Controls all the primary settings for rendering, including predefined and custom settings.
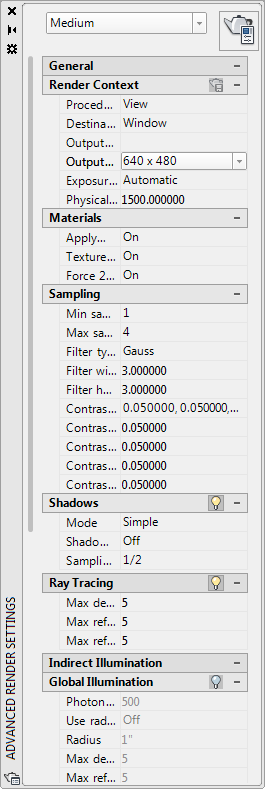
You use the Advanced Render Settings palette to control rendering settings. You can also access the Render Presets Manager from the Render Settings palette.
List of Options
The following options are displayed.
Render Preset List / Select Render Preset
Lists standard render presets ranging from lowest to highest quality, up to four custom render presets and allows access to the Render Presets Manager.
Render Context
Contains settings that affect how your model gets rendered.
- Save File
-
Determines if the rendered image is written to a file.
- Rendering Procedure
-
Controls the model content that gets processed during rendering.
- View. Renders the current view without displaying the Render dialog box.
- Crop. Creates a render area at render time. When you click the Render button with Crop Window selected, you are prompted to specify an area in the drawing before rendering proceeds. This option is available only when Viewport is selected under Destination.
- Selected. Displays a prompt to select objects to render.
- Destination
-
Determines the output site that the renderer uses to display the rendered image.
- Window. Renders to the Render Window.
- Viewport. Renders to a viewport.
- Output File Name
-
Specifies a file name and location where the rendered image will be stored.
- BMP (*.bmp). Still-image bitmap file in the Windows bitmap (.bmp) format.
- PCX (*.pcx). Simple format that provides a minimum of compression.
- TGA (*.tga). File format that supports 32-bit true color; that is, 24-bit color plus an alpha channel, and is typically used as a true color format.
- TIF (*.tif). Multiplatform bitmap format.
- JPEG (*.jpg). Popular format for posting image files on the Internet for minimum file size and minimum download time.
- PNG (*.png). Still-image file format developed for use with the Internet and World Wide Web.
- Output Size
-
Shows the current output resolution setting for the rendered image. Opening the Output Size list displays the following:
- Up to four custom size settings. Note:
Custom output sizes are not stored with the drawing and they are not retained between drawing sessions.
- Four of the most commonly used output resolutions.
- Access to the Output Size dialog box.
- Up to four custom size settings.
- Exposure Type
-
Controls the tone operator setting. This does not need to be stored in the named render preset. Rather it can be stored per drawing in the render context.
- Automatic. Indicates that the tone operator used should be chosen to match the current viewport tone operator strategy.
- Logarithmic. Indicates that the log exposure control should be used.
- Physical Scale
-
Specifies the physical scale. Default = 1500.
Render
Renders the model directly from the Advanced Render Settings palette.
Materials
Contains settings that affect how materials are handled by the renderer.
- Apply Materials
-
Applies the surface materials that you define and attach to an object in the drawing. If Apply Materials is not selected, all objects in the drawing assume the color, ambient, diffuse, reflection, roughness, transparency, refraction, and bump map attribute values defined for the GLOBAL material. For more information, see MATERIALS.
- Texture Filtering
-
Specifies how texture maps are filtered.
- Force 2-Sided
-
Controls if both sides of faces are rendered.
Sampling
Controls how the renderer performs sampling.
- Min Samples
-
Sets the minimum sample rate. The value represents the number of samples per pixel. A value greater than or equal to 1 indicates that one or more samples are computed per pixel. A fractional value indicates that one sample is computed for every N pixels (for example, 1/4 computes a minimum of one sample for every four pixels). Default=1/4.
- Max Samples
-
Sets the maximum sample rate. If neighboring samples find a difference in contrast that exceeds the contrast limit, the area containing the contrast is subdivided to the depth specified by Maximum. Default=1.
The values of the Min Samples and Max Samples lists are "locked" together so that the value of Min Samples can't exceed the value of Max Samples.
- Filter Type
-
Determines how multiple samples are combined into a single pixel value.
