
Tangents describe the entry and exit of curve segments from a key. This menu operates on the shape of curve segments around selected keys. Note that these settings affect only existing animation curves segments’ tangents.
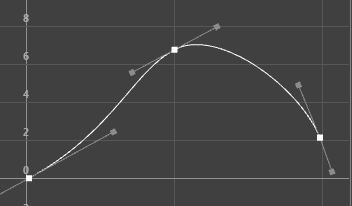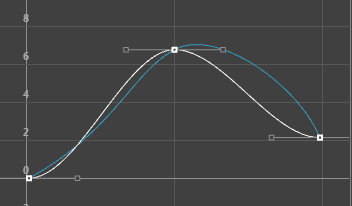
The animations displayed below show how a curve with default Auto tangents is changed by a different tangent choice. The original curve appears in a blue Buffer curve for you to compare how your choice of tangents affects the curve shape.
- Auto
-
Auto tangents clamp curve values between frames to a maximum or minimum point based on the adjacent keyframe values. Auto tangents are the default type for new keys (set as the Default in tangent and Default out tangent in your Animation (Settings) preferences).
-
Specifying Auto tangents creates an animation curve where the first and last keyframes have flat tangents, and keyframes in between do not overshoot the neighboring keyframe value. This type of curve prevents issues with interpenetration of closely animated objects that can occur with other tangent types, such as Spline.
- Spline
-
Specifying a spline tangent creates an animation curve that is smooth between the key before and the key after the selected key. The tangents of the curve are co-linear (both at the same angle). This ensures that the animation curve smoothly enters and exits the key. When animating fluid movement, a spline tangent is an excellent place to start. You use a minimum number of keys to achieve your look.
- Linear
-
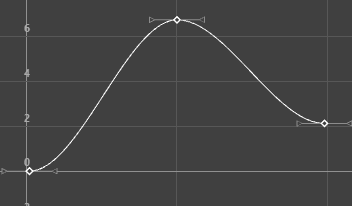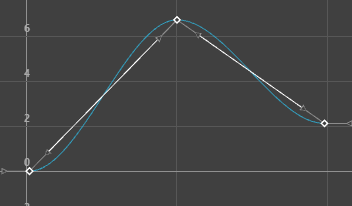
Specifying a linear tangent creates an animation curve as a straight line joining two keys. If the in tangent type is linear, the curve segment before the key is a straight line. If the out-tangent type is linear, the curve segment after the key is a straight line. When animating the color of a heating element on a stove, you would use linear to achieve that gradual change in color from charcoal gray to burning hot red.
- Clamped
-
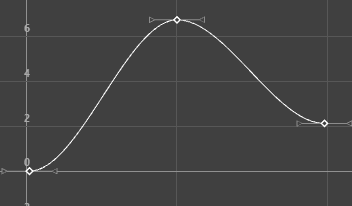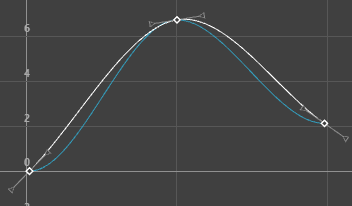
-
Specifying a clamped tangent creates an animation curve that has the characteristics of linear and spline curves.
-
The keys’ tangents will be splines unless the value of two adjacent keys are very close. In this case, the out tangent of the first key and the in tangent of the second key will be interpolated as linear.
-
When animating a skeleton in a walk-cycle, you may notice a slipping of the pelvic and foot joint position. This occurs because the value of the keys on the curve are either the same or close to (within tolerance of) the value of the other. Maya assigns a default spline tangent to describe what occurs between these keys. This is why you get the joint positions slipping.
-
By setting the tangent type to clamped for these keys, the slipping is corrected and the tangents becomes a combination of linear and spline.
In the Maya environment preferences, Clamped is the default tangent type.
- Stepped
-
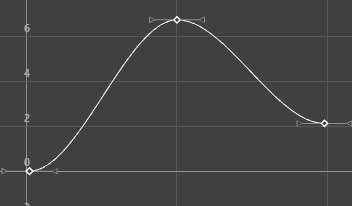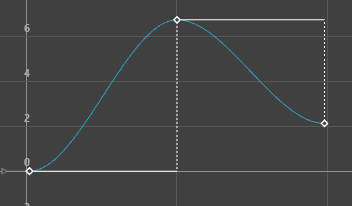
Specifying a stepped tangent creates an animation curve whose out tangent is a flat curve.
