Create a virtual environment (macOS)
A virtual environment is a tool that helps to keep dependencies required by different projects separate. In this setup, we will be creating a virtual environment from which to run the Flow Production Tracking Event Daemon Trigger (shotgunEvents).
To create a virtual environment, start by opening a Terminal and ensuring you are in the directory in which you downloaded the repos. In this example, the directory is Users/newuser/shotgridDemo.
cd Users/newuser/shotgridDemoTo install a virtual environment, use the following command:
pip install virtualenvCreate a virtual environment directory.
mkdir VirtualEnvsChange directories to the virtual environment directory.
cd VirtualEnvsFrom within the VirtualEnvs directory, create a sg_events directory.
mkdir sg_eventsSetup a virtual environment.
python -m venv sg_eventsIf you get an error “zsh: command not found: python”, add python to zsh by running the following in terminal:
echo "alias python=/usr/bin/python3" >> ~/.zshrcThis will configure your zsh profile to run /usr/bin/python3 when python is run. If you are still facing issues, ensure that python=$ where the $ sign should equal the path python is installed on. Restart your terminal. When you open it again, your python command should work successfully. Navigate back to the VirtualEnvs directory and run the python command again.
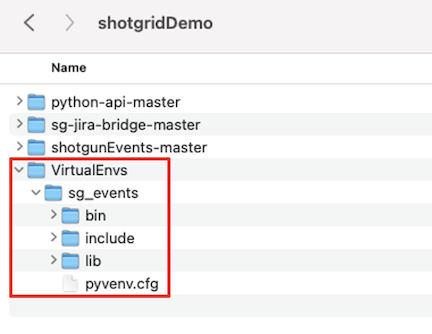
Once run, the python command will create several new directories within the sg_events folder. You should have something like the image below.
Next, from within the VirtualEnvs directory, activate the virtual environment.
. sg_events/bin/activateThe virtual environment should now be active, indicated by parentheses.

