You assign connection types in the Connector Properties dialog box as you build fittings content using the Content Builder (see Adding Connectors to a Parametric Fitting). Assigned connection types are then displayed on the Connection Assignments tab of the Pipe Layout Preferences dialog box. The following table shows the different orientations of pipe connection types:
| Connection type | Connection orientation |
|---|---|
| Flanged, all types |
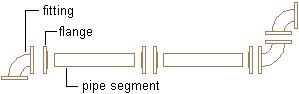 Fitting to pipe: Flanges are typically included on fittings. A separate flange is added to the pipe segment. Pipe to pipe: A separate flange is added to each pipe end to create the connection. Fitting to fitting: Fittings with inherent flanges connect directly to each other. No separate flanges are added to the connection. |
| Threaded, Socket weld, Glued, Brazed |
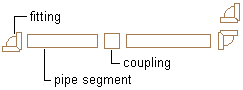 Fitting to pipe: Pipe segments typically have inherent male ends, and fittings are typically female. The pipe inserts directly into the fitting. Pipe to pipe: A female coupling is inserted between the pipe segments. Fitting to fitting: Fittings connect directly to each other. |
| Grooved |
 Fitting to pipe: Fittings and pipe segments are considered to have grooved ends that are ready to accept a coupling. A coupling is added to connect the fitting and pipe. Pipe to pipe: A coupling is added to connect the pipe segments. Fitting to fitting: A coupling is added to connect fittings. |
| Butt weld |
 No extra objects are added. Fittings and pipe segments connect directly to each other. |