You can configure the location for external rules and DLL files, disable DoubleForEquals, and specify the default Microsoft Excel Engine to be used by iLogic.
What's New: R2021
Configure location for external rules and DLL files
- On the ribbon, click
Tools tab
 Options panel
Options panel
 iLogic Configuration.
iLogic Configuration.
- Click
 next to External Rule Directories to add a folder to the list, and use the up and down arrows to define the search order.
next to External Rule Directories to add a folder to the list, and use the up and down arrows to define the search order.
- Choose a file extension in the Default Extension for External Rule Files field.
- .vb files can be edited in Visual Studio.
- .txt files can be edited using a text editor such as Microsoft Notepad.
- .iLogicVb indicates that the file contains standard iLogic rule code to be preprocessed by iLogic.
- Select the folder containing code from other .NET assemblies in the iLogic Addin DLLs Directory field.
- To export an iLogic configuration: Export
 Enter the file name or select an existing file to replace
Enter the file name or select an existing file to replace  Save.
Save.
- To Import an iLogic configuration: Import
 Locate file to import
Locate file to import  Open.
Open.
- Click OK.
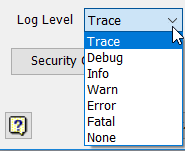
Log Level
Use the Log Level setting to set the log level to use for iLogic Logging and rule tracing in the Rules Editor.
Excel Options
Use the Excel Options setting to specify the default Microsoft Excel Engine to be used by iLogic. This is an application-level option.
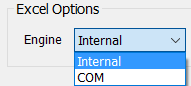
The default Microsoft Excel Engine is Internal. Internal is a library that provides fast access to Excel data, although there are limitations. Excel COM is the Microsoft Office Excel API. It can be used only when Excel is installed on the computer. This is an application-level option. Select Excel COM if you have Excel rules that use the iLogic GoExcel object to do any of the following:
- Write to an embedded spreadsheet.
- Use the GoExcel.Automation object.
- Read (from Excel) a cell value that must be recalculated.
iLogic can detect the first two cases automatically, and it will switch the option over to COM automatically. However, iLogic can't detect the third case. Here are some examples of workflows that will not work with the Internal option and only work with the COM option. If you have these types of rules, select COM as the engine.
- Example 1: If you have a spreadsheet in which cell B1 has a formula that refers to cell A1 and:
- The rule writes to cell A1.
- The spreadsheet recalculates, and the value in cell B1 is modified.
- The rule reads from cell B1.
- Example 2:
If you have a spreadsheet in which cell B1 has a formula that refers to cell B5 and cell B1 holds the value of a linked parameter (the link was created by using the Link button in the Parameters dialog).
- A rule writes to cell B5.
- The spreadsheet recalculates, and the value in cell B1 is modified.
- The spreadsheet is saved (using the GoExcel.Save statement in the rule).
- Inventor reads the new parameter value from cell B1. With the Internal option selected, the spreadsheet will not be recalculated. Therefore the parameter value will not be updated.
- iLogic Configuration dialog box.
- API.
- Environment variables. Environment variables have priority. If one of the following environment variables is set, then setting the default through the dialog box or API can't be used.
- set UseLibXL=false
- set iLogicUseLibXL=false
The UseLibXL variable affects other Excel operations in Inventor. iLogicUseLibXL affects only iLogic.
| Dim auto = iLogicVb.Automation
auto.ExcelEngine = ExcelEngine.COM ' or auto.ExcelEngine = ExcelEngine.Internal |
Security
Click the Security Options button to access the iLogic Security dialog box. Use these settings to enable security checks for identifying unsafe rules
 .
.
Disable DoubleForEquals
DoubleForEquals is the default type for all numeric Inventor parameters used in rules.
Use the following statement at the beginning of a rule to disable this setting:
iLogicOption DoubleForEquals Off
This statement is like the standard Visual Basic Option statement.
