable smoothstep
Connect the cell_noise shader (cell_noise1) to the input of the range shader (range4).
Create a multiply shader (multiply2) . Connect multiply1 to the Input 1 of multiply2.
Connect the range shader (range4) to input2 of multiply2.
Range shader (range 1)
Create a range shader.
- Change the output_max to 3.
Connect the multiply shader (multiply2) to the input of range shader (range1) . This is required for the higher value color intensity values.
Connect the range shader (range1) to the emission_color of the standard_surface shader.
Now it is possible to control the incandescence using the emission_weight (0 to 1). If you require more intensity, increase the output_max value in range shader (range1).
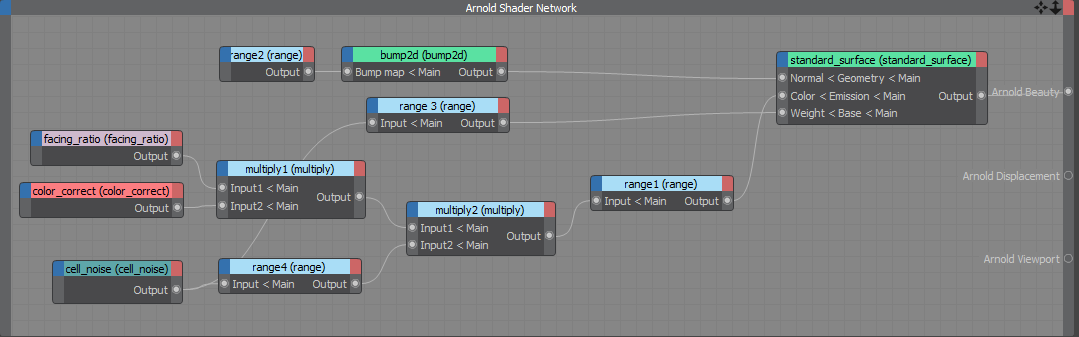
Final shading network