The curve segment is flat (horizontal), so the value changes at the key without gradation.
The light from a strobe light turns on and off. To create a strobe-like effect, you would use a step tangent.
Tip: To get a quick preview of your animation as if all keys have Stepped tangents, right-click the Time Slider and toggle the Enable Stepped Preview option. When Enable Stepped Preview is on, playing back your animation lets you quickly view the position of objects as they hit each keyframe. Curves return to their original tangent types when you turn off Enable Stepped Preview. - Stepped Next
-
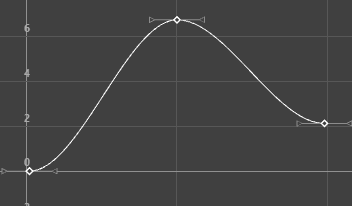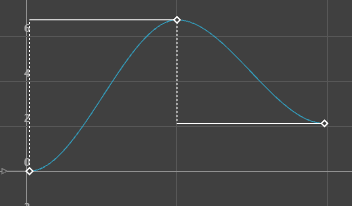
FBIK animation keys use the stepped next tangent type by default. This tangent type differs from regular Stepped tangents in that its interpolation values jump immediately to that of the next key, rather than holding the value of the current key until the next key is reached.
- Flat
-
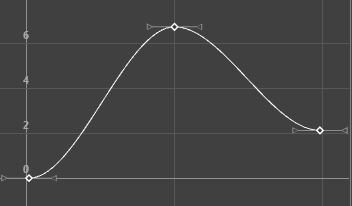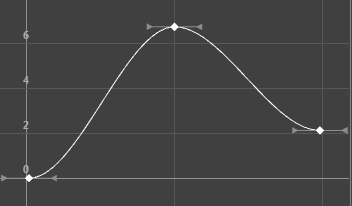
Flat tangents set on a curve with Weighted tangents
Sets the in and out tangents of the key to be horizontal (with a slope of 0 degrees). When a ball reaches its ascent, it hangs in the air for a brief time before starting its descent. You can create this effect by using a flat tangent.
- Fixed
-
Specifying a fixed tangent allows a key’s tangents to remain unchanged as the key is edited.
When animating a ball, you may find the ball isn’t falling from a desired height, yet its impact with the floor and everything else is perfect. Using a fixed tangent lets you change the height of the ball while retaining the tangent’s angle. This is somewhat different from Key > Bake Animation.
This process is useful when you want to:
- Edit a single animation curve instead of all the contributing attributes that affect the behavior of a single attribute, for example, an object affected by a driven key or an Expression.
- Add keys to an existing curve
- Plateau
-
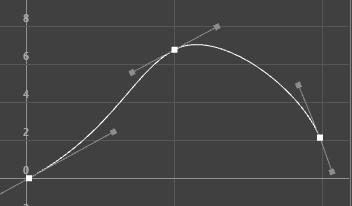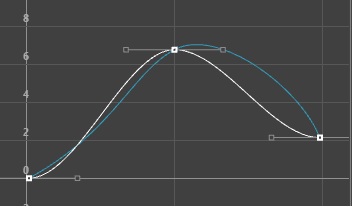
Plateau tangents set on a curve with Weighted tangents
Plateau tangents ease animation curves in and out of their keyframes like spline tangents, but also flatten curve segments that occur between equal-valued keyframes like clamped tangents. The plateau tangent normally behaves like a spline tangent, but ensures that the minimum and maximum values along a curve are all at keyframes.
Plateau tangents are useful when you want the positions of your keyframes to be exact, because they ensure the maximum and minimum values (‘hills and valleys’) of the curve do not extend past their keyframes. For example, picture an animation of a ball rolling off a table, falling to the floor, and then rolling on the floor. With spline tangents, the ball falls through the floor, then comes back up to the floor. With plateau tangents, the ball will not fall through the floor. The tangents guarantee that your animation will not wander beyond the values you keyframed.
To do this, if a spline tangent would produce a minimum or maximum between two keyframes, the plateau tangent flattens the keyframes in question. Keyframes at local minimum and maximum points along the curve are also flattened. Finally, the first and last keyframe along a curve are always flattened if they have plateau tangents.
