3D Camera Parameters
Basics Tab
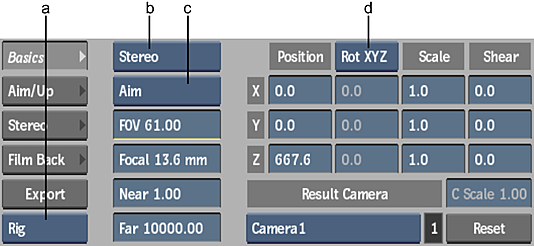
(a) Stereo Camera View Type box (b) 3D Camera Type box (c) Camera Type box (d) Rotation Order box
Export FBX Camera button
Opens the Export Camera file browser to save an FBX camera.
Stereo Camera View Type box
Available when Stereo is selected in the 3D Camera Type box. Select Left, Right, or Rig (for Stereo Rig).
3D Camera Type box
Select whether the 3D camera is stereo or mono.
Camera Type box
Select whether the camera is Free, Aim, or Aim and Up.
| Select: | For: |
|---|---|
| Free | Static scenes and for simple animations (up, down, side-to-side, in and out), such as panning out of a scene. A Free camera views the scene in the direction that you aim the camera. You can simply animate the camera rotation or camera tilt as though it were on a tripod. Use the Rotation fields in conjunction with a Free camera. |
| Aim | Slightly more complex animations (along a path, for example), such as a camera that follows the erratic path of a bird. The Aim camera ensures the camera is specifically aimed at a target object in the scene. Use the Roll and Aim fields in conjunction with the Aim camera. |
| Aim and Up | Complex animations, such as a camera that travels along a looping roller coaster. Use the Aim and Up camera to specify which end of the camera must face upward. Use the Roll, Aim, and Up fields in conjunction with the Aim and Up camera. |
FOV field
Displays the angular field of view value, measured in degrees. Use to adjust the width of the camera frustum. Editable.
Focal Length field
Displays the focal length of the camera lens, measured in millimeters. Increasing zooms the camera in and increases the size of objects. Decreasing zooms the camera out and decreases the size of objects. Editable.
Near Clipping Plane field
Displays the position of the near clipping plane, in pixels, which represents the distance from the camera to the closest point within which image details are processed. Editable.
Far Clipping Plane field
Displays the position of the far clipping plane, in pixels, which represents the distance from the camera to the farthest point within which image details are processed. Editable.
See Moving the Near and Far Clipping Planes.
X Position field
Displays the position of the camera, in pixels, on the horizontal (X) axis. Editable.
Y Position field
Displays the position of the camera, in pixels, on the vertical (Y) axis. Editable.
Z Position field
Displays the position of the camera, in pixels, on the perpendicular (Z) axis. Editable.
Rotation Order box
Select the order in which the camera is rotated, on the horizontal, vertical, and perpendicular (X, Y, and Z) axes.
X Rotation field
Displays the level of rotation of the camera on the horizontal (X) axis, in degrees. Active when Camera Type is set to Free. Editable.
Y Rotation field
Displays the level of rotation of the camera on the vertical (Y) axis, in degrees. Active when Camera Type is set to Free. Editable.
Z Rotation field
Displays the level of rotation of the camera on the perpendicular (Z) axis, in degrees. Active when Camera Type is set to Free. Editable.
X Scale field
Displays the scale of the camera on the horizontal (X) axis, as a percentage. Editable.
Y Scale field
Displays the scale of the camera on the vertical (Y) axis, as a percentage. Editable.
Z Scale field
Displays the scale of the camera on the perpendicular (Z) axis, as a percentage. Editable.
X Shear field
Displays the shearing of the camera (diagonal shift) on the horizontal (X) axis, as a percentage. Editable.
Y Shear field
Displays the shearing of the camera (diagonal shift) on the vertical (Y) axis, as a percentage. Editable.
Z Shear field
Displays the shearing of the camera (diagonal shift) on the perpendicular (Z) axis, as a percentage. Editable.
Result Camera box
Specify which camera is active. The active camera is the one that will be used when processing/rendering your scene.
Camera Scale field
Displays the size of the camera relative to the scene, independently for either Left or Right camera views. For example, if Camera Scale is set to 0.5, the camera's view covers an area half as large, but objects in the camera's view are twice as large. If Focal Length is set to 35, the effective focal length for the camera would be 70. Editable.
Reset button
Resets the 3D Camera menu to its default settings.
FBX Unit Scaling field
This locked field displays the scale factor of the FBX camera used within the application. Use to help set the Pixels to FBX Units field when exporting an FBX camera. Non-editable.
Not shown in the screenshot above.
