The Bevel Profile modifier extrudes a shape using another shape as the path or "beveling profile." It's a variation on the Bevel modifier.
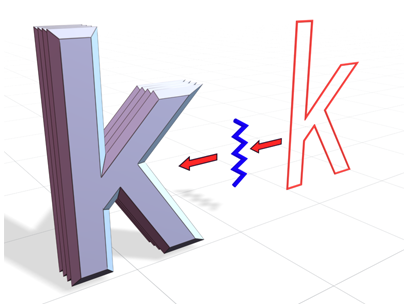
Bevel Profile creates an object using an open spline.
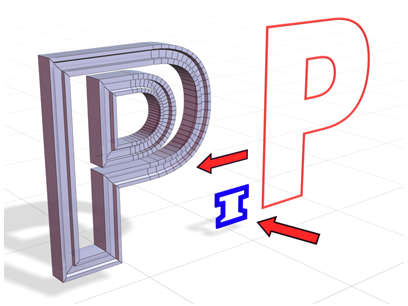
Bevel Profile creates an object using a closed spline, yielding a different result.
Procedures
To use the Bevel Profile modifier:
- Create a shape to bevel (preferably in the Top viewport).
- In the Front (XZ) viewport, create a shape to use as the beveling profile.
- Select the first shape and apply the Bevel Profile modifier.
- Click the Pick Profile button in the Bevel Profile modifier, and then click the profile shape.
Interface
Parameters rollout
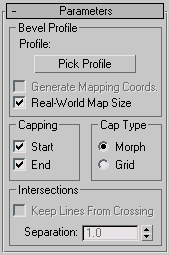
Bevel Profile group
- Pick Profile
-
Selects a shape or NURBS curve to be used for the profile path.
- Generate Mapping Coords
-
Assigns UV coordinates.
- Real-World Map Size
-
Controls the scaling method used for texture mapped materials that are applied to the object. The scaling values are controlled by the Use Real-World Scale settings found in the applied material's Coordinates rollout. Default=on.
Capping group
- Start
-
Caps the bottom of the extruded shape.
- End
-
Caps the top of the extruded shape.
Cap Type group
- Morph Selects a deterministic method of capping that provides the same number of vertices for morphing between objects.
- Grid Creates gridded caps that are better for cap deformations.
Intersections group
- Keep Lines From Crossing
-
Prevents beveled surfaces from self intersecting. This requires more processor calculation and can be time-consuming in complex geometry.
- Separation
-
Sets the distance that sides should be kept apart to prevent intersections.
