To define the modal analysis parameters for new dynamic cases in the structure, do one of the following:
- Select a modal analysis case in the New Case dialog and click OK.
- Select a modal analysis case in the Analysis Type dialog and click Set Parameters.
- Select a modal analysis case in the Calculation Restart dialog and click Define Parameters.
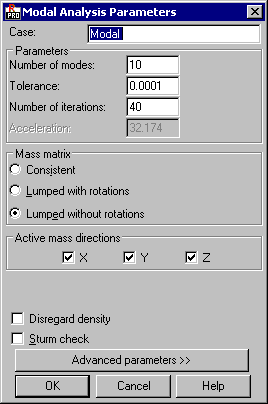
Define the basic parameters for modal analysis of a structure in the Modal Analysis Parameters dialog:
- Parameters - The following modal analysis parameters can be specified: number of modes, tolerance, or number of iterations. Additionally, the value of acceleration of gravity is presented.
- Mass matrix type:
- Consistent (consistent matrix always with regard to the rotational degrees of freedom)
- Lumped with rotations (diagonal matrix with regard to rotational degrees of freedom)
- Lumped without rotations (diagonal matrix without rotational degrees of freedom).
- Disregard density - The density of the structure element (ρ=0) will not be taken into consideration during the dynamic analysis of the structure.
- Sturm check - Sets the algorithm for detecting the skipped eigenvibrations. If a skipped mode is found, an iteration will be run again.
The Active mass directions option allows you to select a direction for which to consider masses in the modal analysis (structure eigenvibrations). To select a direction, that is to activate the mass in the global directions X, Y or Z,select the X, Y or Z option. A default setting for the modal analysis is that the mass is taken into account for all directions.
You may need to deselect a direction when performing the seismic analysis. If you deselect the mass in the Z direction, for the modal analysis that precedes the seismic case, it eliminates local vertical vibration modes for floor slabs. In the seismic analysis for such model you will consider only transversal vibrations. Another example is the Footfall analysis, where the active mass for the Z direction is a default setting. In this case you consider vertical vibrations and ignore transversal vibrations of the model.
Click Advanced parameters >> to access additional modal analysis parameters for a load case:
- Analysis mode:
- Modal - The modal analysis of the structure will be conducted. n vibration modes will be found, the iterations will be completed if a convergence condition is reached.
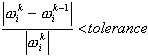
Activation of Sturm Check, which allows for searching for the omitted pulsations, is possible.
- Seismic - During modal structure analysis, n vibration modes will be selected (not necessarily in the appropriate order). Those eigenvibration modes will be set, which are important to seismic analyses, therefore those which are characterized by a large mass participation factor.
A Sturm Check is not possible for this structure analysis mode.
- Seismic pseudomodal - Spectral and seismic analysis will be conducted using the pseudomodal method. This should be used only when applying classic analysis methods based on modal decomposition results in a very long structure analysis time.
- Modal - The modal analysis of the structure will be conducted. n vibration modes will be found, the iterations will be completed if a convergence condition is reached.
- Method - The eigenproblem solution method: Block subspace iteration, Subspace iteration, Lanczos algorithm and Base reduction.
- Limits - The number of defined structure vibration modes may be limited by assigning the limit values for frequency, pulsation, and periods. Select Active option and click Limit Definition.
- Definition of eccentricities - Click to access Definition of mass eccentricities and consider mass ecentricity in the seismic analysis.
- Mass Participation Percentage - The method of assigning the number of modes based on the participation mass percentage condition.
Include damping in calculations (according to PS92) accounts for support with damping during the modal analysis. Defined damping coefficients are used in the seismic code PS92 formula. 5 section 6.2.3.4 of the French seismic code PS 92 (NF P 06-013) necessitates structure-ground interactions, and thus influence of the ground on a value of the structural damping of a structure.
See also:
Parameters of modal analysis recognizing static forces
Description of modal analysis recognizing static forces
Description of the method of block subspace iteration