- Filter Width and Filter Height
-
Specifies the size of the filtered area. Increasing the value of Filter Width and Filter Height can soften the image; however, it will increase rendering time.
- Contrast Color
-
Clicking [...] opens the Select Color dialog box where you interactively specify the R,G,B threshold values.
- Contrast Red, Blue, Green
-
Specifies the threshold values for the red, blue, and green components of samples. These values are normalized, and range from 0.0 to 1.0, where 0.0 indicates the color component is fully unsaturated (black, or 0 in eight-bit encoding) and 1.0 indicates the color component is fully saturated (white, or 255 in eight-bit encoding).
- Contrast Alpha
-
Specifies the threshold value for the alpha component of samples. This value is normalized, and ranges from 0.0 (fully transparent, or 0 in eight-bit encoding) to 1.0 (fully opaque, or 255 in eight-bit encoding).
- Box. Sums all samples in the filter area with equal weight. This is the quickest sampling method.
- Gauss. Weights the samples using a Gauss (bell) curve centered on the pixel.
- Triangle. Weights the samples using a pyramid centered on the pixel.
- Mitchell. Weights the samples using a curve (steeper than Gauss) centered on the pixel.
- Lanczos. Weights the samples using a curve (steeper than Gauss) centered on the pixel, diminishing the effect of samples at the edge of the filter area.
Shadows
Contains settings that affect how shadows appear in the rendered image.
- Enable
-
Specifies if shadows are computed during rendering.
- Mode
-
- Simple. Generates shadow shaders in a random order.
- Sort. Generates shadow shaders in order, from the object to the light.
- Segments. Generates shadow shaders in order along the light ray from the volume shaders to the segments of the light ray between the object and the light.
- Shadow Map
-
Controls if shadow mapping is used to render shadows. When on, the renderer renders shadow-mapped shadows. When off, all shadows are ray-traced.
- Sampling Multiplier
-
Globally limits shadow sampling for area lights. This is part of the rendering preset data. This allows draft and low quality presets to reduce area light sampling. It’s effect is to modulate the inherent sampling frequency specified for each light. The default value=1 for new presets. Values are 0, 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1, 2. Draft: 0; Low:1/4; Med:1/2; High:1; Presentation:1.
Ray Tracing
Contains settings that affect the shading of a rendered image.
- Enable
-
Specifies if ray tracing should be performed when shading.
- Max Depth
-
Limits the combination of reflection and refraction. Tracing of a ray stops when the total number of reflections and refractions reaches the maximum depth. For example, if Max Depth equals 3 and the two trace depths each equal the default value of 2, a ray can be reflected twice and refracted once, or vice versa, but it cannot be reflected and refracted four times.
- Max Reflections
-
Sets the number of times a ray can be reflected. At 0, no reflection occurs. At 1, the ray can be reflected once only. At 2, the ray can be reflected twice, and so on.
- Max Refractions
-
Sets the number of times a ray can be refracted. At 0, no refraction occurs. At 1, the ray can be refracted once only. At 2, the ray can be refracted twice, and so on.
Global Illumination
Affects how your scene is illuminated.
- Enable
-
Specifies if lights should cast indirect light into the scene.
- Photons/Samples
-
Sets how many photons are used to compute the intensity of the global illumination. Increasing this value makes global illumination less noisy but also more blurry. Decreasing this value makes global illumination more noisy but less blurry. The larger the Samples value, the greater the rendering time.
- Use Radius
-
Determines the size of photons. When on, the spinner value sets the size of photons. When off, each photon is calculated to be 1/10 of the radius of the full scene.
- Radius
-
Specifies the area within which photons will be used when illuminance is computed.
- Max Depth
-
Limits the combination of reflection and refraction. Reflection and refraction of a photon stop when the total number of both equals the Max Depth setting. For example, if Max Depth equals 3 and the trace depths each equal 2, a photon can be reflected twice and refracted once, or vice versa, but it can’t be reflected and refracted four times.
- Max Reflections
-
Sets the number of times a photon can be reflected. At 0, no reflection occurs. At 1, the photon can be reflected once only. At 2, the photon can be reflected twice, and so on.
- Max Refractions
-
Sets the number of times a photon can be refracted. At 0, no refraction occurs. At 1, the photon can be refracted once only. At 2, the photon can be refracted twice, and so on.