Aim/Up Tab
When Camera Type is set to Aim or Aim and Up, the available options are enabled in the Aim/Up tab.
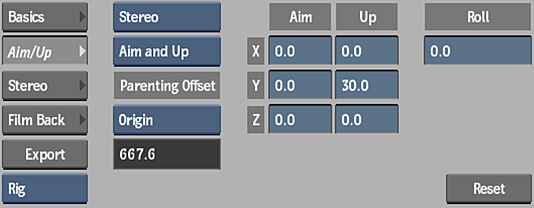
3D Camera Type box
Select whether the 3D camera is stereo or mono.
Camera Type box
Select whether the camera is Free, Aim, or Aim and Up.
| Select: | For: |
|---|---|
| Free | Static scenes and for simple animations (up, down, side-to-side, in and out), such as panning out of a scene. A Free camera views the scene in the direction that you aim the camera. You can simply animate the camera rotation or camera tilt as though it were on a tripod. Use the Rotation fields in conjunction with a Free camera. |
| Aim | Slightly more complex animations (along a path, for example), such as a camera that follows the erratic path of a bird. The Aim camera ensures the camera is specifically aimed at a target object in the scene. Use the Roll and Aim fields in conjunction with the Aim camera. |
| Aim and Up | Complex animations, such as a camera that travels along a looping roller coaster. Use the Aim and Up camera to specify which end of the camera must face upward. Use the Roll, Aim, and Up fields in conjunction with the Aim and Up camera. |
Parenting Offset box
Select an offset option for viewing an image when parenting a camera node. Origin sets the image to the camera origin; Target sets the image to the default viewplane distance relative to the camera; and Live Target sets the image to the current viewplane distance based on the FOV.
Parenting Offset field
Displays the offset value, as computed from the default camera field of view and the default image size. This value does not change even if other camera parameters are changed. Non-editable.
X Aim field
Displays the position of the aiming target of the camera on the horizontal (X) axis, in pixels. Editable.
Y Aim field
Displays the position of the aiming target of the camera on the vertical (Y) axis, in pixels. Editable.
Z Aim field
Displays the position of the aiming target of the camera on the perpendicular (Z) axis, in pixels. Editable.
X Up field
Displays the up direction on the horizontal (X) axis, in pixels. Editable.
Y Up field
Displays the up direction on the vertical (Y) axis, in pixels. Editable.
Z Up field
Displays the up direction on the perpendicular (Z) axis, in pixels. Editable.
Roll field
Displays the amount of camera roll, in degrees. A positive value rolls the camera clockwise, where a negative value rolls it counter-clockwise. Available only with the Aim, and Aim and Up cameras. Editable.
Stereo Tab
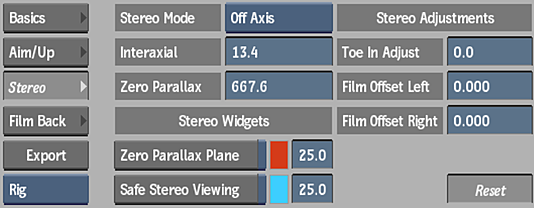
Stereo Mode box
Select the method for computing the zero parallax plane.
| Select: | To: |
|---|---|
| Converged | Compute the zero parallax plane by toeing-in the cameras. You can compare this effect to our focusing on an object by rotating our pupils inwards. However, a dangerous side effect may occur where you get a keystone effect on the pairs of render images, causing visual confusion in other elements in the scene. In a rendered image, our focus tends to cascade over the entire image and we are not focusing on a single object, which is not true in real life. You should only use Converged when an object is at the center of the screen with no scene elements at the render borders on either the left or right camera frustum. |
| Off-axis | Compute the convergence plane by shifting the frustum using camera film back. This is the safer way to compute stereo image pairs and avoids keystone artifacts. Off-axis is the default setting. |
| Parallel | Create a parallel camera setup where there is effectively no convergence plane. This is useful for landscape settings where objects exist at infinite focus. |
Interaxial Separation field
Displays the distance between the left and right cameras, in pixels. Editable.
Zero Parallax field
Displays the distance on the camera view axis, in pixels, where the zero parallax plane occurs (the point where objects appear off screen). Objects in front of the zero parallax plane have negative parallax. Objects behind the zero parallax plane have positive parallax. Editable.
Zero Parallax Plane button
Enable to display the zero parallax plane.
Zero Parallax colour pot
Displays the colour used for the zero parallax plane. Editable.
Zero Parallax Transparency field
Displays the level of transparency for the zero parallax plane. Editable.
Safe Stereo Viewing Volume button
Enable to display the safe viewing volume created by the intersection of the frustum of the left and right cameras.