- In Tangent
-
Lets you specify a type of tangent for the In Tangent only. The In Tangent defines the type of curve segment that comes before a key. See the animations above for a depiction of how different tangent types affect a curve.
Note: You can also set the Default In Tangent for new keys in the Preferences window. See Default In Tangent in the Animation (Settings) preferences menu. - Out Tangent
-
Lets you specify a type of tangent for the Out Tangent only. The Out Tangent defines the type of curve segment that comes after a key.
Note: You can also set the Default Out Tangent for new keys in the Preferences window. See Default Out Tangent in Animation (Settings) preferences. - Unify Tangents
-
Note: This setting is only for Broken tangents; once unified, the broken tangents are rejoined, but they keep the new angle.
Lets you preserve the angle and length of tangents. Unify Tangents retains the relative position of the tangent handles even after tangents are individually adjusted (by editing tangents separately after choosing ).
- Default In tangent
-

Specifies the default in tangent type. The In Tangent setting controls the shape of the animation segment before a key.
Note: You can also configure these defaults in the Tangents section of the Animation (Settings) Preferences.Options include:
- Auto
-
(Default) An Auto In Tangent compares the current keyframe value to the previous keyframe value, and flattens the curve segment if it travels above or below those keyframe values. (See also Auto Tangents in the Graph Editor Tangents menu.)
- Spline
-
A spline tangent rounds the animation curve smoothly before the key. If the key’s Out Tangent is also a spline, the tangents of the curve are then co-linear (both at the same angle). This ensures that the animation curve smoothly enters and exits the key.
- Linear
-
A linear tangent creates an animation curve as a straight line before the key.
- Clamped
- The clamped tangent smoothly rounds the animation curve (like the Spline selection) before a key unless the next key is very close. If so, the In Tangent and the previous key’s Out Tangent are both straight (like the Linear selection), making the animation curve between the keys straight.
- Flat
-
A flat tangent type sets the tangents before the key to be horizontal with a slope of 0 degrees (flat).
- Plateau
-
A Plateau tangent type eases animation curves in and out of their keyframes, flattens curve segments that occur between equal-valued keyframes, flattens keyframes at the points in their curves where hills and valleys occur, and flattens the first and last keyframes on their curves.
- Default out tangent
-

Specifies the default out tangent type. The Out Tangent setting controls the shape of the animation curve right after a key. See the animations above for a depiction of how different tangent types affect a curve.
-
Options include:
- Auto
-
(Default) An Auto out tangent compares the current keyframe value to the next keyframe value, and flattens the curve segment if it travels above or below those keyframe values. (See also Auto Tangents in the Graph Editor Tangents menu.)
- Spline
-
A spline out tangent rounds the animation curve smoothly after the key. If the key’s In Tangent is also a spline, the tangents of the curve are then co-linear (both at the same angle). This ensures that the animation curve smoothly enters and exits a key.
- Linear
-
A linear tangent creates an animation curve as a straight line after a key.
- Clamped
-
Specifies the animation curve is smoothly rounded (like the Spline selection) after a key unless the next key is very close. If so, the Out tangent and the previous key’s In tangent are both straight (like the Linear selection), making the animation curve between the keys straight.
- Flat
-
A flat tangent type sets the tangents after the key to be horizontal with a slope of 0 degrees (flat).
- Stepped
-
A stepped tangent type forces the animation curve to hold its value from the one key to the next key.
- Plateau
-
A plateau tangent type eases animation curves in and out of their keyframes, flattens curve segments that occur between equal-valued keyframes, flattens keyframes at the points in their curves where hills and valleys occur, and flattens the first and last keyframes on their curves.
- Break Tangents
-
Allows manipulation of the in and out tangent handles individually so you can edit the curve segment entering or exiting the key without affecting its opposite handle.
- Lock Tangent Length
-
Formerly named Lock Tangent Weight in previous versions of Maya.

Specifies that when you move a tangent, only its angle can be changed. This forces the associated curve segment to retain the weight of the tangent. This applies only to weighted curves. When tangent handles are locked, they turn black.
- Free Tangent Length
-
Formerly named Free Tangent Weight in previous versions of Maya.
Specifies that when you move a tangent, its angle and weight can be changed. This allows the weight of a tangent to be adjusted as well as the angle. This only applies to weighted curves. When tangent handles are free, they are pale grey.
