In sequential searches, the input type specifies how the user communicates the next sub-searches. The main difference is in the execution of the search, as in the following input types:
- Selection List (default)—You can select further search items from a combo box. In this case, the select statement has already been executed.
- Text Box—You have to enter the search text. Then, the query is executed. The search text is part of the WHERE clause in the SQL statement.
- Text Box With Auto Complete— You do not have to enter the complete search text. The search starts as soon as you start to enter the text. The search text is part of the WHERE clause in the SQL statement.
Text Box Examples
To find table names, define the following SQL statement:
select f_class_name from tb_dictionary where upper(f_class_name) like upper('{0}')
Using this definition in AutoCAD Map 3D toolset, for example, you enter "lm_b*". At runtime, the placeholder {0} is replaced by the character the user has entered. The * is replaced with a "%" and all tables starting with LM_B* are displayed.
To find street names with a text box, use the following SQL statement that includes a LIKE statement and uses the placeholder {0}.
select distinct LABEL_TEXT from LM_STREET_TBL where LABEL_TEXT like ('{0}') and GEOM is not NULL order by LABEL_TEXT
Text Box With Auto Complete Example
To find table names, use the same SQL statement:
select f_class_name from tb_dictionary where upper(f_class_name) like upper('{0}')
For example, using this definition in AutoCAD Map 3D toolset, you start to enter any character. At runtime, the placeholder {0} is replaced by the character the user has entered plus a prefix %. The result is all tables that start with A, as shown in the following SQL statement:
select f_class_name from TB_dictionary where UPPER (f_class_name) like UPPER ('A%')
Selection List Example
To find street names, use the following SQL statement:
select distinct LABEL_TEXT from LM_STREET_TBL where GEOM is not NULL order by LABEL_TEXT
The following diagram shows the workflow with different input types.
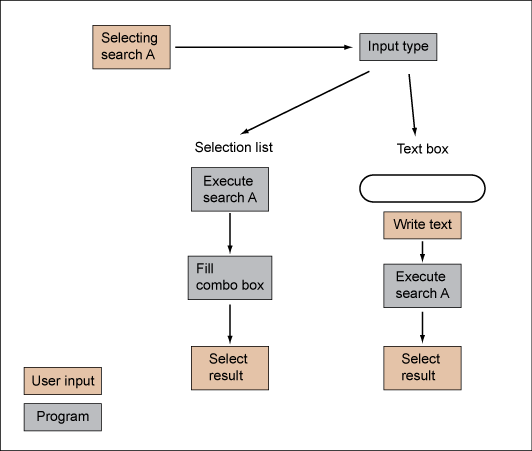
Feature Search: Sequential search workflow with different input types.