Final Gather
Calculates global illumination.
- Mode
-
Controls the final gathering dynamic settings.
- On. Turns on the global illumination in final gather.
- Off. Turns off the calculation of global illumination in final gather.
- Auto. Indicates that the final gather should be dynamically enabled or disable at render time based on the skylight status.
- Rays
-
Sets how many rays are used to compute indirect illumination in a final gather. Increasing this value makes global illumination less noisy, but also increases rendering time.
- Radius Mode
-
Determines the radius mode for final gather processing. Settings are On, Off, or View.
- On. Specifies that the setting means the Max Radius setting is used for final gather processing. The radius is specified in world units, and defaults to 10 percent of the maximum circumference of the model.
- Off. Specifies the maximum radius is the default value of 10 percent of the maximum model radius, in world units.
- View. Specifies the Max Radius setting in pixels instead of world units and is used for final gather processing.
- Max Radius
-
Sets the maximum radius within which final gathering is processed. Reducing this value can improve quality at a cost of increased rendering time.
- Use Min
-
Controls whether the Min Radius setting is used during final gather processing. When on, the minimum radius setting is used for final gather processing. When off, the minimum radius is not used.
- Min Radius
-
Sets the minimum radius within which final gathering is processed. Increasing this value can improve quality but increase rendering time.
Light Properties
Affects how lights behave when calculating indirect illumination. By default, the energy and photon settings apply to all lights in a scene.
- Photons/Light
-
Sets the number of photons emitted by each light for use in global illumination. Increasing this value increases the accuracy of global illumination, but also increases the amount of memory used and the length of render time. Decreasing this value improves memory usage and render time, and can be useful for previewing global-illumination effects.
- Energy Multiplier
-
Multiplies the global illumination, indirect light, intensity of the rendered image.
Visual
Helps you understand why the renderer is behaving in a certain way.
- Grid
-
Renders an image that shows the coordinate space of objects, the world, or camera.
- Object. Shows local coordinates (UVW). Each object has its own coordinate space.
- World. Shows world coordinates (XYZ). The same coordinate system applies to all objects.
- Camera. Shows camera coordinates, which appear as a rectangular grid superimposed on the view.
- Grid Size
-
Sets the size of the grid.
- Photon
-
Renders the effect of a photon map. This requires that a photon map be present. If no photon map is present, the Photon rendering looks just like the nondiagnostic rendering of the scene: the renderer first renders the shaded scene, then replaces it with the pseudocolor image.
- Density. Renders the photon map as it is projected into the scene. High density is displayed in red, and lower values render in increasingly cooler colors.
- Irradiance. Similar to the Density rendering, but shades the photons based on their irradiance. The maximum irradiance is rendered in red, and lower values render in increasingly cooler colors.
- BSP
-
Renders a visualization of the parameters used by the tree in the BSP ray-trace acceleration method. If a message from the renderer reports excessively large depth or size values, or if rendering seems unusually slow, this can help you locate the problem.
- Depth. Shows the depth of the tree, with top faces in bright red, and increasingly deep faces in increasingly cool colors.
- Size. Shows the size of leaves in the tree, with differently sized leaves indicated by different colors.
Processing
- Tile Size
-
Determines the tile size for rendering. To render the scene, the image is subdivided into tiles. The smaller the tile size, the more image updates are generated during rendering. When the tile size is reduced, the number of image updates increases, meaning that a rendering take longer to complete. If the tile size is increased, fewer image updates occur and the rendering takes less time to complete.
- Tile Order
-
Specifies the method used (render order) for tiles as an image is rendered. You can choose a method based on how you prefer to see the image appear as it renders in the Render Window.
- Hilbert. Next tile to be rendered is based on the cost of switching to the next one.
- Spiral. Tiles are rendered beginning at the center of the image, and spiral outward.
- Left to Right. Tiles are rendered in columns, from bottom to top, left to right.
- Right to Left. Tiles are rendered in columns, from bottom to top, right to left.
- Top to Bottom. Tiles are rendered in rows, from right to left, top to bottom.
- Bottom to Top. Tiles are rendered in rows, from right to left, bottom to top.
- Memory Limit
-
Determines the memory limit for rendering. The renderer keeps a count of the memory it uses at render time. If the memory limit is reached, the geometry for some objects is discarded in order to allocate memory for other objects.