Maya lets you create polygon models that have symmetry. Symmetry is when a form has balanced proportions across a dividing line or axis. There are many types of symmetry possible. The most common types of symmetry are bilateral symmetry and radial symmetry.
In Maya you can model a polygon mesh symmetrically using the following features:
- Using Duplicate Special to create a symmetrical mesh
- Using Mirror Geometry to create a symmetrical mesh
- Using Mirror Cut to create a symmetrical mesh
Using Duplicate Special to create a symmetrical mesh
The Duplicate Special feature lets you copy any object across the X, Y, or Z axis using the object’s pivot point as a reference point. Duplicating an object in this way creates an identical copy that is separate from the original.
To mirror a polygon mesh across its pivot point using the Duplicate Special feature
- Select the polygon mesh and choose Edit > Duplicate Special >
 .
. - Set the Translate and Rotate values to 0.
- Set the scaling to -1 for the axis (X, Y, or Z) across which you want to mirror the polygon mesh.
- Click Duplicate Special. Note:
When you scale an object by -1 across its axis of symmetry, the surface normal will be flipped. Keep this in mind when you need to perform other modeling operations on the mesh. You can reverse the normals using Normals > Reverse.
Using Mirror Geometry to create a symmetrical mesh
Use the Mirror Geometry feature when you have created one half of a model and want to create an identical duplicate mirrored half. The original half of the polygon mesh is duplicated across an axis of symmetry based on its bounding box or pivot point. You can also merge the duplicated polygon mesh with the original mesh to create one resulting polygon mesh.
To mirror a polygon mesh across its bounding box using the Mirror Geometry feature
- Select the polygons and choose Mesh > Mirror Geometry >
 .
. - Choose the direction to mirror the polygons and whether to merge the duplicated polygons into the original mesh.
- Click Mirror.
Using Mirror Cut to create a symmetrical mesh
You can model a polygon mesh and then copy it across a user defined axis of symmetry using the Mirror Cut feature. The Mirror Cut feature lets you manually position the axis that the mesh will be duplicated across. You can also merge the duplicated polygon mesh with the original mesh to create one resulting polygon mesh. Mirror Cut can provide for interesting symmetry results depending on where you locate the axis of symmetry.
To model a polygon mesh symmetrically with Mirror Cut
- Select a polygon mesh.
- Select Mesh > Mirror Cut.
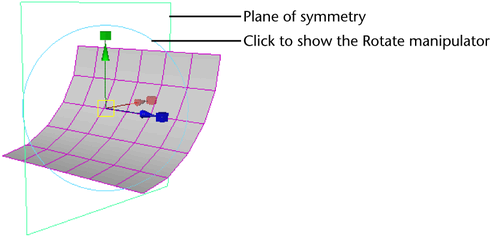
- Use the manipulator to adjust the plane of symmetry. Note:
- If you position the plane of symmetry so it is beyond the positive edge of the original object, then both the original object and its mirror image will disappear (except for one face on each). If you want to mirror the object in the direction of its positive edge, then move the symmetry plane so it intersects the original object and rotate the symmetry plane 180 degrees.
- When you delete history of an object on which you have applied Mesh > Mirror Cut, the plane of symmetry is not deleted. You must manually delete the plane of symmetry.