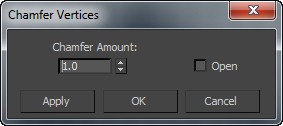
Chamfering creates new faces around the chamfered entity, along with connecting edges. Or, with the Open option, you can create an open (empty) area instead. For vertices, edges, and borders, you can set the chamfer amount numerically and toggle the Open option. The Segments setting applies only to edges and borders.

Interface
Chamfer uses the caddy interface when Enable Caddy Controls is on; when off, the standard settings dialog is used. For details on using the caddy controls, see The Caddy Interface.
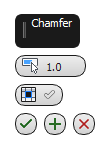
Chamfering vertices:
Left: The caddy interface
Right: The standard dialog
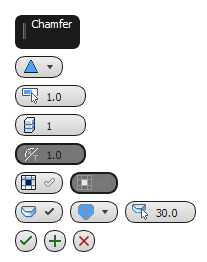
Chamfering edges/borders:
Left: The caddy interface
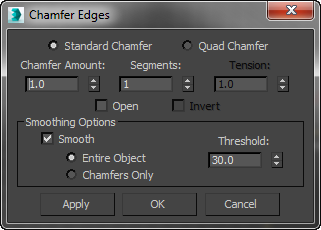
Right: The standard dialog
- Chamfer Type
- Choose the basic chamfering method:
 Standard Chamfer - Chamfering generates quadrilaterals and triangles.
Standard Chamfer - Chamfering generates quadrilaterals and triangles. 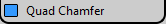 Quad Chamfer - Chamfering generates quadrilaterals only. Ancillary generated geometry (such as areas adjacent to the chamfered sub-objects) might include triangles.
Quad Chamfer - Chamfering generates quadrilaterals only. Ancillary generated geometry (such as areas adjacent to the chamfered sub-objects) might include triangles.

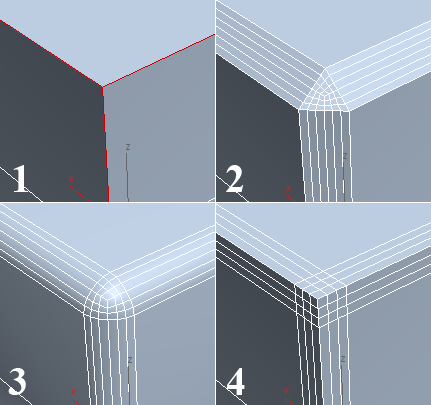
1. Original edge selection
2. Quad Chamfer (Segments=2; Tension=0.5). The new polygons at the corner are all quads.
3. Standard Chamfer (Segments=2). The new polygons at the corner are quads and triangles.
 Chamfer Amount
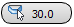
Chamfer Amount - The extent of the chamfer in distance units. Default=1.0.
 Segments
Segments - (Edges only) Adds polygons over the area of the chamfer. The result depends on the chamfer type.
- Standard Chamfer - The chamfering process replaces each chamfered edge with the Segments-value number of polygons. Also with this, increasing the Segments value of chamfered edges between non-coplanar polygons can cause rounding of the chamfered area.
- Quad Chamfer - Creates (2 x Segments value) new polygons around each chamfered edge. So, for example, setting Segments to 3 results in six new polygons per edge. The higher the Segments value you use, the more the chamfer can be rounded off, depending on the Tension value.
The preceding illustration shows the difference in the number of polygons generated by the two methods, using the same Segments value.
 Tension
Tension - (Quad Chamfer only) Determines the angle between new polygons generated by chamfering edges between non-coplanar polygons. At the default value of 1.0, all new polygons from each chamfered edge lie flat (coplanar). Lowering the Tension value increases the angle; with a high enough Segments value and original angle between the polygons on either side of the edge, this can produce curvature of the new polygons. At 0.0, the new polygons occupy the same positions as the original polygons.
The Tension setting does not affect polygons generated from edges between coplanar polygons. The greater the angle between the original polygons adjacent to a chamfered edge, the more curvature is available.
1. Original edge selection
2. Tension=1.0
3. Tension=0.5
4. Tension=0.0
Tip: If you don't get the desired curvature by reducing the Tension value, try increasing the Segments value.  Open Chamfer
Open Chamfer - After chamfering, deletes all faces created by the chamfering operation.
 Invert Open
Invert Open - (Quad Chamfer only) After chamfering, deletes all faces except those created by the chamfering operation. Available only when Open Chamfer is on.
 Smooth
Smooth - When on, applies smoothing groups after chamfering. Also enables the Smooth Type and Smooth Threshold settings (see following).
 Smooth Type
Smooth Type - When Smooth is on (see preceding), choose how smoothing is applied to the chamfered geometry:
 Smooth Entire Object - Applies smoothing groups to the entire object based on the angles between adjacent polygons. Any two adjacent polygons will be put in the same smoothing group if the angle between their normals is less than the Smooth Threshold angle (see following).
Smooth Entire Object - Applies smoothing groups to the entire object based on the angles between adjacent polygons. Any two adjacent polygons will be put in the same smoothing group if the angle between their normals is less than the Smooth Threshold angle (see following).  Smooth Chamfers Only - Applies smoothing groups to the new polygons created by the chamfering process based on the angle between adjacent polygons. Any two adjacent polygons will be put in the same smoothing group if the angle between their normals is less than the Smooth Threshold angle (see following).
Smooth Chamfers Only - Applies smoothing groups to the new polygons created by the chamfering process based on the angle between adjacent polygons. Any two adjacent polygons will be put in the same smoothing group if the angle between their normals is less than the Smooth Threshold angle (see following).
 Smooth Threshold
Smooth Threshold - When Smooth is on (see preceding), two adjacent faces are placed in the same smoothing group if the angle between their normals is less than the Threshold value.
_____
 OK
OK - Applies the settings to the current selection and closes the caddy. Keyboard equivalent:

 Apply and Continue
Apply and Continue - Applies the settings to the current selection, retaining them for the preview if you then change the selection. Keyboard equivalent:
 +
+
 Cancel
Cancel - Closes the caddy without applying the settings to the current selection. Does not reverse previous uses of Apply And Continue. Keyboard equivalent:

 +click
+click