With the data model administrator, while creating feature classes, you can set spatial properties to control the spatial behavior during spatial selections. This option is available for Oracle enterprise industry models only, but SQL Spatial and SQLite industry models can apply spatial masks that use these operators (or their equivalents). See "About Displaying Features Using an Oracle Spatial Filter" in the AutoCAD Map 3D toolset User's Guide.
You can define geographic selections with topology queries or spatial operators. For example, in when using the Advanced Generate Graphic dialog box in the AutoCAD Map 3D toolset Maintenance workspace, use the Advanced Settings button.
The SDO_RELATE operator performs both primary and secondary filter operations, where the mask parameter specifies the topological relation of interest.
Examples: Spatial Operator SDO_RELATE
Topological relations:
- SDO_RELATE: spatial operator for evaluation of topological relations.
- Each spatial object has an interior, boundary, and exterior.
- The boundary separates interior and exterior.
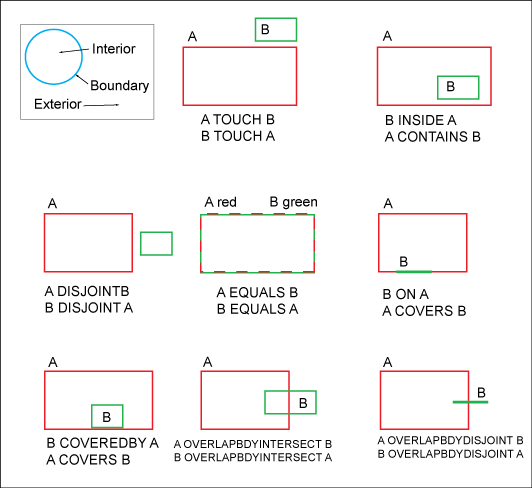
Oracle Spatial SDO_RELATE operator: Intersection patterns
Names of topological relationships:
These are the following spatial intersection patterns:
- CONTAINS
The interior and boundary of one object is completely contained in the interior of the other object.
- COVERS
The interior of one object is completely contained in the interior of the other object, and their boundaries intersect.
- COVEREDBY
The opposite of COVERS. A COVEREDBY B implies that B COVERS A (Demarcations of two objects which partially cover themselves, and the interior of the other object is completely contained within the object).
- DISJOINT
The boundaries and interiors do not intersect.
- EQUAL
The two objects have the same boundary and interior.
- INSIDE
The opposite of CONTAINS. A INSIDE B implies that B CONTAINS A (Boundary and interior of one object are completely inside the other object).
- OVERLAPBDYINTERSECT
The boundaries and interiors of the two objects intersect.
- OVERLAPBDYDISJOINT
The interior of one object intersects the boundary and interior of the other object, but the two boundaries do not intersect. Example: When a line originates outside a polygon and ends inside that polygon.
- TOUCH
The boundaries intersect, but the interiors do not intersect.
For more information, see Oracle Spatial Users Guide and Reference.