AEC Best Practices
Architectural (AEC) engineering analyses can be classified into three major categories:
- Mechanical Ventilation
- External Flow or Wind Loading
- Natural Ventilation
The typical objectives of most AEC analyses include:
Understand temperature distribution through an occupied zone to ensure interior comfort and maintain operational efficiency
Quantify and account for occupant-dissipated heat
Reduce air changes per hour and operational costs by optimizing air distribution system efficiency
Examine diffuser throws and flow patterns to evaluate effectiveness in custom HVAC installations
This set of topics describes the application-specific procedures and techniques to effectively simulate each of the major types of AEC applications. Additionally, a set of topics is presented that describes modeling guidelines that apply to all AEC analyses.
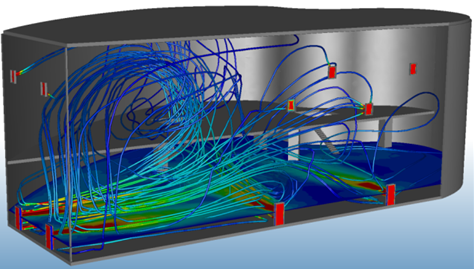
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical Ventilation analyses simulate the air flow in spaces that are controlled with air management systems. Such systems typically include a network of diffusers, fans, and returns designed to ensure proper air flow and temperature control within the occupied area.
Examples include:
- HVAC system studies
- Datacenters
- Lab spaces
- Contaminant or smoke extraction analyses
For more about Mechanical Ventilation AEC analyses...
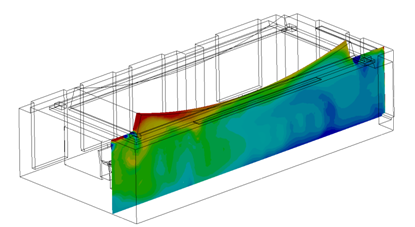
Wind Loading
Wind loading analyses simulate the air flow and resultant structural loading on buildings, large signs, and other structures.
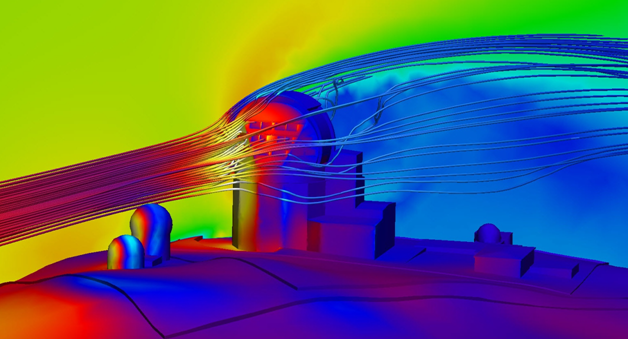
Examples include:
- Flow over and around buildings
- The effect of attached and unattached obstructions on the external air flow
- Wind loading on windows
- Wind loading on industrial signs
- Wind loading on light boards
- Effect of impinging air flow on building façades
For more about Wind Loading AEC analyses...
Natural Ventilation
Air movement in natural ventilation applications is generally the result of density gradients caused by temperature variations throughout the structure. Fans and other mechanical devices may be present, but do not dominate air movement. In many structures, buoyancy-driven ambient air passing through doors and windows is the primary source of natural ventilation.
Examples include:
- Natural flow and thermal phenomena, typically involving buoyancy-driven flow
- Natural ventilation in municipal buildings
- Condensation and thermal stratification in atria
For about Natural Ventilation AEC analyses...
AEC Analysis Strategies
In addition to the techniques described in the application-specific topics, several analysis strategies are universally applicable to all AEC simulations. These topics describe how specific Autodesk® CFD functionality is applied to AEC analyses to achieve efficient simulation. In many cases, additional details are provided in other areas of the Help, and are linked appropriately.
Geometry Modeling Techniques for AEC Applications
