This option is used to create load case combinations described by codes selected from Tools > Job Preferences > Codes/Code Combinations. Open the dialog using either method
- Clicking Loads> Automatic Combinations.
- Clicking
 .
.
Automatic code combinations (ponderations) in Robot give you an easy way to define and calculate selected combinations.
The dialog has 6 tabs: Cases, Combinations, Groups, Relations, Simplified and Selection. After you have defined the structure parameters (load cases, combination templates, and additional relations, and so on.), click Generate.
The current code combination calculations are based on all possible (theoretically allowed) combination cases. SLS (ULS, accidental, special - such as, for fire in timber structures) cases are created for a detailed analysis of code combinations. They let you see results for each combination separately (composite combinations), as well as for composite combinations. These cases are used for code combinations. For a tabular display of maximum and minimum value, cases marked ULS+, ULS- (SLS+, SLS-, ALS+, ALS-) are created. They display the appropriate extreme values. There are no differences in the display of ULS, ULS+, ULS- cases. Code combinations are generated based on the parameters defined in the code combination file *.rgl (description of code combination regulations).
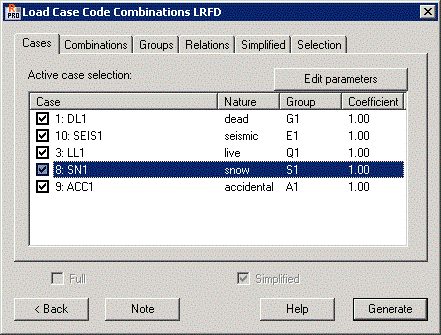
Cases tab
The Cases tab is used to select the load cases, which are already defined for the structure and will be used to create code combinations. The Active Case Selection field has a list of defined load cases with assigned natures. Appropriate coefficients used during the creation of the combination are defined for each load case defined by a selected nature. By default, all cases selected in the Selection of Active Cases, are considered when creating the code combinations. If any of the load cases should not be in the code combination, click on it with the left mouse button.
When a load case is selected on the list, the Edit parameters button becomes available. Clicking it opens an additional Parameters dialog in which 2 parameters of a load case can be changed: prefix (it can be applied when displaying the generated code combinations) and the value of a coefficient for a given load case.
The prefix is defined for load cases by Robot. For most load cases, the prefix is generated automatically by Robot (snow/wind loads, seismic loads, and so on) and can be modified in the Parameters dialog. Generated code combinations can be displayed as (you can select the format for displaying combinations in the Table Columns dialog.):
- 1 * 1.10 + 2 * 1.10 + 3 * 1.40 + 4 * 1.40 (The numbers of the load cases and coefficients for these cases are applied.)
- CW * 1.10 + STA1 * 1.10 + SN1 * 1.40 + SN2 * 1.40 (The prefixes of the load cases and coefficients for these cases are applied.)
Combinations tab
The Combinations tab, shown in the following image, is used to define the code combinations that are created.

The code used to create the code combinations is displayed in the previous dialog. You can select codes from the Job Preferences dialog (Design codes > Loads > Code Combinations option). In addition, you can select the templates, which are used to create code combinations.
The list of combination types depends on a combination code selected in the Job Preferences dialog. You can decide which combination types will be generated. Selecting all, results in a full combination list based on the templates.
Groups tab
The Groups tab is used to define or display groups, that is, sets of load combinations connected by logical relationships.

In the current version of Robot, all dead loads are connected in one group of combined (acting simultaneously) loads. Snow and wind loads create a separate group of self-exclusive loads for which the occurrence of one case excludes the other. All other live loads occur as loads which are not inter-related.
Relations tab
You can also define relationships between load cases in particular groups. This is done using logical operators (and, inclusive or, and exclusive or) on the Relations tab.
Robot creates the groups and relationships automatically. This solution resolved the problem of base combinations. For more advanced combinations, options found on the Relations tab can be used. This lets you create logical operations on groups of cases within natures. AND, OR (INCLUSIVE) and OR (EXCLUSIVE) are the logical operators. When creating the operations, you can use brackets to join or exclude selected groups of cases.
For example, suppose the following 3 groups of load cases are defined in a structure: G1, G2 and G3. The logical operators function in the following manner:
- AND - This operator simultaneously activates all loads (loads from load cases G1, G2 and G3 are applied simultaneously to the structure). You can represent it symbolically as: G1 G2 G3
- OR (EXCLUSIVE) - This operator is used when loads from a particular load group are mutually exclusive (loads from load case G1, or G2, or G3, will be applied to the structure). You can represent it symbolically as:
G1
G2
G3
- OR (INCLUSIVE) - This operator allows all possible combinations between groups of load cases. You can represent it symbolically as:
G1
G2
G3
G1 G2
G1 G3
G2 G3
G1 G2 G3.

See also:
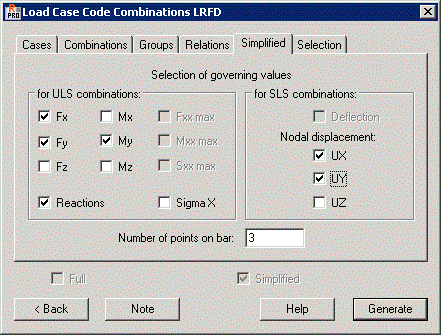
Simplified tab
For more elaborate tasks (over 10 load cases for which to create code combinations), creating code combinations can be time consuming. The Simplified tab is used for defining simplified code combinations that generate extreme combinations, because of a specific result or their combination.
For this type of case, you give a list of points and define the determining value (indicated force, moment, or stress). Robot decides which combinations meet these conditions, and only those values are saved as a code combination for the selected bar. For an interaction between 2 selected values, Robot tries to select the extents of those variables.
Selection tab
For more complex tasks, you can create simplified code combinations for selected structure nodes and or bars using the Selection tab:
- All bars (values selected on the Simplified tab) are verified for all bars of a structure or bars from a given list (values selected on the Simplified tab) are verified for the bars of a structure you specify.
- All nodes (values selected on the Simplified tab) are verified for all nodes of a structure or nodes from a given list (values selected on the Simplified tab) are verified for the nodes of a structure you specify.

See also:
Definition of abbreviated case names (snow/wind loads) in generation of code combinations