統合フェーズ 5: キャラクタにパスの計算およびパスの追従を設定する
パスの追従は、単に A * の計算を実行してパスを見つけるよりも、はるかに複雑な問題になります。パス追従は動的で、場合によっては制限される、移動およびステアリング システムとの連携を伴います。キャラクタの近くの NavData が変更された場合など、動的なイベントによって、パスの変更が必要になる場合があります。動く障害物やその他のキャラクタなどとの衝突を回避するため、動的な回避システムが必要になります。
統合のこのフェーズでは、キャラクタがパス ファインディングを行いパスに追従するように、Gameware Navigation のパス フォローイング レイヤによって提供されているツールを使用します。
Bot のライフサイクル
パス フォローイング レイヤで重要なコンポーネントとなるのは、Bot クラスです。一般的に、Gameware Navigation パス ファインディングおよびパス フォローイング システムを使用する、各ゲーム キャラクタを表すクラスに Bot クラスのインスタンスを割り当てます。(プレイヤーのキャラクタなど、その他の種類のキャラクタは一般的に CylinderObstacle によって表されます。「動的な障害物や TagVolume を使用する」を参照してください。)Bot は、指定したターゲットへのパスを計算するために、パス ファインディング クエリを使用し、フレームごとに要求された速度を計算することによってそのパスを「追従」します。
Bot のライフサイクルは、初期化、各フレームでの更新、および破棄という少なくとも 3 つの場所で、対応するゲーム エンティティからの直接の連携を伴います。
統合を続けるうちに、この同じ考え方が動的な障害、TagVolume、インタレスト ポイントなどの他のクラスに使用されていることがわかるようになります。
初期化
- BotInitConfig オブジェクトのインスタンスを作成し、必要に応じてそのクラス メンバーを設定して、Bot::Init()の呼び出しに渡します。最低でも BotIni Config::m_database メンバーに、キャラクタがパス プランニングとパス フォローイングに使用する NavData の入った Database を指定する必要があります。
- Bot がパスを計算することができるように、Bot::ComputeNewPathToDestination() メソッドを使用して、パス ファインディング クエリのインスタンスを作成します。これを次の例に示します。Bot::ComputeNewPathToDestination() メソッドは、現在の Bot の NavigationProfile を呼び出す前に、以前に実行しているクエリをキャンセルし、ProfileID を使用して AStarQuery をインスタンス化します。次に、Bot::InitAStarQueryForBot() メソッドが呼び出されて、BotConfig を使用してクエリを設定します。最後に、Bot::ComputeNewPathAsync() メソッドが呼び出されて、非同期にクエリを計算し、Bot のパスを適切に変更します。
注:ユーザ自身で AStarQuery を初期化し、その後に Bot::ComputeNewPathAsync() メソッドを呼び出すことができます。ただし、Bot::ComputeNewPathAsync() メソッドを呼び出す前に、Bot::IsComputingNewPath() メソッドを使用して計算のステータスを確認する必要があります。
- Bot::AddToDatabase()を呼び出して Bot を Database で有効にします。これは、この Bot がパスをプランできるようにし、他の Bot との衝突を避けるようにするためです。これは通常、ゲーム キャラクタをスポーンするときに行われます。
更新
各フレームで、ゲーム キャラクタは、必要なときに新しいパスの計算を開始するために Bot と連携したり、Bot の現在の状態を更新したり、パス フォローイング システムの結果を解釈して適用する必要があります。
- Bot がパスに追従している間、キャラクタ クラスは、m_navBot->GetBotOutput().m_outputVelocity を呼び出して、各フレームにおける推奨された速度を得る必要があります。アニメーションやステアリング システムとの互換性のために、必要に応じて目的のモーション パスを修正します。ゲームのキャラクタには、最終的な結果を適用する必要があります。
- キャラクタの位置または速度が変化するたびに、Bot を適切に更新する必要もあります。Bot クラスのメンバー関数を使用して、Bot の位置と速度を更新することができます。たとえば、Bot の位置にアクセスするには、Bot::SetPosition() を呼び出します。
- また、さまざまな方法によってパス フォローイング システムの現在の状態の読み込みおよび対応が必要になる場合があります。以下のサンプルには、ターゲットに到達するための簡単なテストが含まれています。詳細については、「パス フォローイングをモニタする」を参照してください。
破棄
- World 内の他の Bot の考慮対象からその Bot を削除するために Bot::RemoveFromDatabase() メソッドを呼び出します。
- ゲームで Bot オブジェクトに保存したすべてのポインタを KY_NULL に設定します。これにより、参照カウント メカニズムがデクリメントされます。参照がなくなると、オブジェクトは透過的に破棄されます。
サンプル
次のサンプルでは、ゲーム キャラクタ クラス MyGameEntity による Bot クラスの比較的単純な使用法を示します。スポーンされた後、キャラクタは、初期位置と指定された位置の間でパスのプランおよび追従を繰り返します。
[Tutorial_FirstIntegration.cpp からのコード]
#include "gwnavruntime/world/bot.h"
...
