A fillet is a surface that creates a smooth tangent-continuous blend between two surfaces. This figure shows a fillet surface that blends two flat surfaces.
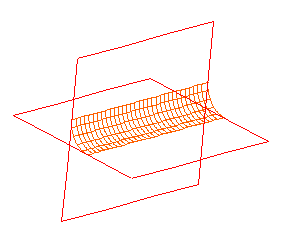
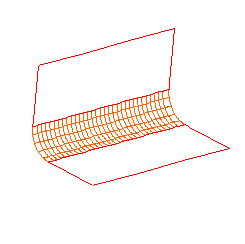
This figure shows the same fillet with the surfaces automatically trimmed against the two fillet boundaries.
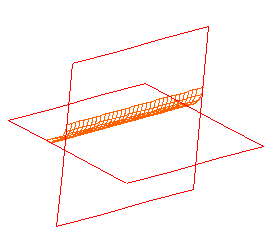
Just like the case of an arc between two lines, there is more than one possible fillet between two surfaces. This figure shows the same two flat surfaces with a fillet on another corner.
A constant radius or rolling ball fillet is created by setting the Begin radius and End radius to the same value. A variable radius fillet is created by entering different values for the two radii.
Filleting multi-step process:
- Intersect the two surfaces. If you explicitly specify the intersection curve this step is skipped. The most common reason for explicitly entering the intersection curve is to calculate the curve separately and then extend it so that the fillet extends beyond the surface boundaries.
- Construct fillet surface.
- Optionally trim one surface against the top of the fillet. The top boundary curve of the fillet must be a valid trimming curve for the top surface.
- Optionally trim the other surface against the bottom of the fillet. The bottom boundary curve must be a valid trimming curve for the bottom surface.
It is possible to create a valid fillet surface that does not allow you to trim the surfaces against the fillet. In this example, the fillet is in the middle of both surfaces and as a result the boundaries of the fillet are not valid trimming curves. See Trimming restrictions for the rules of valid trimming curves.