
To open the Move Tool, click the Move Tool icon  in the Tool Box.
in the Tool Box.
Move Settings
- Axis Orientation
-
Specifies the coordinate system for the Move Tool.
- Object
-
Moves an object in object space coordinate system. Axis orientation includes rotations on the object itself. If several objects are selected, each object moves the same amount relative to its own object space coordinate system.
- Parent
-
Aligns the object to the rotation of the parent object. Movement is constrained to those axes in the local space coordinate system. The object is aligned to the rotation of the parent object and does not include the rotations on the object itself. If several objects are selected, each object moves the same amount relative to its own object space coordinate system.Note:
 In Maya 2015 and earlier versions, Parent mode was called Local mode.
In Maya 2015 and earlier versions, Parent mode was called Local mode. - World
-
Moves in the world space coordinate system. The object is aligned to the world space axis. This is the default.
- Normal
-
Moves selected vertices or CVs in the U or V direction of the surface. Typically you would use this option for small sets of CVs. The manipulator indicates the surface Normal, U, and V directions.
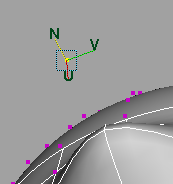
When you select Normal, the Update [UVN] Triad check box appears. Turned on, this option causes the manipulator orientation to reflect the moved surface rather than the original surface. This is the default. Turned off, the manipulator retains the orientation for the original surface.
- Component
-
Moves selected vertices or CVs along the average of their combined normals.
When an object is selected, moves the object in object space coordinate system.
Note: In Maya 2015 and earlier versions, Component mode was called Normals average mode.
In Maya 2015 and earlier versions, Component mode was called Normals average mode. - Along rotation axis
- Aligns to the Rotate Tool's axes on the object. If you have set the Rotate Axis in the object's Transform Attributes to a different value (which offsets the orientation of the object relative to the orientation of the object's local rotation axis) this attribute will have an affect; otherwise, Along rotation axis is the same as Object.
- Along live object axis
-
(This setting does not work with Reflection on.) Sets the Move Tool to move objects along the axis of a live object. Most commonly, you would make a construction plane live, but any object can be set live. When you have a live object and select this option, the move arrows of the Move Tool align to the live construction plane. (The geometry of the live object doesn’t matter; the move aligns to the axes of the live object.)
- Custom
-
Lets you set a custom orientation. Custom axis orientation is automatically selected when you activate custom pivot editing mode. The offset coordinates update as you edit the orientation of the custom pivot. See Activate custom pivot editing mode.
- Set Orientation to Component
-

Lets you orient the Move Tool's X-axis by selecting a component in the scene. See Set a custom axis orientation.
Note: Set Orientation to Component replaces Set to Point, Set to Edge, and Set to Face. - Edit Pivot
-

Activates custom pivot editing mode. See Activate custom pivot editing mode.
- Reset
-

Resets the custom pivot's position and orientation. See Reset the custom pivot.
- Preserve Child Transform
-
When on, moving a parent object does not move its children.
- Pin Component Pivot
-
 When on, locks your edits to the custom pivot in place, letting you use the same custom pivot to transform different components on one mesh. See Pin the custom pivot.Note: Pivot pinning is only available when a custom pivot is set. See Change the pivot point.
When on, locks your edits to the custom pivot in place, letting you use the same custom pivot to transform different components on one mesh. See Pin the custom pivot.Note: Pivot pinning is only available when a custom pivot is set. See Change the pivot point. - Preserve UVs
-
When this option is selected, moving components in the scene view causes the corresponding UVs to move accordingly in the UV space. The net result is that the texture does not become warped.
- Discrete move
-
Enables the Relative option and lets you specify the amount an object is moved in increments (determined by the Step Size value).
- Relative
-
While Maya moves the object, relative spacing is maintained. Turn this option off if you don’t want to preserve relative spacing while translating.
- Step Size
-
Enter a value to determine the amount an object is moved in increments when the Discrete Move option is selected.
- Tweak mode
-
Allows you to quickly move components, position objects in a scene, and make adjustments to a specific mesh. See Move components with the Tweak mode.Note: If you set the active handle of the Show Manipulator tool to a particular axis while in Tweak mode, then the active handle will remain on the same axis even if you select multiple faces. If you want to use Tweak mode with the center handle, then make the center handle the default handle.
Joint Orient Settings
- Automatically Orient Joints
-
When on, joint offset values are automatically updated when you move joints in a skeleton, ensuring that the parent joint points correctly toward the first child joint.
See also Move joints.
Orientation Settings
- Orient Joint to World
- When on, all joints you create with the Joint Tool are set to align with the world frame. Each joint’s local axes have the orientation of the world axis, and the other Orient Joint settings are disabled. When off, you can specify the joint alignment using the other Orient Joint settings described below.
- Primary Axis
- Lets you specify the primary local axis for the joint. This is the axis that points down the bone that extends from this joint. Tip:
If you want a joint to rotate about a particular axis, that axis must not be the Primary Axis. For example, a joint cannot rotate about its local X-axis if its Primary Axis orientation is set to X.
- Secondary Axis
- Lets you specify which local axis to use as the secondary orientation for the joint. Select one of the two remaining axes. To have Maya determine the Secondary Axis automatically, set to None. Note:
You cannot set the same axis for both the Primary and Secondary orientation. If you set either option to use an axis already specified, Maya automatically switches the other option to use a different axis.
- Secondary Axis World Orientation
-
Lets you set the direction (positive or negative) in which the secondary axis points.
- Orient children of selected joints
-
When on, the Orient Joint Options affect all the joints below the current joint in the skeleton’s hierarchy. When off, only the current joint is affected by the Orient Joint Options.
- Reorient the local scale axes
-
When on, the local scale axes of the current joint are also reoriented.
- Toggle Local Axes Visibility
- Toggles the display of the local axes on the selected joints.
Move Snap Settings
The following settings let you snap to polygon face centers and vertices while translating.
- Retain Component Spacing
-
Turned on by default. This means that while Maya moves the component, relative spacing is maintained. Turn this option off if you don’t want to preserve relative spacing while translating and snapping polygonal components.
- Snap to Live Polygon—Face Center or Vertex
-
These settings let you move and snap to a live polygon’s components (face centers and vertices). See Snapping with live objects.
Common Selection Options
- Selection Style
-
Determines what happens when you drag the mouse in the scene.
- Marquee
-
When you drag your cursor over components in the scene, a marquee appears. When you release the mouse button, components within the marquee are selected.
Tip: You can quickly toggle selection styles. Holding Tab after making a marquee selection temporarily activates Tab Drag select, letting you quickly add and remove components from your existing marquee selection. See Resize a marquee selection with drag select.
You can quickly toggle selection styles. Holding Tab after making a marquee selection temporarily activates Tab Drag select, letting you quickly add and remove components from your existing marquee selection. See Resize a marquee selection with drag select. - Drag
-
When you drag your cursor over components, all components under the cursor are selected.
If Camera based paint selection is enabled, you can only select components that are not obstructed by other components relative to the current camera.
- Highlight backfaces
-

When on, backfacing components are highlighted for preselection and can be selected. When this option is off, backfacing components can still be selected, but they are not highlighted for preselection. See Highlight components before selecting them.
Soft Selection
Symmetry Settings
See Symmetry Settings.