class MyGameEntity
{
public:
MyGameEntity()
: m_startPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_destinationPosition(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_position(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_velocity(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f)
, m_navBot(KY_NULL)
{}
void Initialize(Kaim::World* world, const Kaim::Vec3f& startPosition, const Kaim::Vec3f& destination);
void Destroy();
void Update(KyFloat32 simulationStepsInSeconds);
bool HasArrived();
public:
Kaim::Vec3f m_startPosition;
Kaim::Vec3f m_destinationPosition;
Kaim::Vec3f m_position;
Kaim::Vec3f m_velocity;
Kaim::Ptr<Kaim::Bot> m_navBot;
};
void MyGameEntity::Initialize(Kaim::World* world, const Kaim::Vec3f& startPosition, const Kaim::Vec3f& destination)
{
m_position = startPosition;
m_startPosition = startPosition;
m_destinationPosition = destination;
m_navBot = *KY_NEW Kaim::Bot;
// We initialize the Bot at our desired start position
Kaim::BotInitConfig botInitConfig;
botInitConfig.m_database = world->GetDatabase(0);
botInitConfig.m_startPosition = m_position;
m_navBot->Init(botInitConfig);
...
// We add the Bot to our Database.
m_navBot->AddToDatabase();
...
}
void MyGameEntity::Destroy()
{
m_navBot->RemoveFromDatabase();
m_navBot = KY_NULL;
}
void MyGameEntity::Update(KyFloat32 simulationStepsInSeconds)
{
if (m_navBot->GetFollowedPath() == KY_NULL && m_navBot->IsComputingNewPath() == false) // We need to compute a Path!
{
// Here, we ask the Bot to launch a path computation.
// We should test the return code of this function, but as this tutorial is pretty simple, we are sure it cannot fail:
// - The AStarQuery is set from the default NavigationProfile.
// - We do not ask for a path computation while another path computation is in process.
// Note that Kaim::Bot::ComputeNewPathToDestination() will run the query during the Kaim::World::Update().
m_navBot->ComputeNewPathToDestination(m_destinationPosition);
}
// If we are arrived...
if (HasArrived())
{
m_velocity = Kaim::Vec3f::Zero();
// Clear the followed path.
m_navBot->ClearFollowedPath();
// Swap the positions.
Kaim::Vec3f swap = m_destinationPosition;
m_destinationPosition = m_startPosition;
m_startPosition = swap;
// Restart a move.
m_navBot->ComputeNewPathToDestination(m_destinationPosition);
}
// Retrieve the velocity suggested by the path following system, if available.
m_velocity = m_navBot->GetBotOutput().m_outputVelocity;
// Perform a simple integration.
m_position += m_velocity*simulationStepsInSeconds;
// Inform our Bot that the entity has moved.
// Note that the update will be effective after next World::Update() call
m_navBot->SetPosition(m_position);
m_navBot->SetVelocityAndFrontDirection(m_velocity);
}
bool MyGameEntity::HasArrived()
{
KyFloat32 arrivalPrecisionRadius = m_navBot->GetConfig().m_pathProgressConfig.m_checkPointRadius;
if (m_navBot->HasReachedPosition(m_destinationPosition, arrivalPrecisionRadius))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
class MyGameLevel
{
public:
...
void Update(float deltaTimeInSeconds);
...
protected:
...
MyGameEntity m_entity;
};
bool MyGameLevel::Initialize(Kaim::World* world)
{
... Do all other initializations
// Initialize my entity
m_entity.Initialize(world, Kaim::Vec3f(-11.5963f,1.06987f,10.4563f), Kaim::Vec3f(-16.636f,-26.7078f,8.10107f));
...
return true;
}
...
void MyGameLevel::Update(float deltaTimeInSeconds)
{
...
m_entity.Update(deltaTimeInSeconds);
}
void MyGameLevel::Destroy()
{
// Destroy my entity.
m_entity.Destroy();
... Do all other destructions and releases.
}
上記のほとんどのコードでは、パス フォローイング システムのデフォルトの動作を使用します。しかし、パス フォローイング システムは、設定が非常に調整しやすくなっています。ゲームのニーズに合わせてさまざまな方法でカスタマイズして調整し、キャラクタがパスを追従するときに発生するイベントに対応し、必要があれば関連するクラスのユーザ独自の実装を記述することさえできます。詳細は、「パス ファインディングとパス フォローイング」を参照してください。
テスト
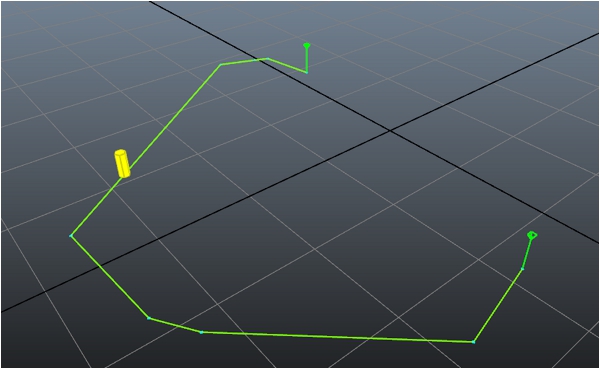
ゲームに Navigation Lab を接続すると、キャラクタを表す黄色の円柱が表示されます。これが、AstarQuery に設定した始点と終点の間の移動を繰り返します。例:
- 地面に沿ってキャラクタを配置するための物理的な要素がゲーム内にまだない場合は、キャラクタが地形より下に通り抜けたり、浮き上がったりする場合があります。
- NavMesh を介したパスのリファインの方法にはわずかな違いがあるため、両方向でまったく同じにはならない場合があります。