Use the material volumes functionality to extract and report sectional material volumes, based on sample line groups.
You can create tables and reports for:
- Volumes along an alignment, comparing various design surfaces and existing ground surfaces.
- Volumes for shapes, which are closed cross-sectional areas created by a single subassembly. For example, a curb (a closed area within a concrete curb or curb and gutter).
You can display material volume information using standard Autodesk Civil 3D table formats, or view and export the information in an XML format file.
Material volume reporting uses criteria settings that are portable and extensible. You can create criteria based either on existing data, including surfaces and sample line groups, or on standard surface names.
You prepare to generate material volume information by creating a list of materials and applying the predefined criteria to it, mapping existing surfaces or other objects to the names in the criteria. After the material list is generated, the settings and volume calculations are stored with the sample line group and can be used to generate tables and reports.
Sectional Volume Methods
When you compute the materials for a sample line group, you can use three different volume calculation methods: Average End Area, Prismoidal, or Composite.
- If the cut/fill areas between two successive stations are of similar shape, then the Average End Area Method can be used.
- If the terrain has greater changes between stations, then the Prismoidal Method can be more accurate.
- The Composite Method uses the actual surface data and does not use formulas to interpolate the volume between sample lines. This method is particularly useful if the any of the surface triangle edges are smaller than the sample line interval.
You can specify which volume method to use in the following dialog boxes:
- Compute Materials. For more information, see To Generate a Material List for a Sample Line Group.
- Edit Material List. For more information, see To Generate a Material List for a Sample Line Group.
- Sample Line Group Properties, Material List tab. For more information, see To Edit Sample Line Group Properties.
Average End Area Method
The Average End Area method calculates volumes by adding the area of a material type at one station to the area of the material type at the next station and dividing the sum by two, then multiplying the result by the distance between the sections (L).
Prismoidal Method
The Prismoidal method is similar to the Average End Area method but uses an additional cross section at the middle of the two successive stations.
Composite Method
The Composite method is limited to material lists that have only two surfaces and cannot be used for material lists that contain corridor shapes.
To calculate composite volumes, Autodesk Civil 3D creates polygons between sample lines and then computes the bounded volumes of those polygons. The polygons are created by joining the offsets of the sample lines between two successive stations, as shown in the following illustration.
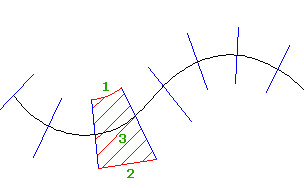
- If the offsets are uniform, then a line that matches the curvature of the centerline is used to join the sample lines (1).
- If the offsets are not uniform, then a straight line is used to join the sample lines (2).
- The composite volume is then calculated for the area within the polygon (3) for each material in the material list of the sample line group.
The volume is recorded at the second sample line of the polygon. The first sample line in the sample line group will therefore have zero volume associated with it.