Plasticity in Compression
Prior to the load drop, the compressive plasticity model is the same as the tensile plasticity model. The plasticity response is driven by the effective plastic strain, εp,eff which evolves regardless if the instantaneous stress state is tensile or compressive. In other words, we perform the same calculations for tension and compression to determine the evolution of the effective plastic strain for each prescribed increment.
If the stress or strain state happens to be tensile, we use the tensile version of the plasticity parameters: σ0+, n+, α+, and β+. If the stress or strain state happens to be compressive, we use the compressive version of the plasticity parameters: σ0-, n-, α-, and β-.
Determine State of Loading
We perform two checks to determine whether the load state is tensile or compressive dominated. First, we use the strain state. To do so, we evaluate the hydrostatic strain of the composite which is defined as:
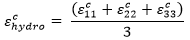
If εchydro < 0, the composite strain state is compression dominated and we skip the second check. If εchydro > 0, the composite strain state is tension dominated and we perform a second check using the hydrostatic stress of the composite.
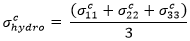
If σchydro < 0, the composite stress state is compression dominated. If σchydro > 0, the composite stress state is tension dominated.