Safe Stereo Volume colour pot
Displays the colour used for the safe stereo viewing volume. Editable.
Safe Stereo Volume Transparency field
Displays the level of transparency for the safe stereo viewing volume. Editable.
Toe In Adjust field
Displays the offset, in degrees, applied to the computed toe-in effect when Stereo Mode is set to Converged. Editable.
Film Offset Left Cam field
Displays the horizontal film offset for the left camera. Editable.
Film Offset Right Cam field
Displays the horizontal film offset for the right camera. Editable.
Film Back Tab
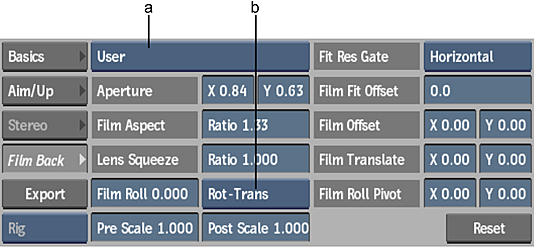
(a) Film Gate box (b) Film Roll Rotation Order box
Film Gate box
Select a preset film frame format type. This action automatically sets the corresponding Camera Aperture, Film Aspect Ratio, and Lens Squeeze Ratio. To set these attributes individually, set Film Gate to User. The default setting is User.
Camera Aperture X field
Displays the width of the camera Film Gate setting, measured in inches. This setting has a direct effect on the camera's angle of view and automatically updates Film Aspect Ratio. Editable.
Camera Aperture Y field
Display the height of the camera Film Gate setting, measured in inches. This setting has a direct effect on the camera's angle of view and automatically updates Film Aspect Ratio. Editable.
Film Aspect Ratio field
Displays the ratio of the camera aperture width versus height. Modifying this field automatically updates the Camera Aperture fields. Editable.
Lens Squeeze Ratio field
Displays the amount horizontal compression that is applied to the image. Used with some cameras (for example, anamorphic cameras), which compress the image horizontally to record a wider aspect ratio image onto a square area on film. Editable.
Film Roll Value field
Displays the amount of rotation applied to the film back. The rotation occurs around the specified pivot point. Used to compute a film roll matrix, which is a component of the post-projection matrix. Editable.
Film Roll Rotation Order box
Select how the roll is applied with respect to the pivot value.
| Enable: | To: |
|---|---|
| Rotate-Translate | First rotate the film back, then translate it by the pivot point value. |
| Translate-Rotate | First translate the film back, then rotate it by the film roll value. |
Pre Scale field
Displays the artificial 2D camera zoom that is applied before the film roll. Used in 2D effects. Editable.
Post Scale field
Displays the artificial 2D camera zoom that is applied after the film roll. Used in 2D effects. Editable.
Film Fit Resolution Gate box
Select the size of the resolution gate relative to the film gate (Film fit). If the resolution gate and the film gate have the same aspect ratio, then the Film Fit setting has no effect.
| Select: | To: |
|---|---|
| Fill | Fit the resolution gate within the film gate. |
| Horizontal | Fit the resolution gate horizontally within the film gate. |
| Vertical | Fit the resolution gate vertically within the film gate. |
| Overscan | Fit the film gate within the resolution gate. |
Film Fit Offset field
Displays the offsets of the resolution gate relative to the film gate either vertically (if Film Fit Resolution Gate is Horizontal) or horizontally (if Film Fit Resolution Gate is Vertical). Film Fit Offset has no effect if Film Fit Resolution Gate is Fill or Overscan. Editable.
Film X Offset field
Displays the horizontal offset, in pixels, of the resolution gate and the film gate relative to the scene. Changing the Film X Offset produces a two-dimensional track. Editable.
Film Y Offset field
Displays the vertical offset, in pixels, of the resolution gate and the film gate relative to the scene. Changing the Film Y Offset produces a two-dimensional track. Editable.
| Enter: | To: |
|---|---|
| 1 | Have the view guide fill the view. The edges of the view guide may be exactly aligned with the edges of the view, in which case the view guide is not visible. |
| > 1 | Increase the space outside the view guide. The higher the value, the more space is outside the view guide. |
Film X Translate field
Displays the artificial 2D horizontal camera pan. Used in 2D effects. Editable.
Film Y Translate field
Displays the artificial 2D vertical camera pan. Used in 2D effects. Editable.
Film Roll X Pivot field
Displays the horizontal pivot point from the center of the film back, which is used during the rotating of the film back. Used to compute the film roll matrix, which is a component of the post projection matrix. Editable.
Film Roll Y Pivot field
Displays the vertical pivot point from the center of the film back, which is used during the rotating of the film back. Used to compute the film roll matrix, which is a component of the post projection matrix. Editable.
