Environmental impact
Users have the option to consider the environmental aspects of the materials being used.
Materials will typically be selected on criteria such as strength and functionality of the finished part. Once these primary considerations have been met, environmental factors can help finalize material selection.
Note: The classifications are for the base polymer only. The effect of fillers and additives should be reviewed seperately.
Energy usage indicator
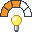
The Energy usage indicator is a relative assessment of the energy requirements of the molding phase of a part, based on the material selected. The result of this assessment is a relative value derived from the injection pressure and cooling time predictions for a suite of typical geometries and thicknessess using the material's recommended conditions and processing inputs determined by an optimization calculation.
These results were standardized and an Energy usage indicator value was applied.
It is expected that existing polymer Energy usage indicator ratings will change as more environmentally efficient polymers are developed.
| Energy usage indicator | Value |
|---|---|
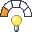 | Least energy required for the production of a part |
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 | Most energy required for the production of a part |
 | Not available |
Note: The Energy usage indicator may not available for two reasons:
- Legacy material data from a personal database or a previous study may not include environmental information. Reload the material from the current database to view these parameters.
- The calculations for a small number of materials cannot return an injection pressure or cooling time for all the geometries tested.
Resin identification code
This code identifies the resin family to which the material belongs.
Note: Any materials that are a blend or contain fillers have been included in the Other category.
| Icon | Plastic family |
|---|---|
 | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET, PETE) |
 | High density polyethylene (HDPE) |
 | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
 | Low density polyethylene (LDPE) |
 | Polypropylene (PP) |
 | Polystyrene (PS) |
 | Other. Incudes any resin not specifically listed. This category also includes all materials that are blends or contain fillers. |
 | Undetermined, for example, legacy data |
Biodegradable
This describes the biodegradability of the material. A material is considered biodegradable if it is capable of being decomposed by bacteria or other living organisms, and thereby avoids pollution.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Yes | The material is biodegradable. |
| No | The material is not biodegradable. |
| Unknown | The biodegradability of the material is not known. |
Note: Biodegradable information may not be available for two reasons:
- Legacy material data from a personal database, or from a previous study, may not include this environmental information.
- As this property is new, not all material grades in the public database contain this information.
Potential biomass-sourced feedstock
Feedstock refers to the raw material components that are used to produce the polymer. Potential biomass-sourced refers to the amount of feedstock that may be derived from biological sources. Material components sourced from biomass sources are typically considered to be more environmentally friendly. The properties of the material are unaffected by the amount of biomass-sourced feedstock.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Minimum | The minimum percentage of the material potentially sourced from biomass. |
| Maximum | The maximum percentage of the material potentially sourced from biomass. |
Note: If the value is constant then the minimum and maximum values are equal.
Note: When entering data both the minimum and the maximum values must be supplied
Note: Potential biomass-sourced feedstock information may not be available for two reasons:
- Legacy material data from a personal database, or from a previous study, may not include this environmental information.
- As this property is new, not all material grades in the public database contain this information.
Recycled content
Recycled content refers to the amount of non-virgin material blended into the polymer, regardless of the Recycled source. Virgin material is material that has not been used or processed. Processing a material in processes like injection molding can significantly change the chemical, mechanical, thermal, or physical properties of the material. Some polymer families can be recycled many times without significant property degradation; others can be only used once. The material properties of the material may be affected significantly by the amount of recycled content used and the recycling method. For accurate simulation, specific material test data for percentages of recycled content being used is recommended.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Minimum | The minimum percentage of recycled content. |
| Maximum | The maximum percentage of recycled content. |
Note: If the value is constant then the minimum and maximum values are equal.
Note: When entering data both the minimum and the maximum values must be supplied
Note: Recycled content information may not be available for two reasons:
- Legacy material data from a personal database, or from a previous study, may not include this environmental information.
- As this property is new, not all material grades in the public database contain this information.
Recycling method
The recycling method refers to the process used to generate the blend of virgin and recycled material.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Unknown | How the material was produced is not known. |
| Mechanical | Produced by mechanical processes such as grinding or extrusion. |
| Chemical | Produced by a chemical process. |
| Other | Produced by a non-mechanical or non-chemical process. |
| None | Virgin Material - contains no recycled content. |
Note: Recycling method information may not be available for two reasons:
- Legacy material data from a personal database, or from a previous study, may not include this environmental information.
- As this property is new, not all material grades in the public database contain this information.
Recycled source
The recycling source refers to the stage in the process the recycled material is collected.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Unknown | The recycled source is not known. |
| Post-industrial recycling | The material is separated from the waste stream during the manufacturing process. |
| Post-consumer recycling | The material is made from the items that consumers recycle. |
| Post-industrial and Post-consumer recycling | The material is sourced from both Post-industrial and Post-consumer sources. |
| Other | Recycled material is sourced from other sources. |
| None | Virgin Material - contains no recycled content. |
Note: Recycled source information may not be available for two reasons:
- Legacy material data from a personal database, or from a previous study, may not include this environmental information.
- As this property is new, not all material grades in the public database contain this information.
Comments on environmental impact
Additional environmental information or environmental credentials of interest to consumers of the material.
