The contents of an Inspect element list vary, depending on the data type of the object being inspected.
The following table identifies the list contents for each data type.
|
Inspect element lists |
|
|---|---|
|
Data type |
Contents of element list |
|
INT (integer) |
The integer number represented in binary, octal, decimal, hexadecimal, and character formats. Character format means the ASCII character that corresponds to the number (for large numbers it takes the last byte).  |
|
REAL (floating point number) |
Real numeric value; does not have an element list.  |
|
STRING |
The sequence of characters in the string, which may in turn be inspected as integers. 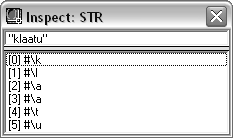 Double-click on a listed character to see its ASCII number representation. |
|
SYMBOL |
Three elements: value, print name, and flags. Flags may be one of the following: Pa Protect Assign Tr Trace De Debug on entry Ea Export to ACAD 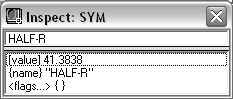 Right-click over the Object Line and click Symbol Service to view or change the information related to the symbol in the Symbol Service dialog box. |
|
LIST (for proper lists) |
Items of the inspected list. 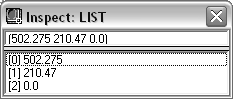 |
|
LIST (for improper lists) |
Two elements: the car and cdr fields. It serves for all cases that are not proper lists, that is, where the last cdr is not nil. For example, a list constructed by (cons 4 '(5 . 0)) is represented as follows: 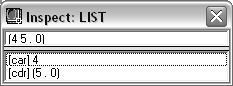 |
|
FILE |
The name of the corresponding file and the file's opening attributes. 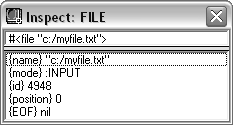 File Inspect fields include the following: Name is string that contains the file name used in the open function. Mode indicates whether the file is open for input, output, append, or whether the file is closed. ID shows the internal file identifier. Position shows the current position in the file. EOF indicates whether or not the end of the file has been reached. This field does not appear if a file is open for output. |
|
SUBR, EXRXSUBR, and USUBR |
The name of the function (the name that was specified in defun or at load time). SUBR refers to internal and compiled functions, EXRXSUBR refers to external ARX functions, and USUBR identifies user-defined functions. The SUBR data type represents functions that cannot be debugged with the Visual LISP debugging tools (for example, you cannot set breakpoints). These are internal AutoLISP functions, or functions loaded from FAS or VLX files. The SUBR Inspect window shows a string containing the name of the symbol, as in the following example:  The USUBR data type represents functions that can be debugged with the Visual LISP debugging tools (for example, you can set breakpoints and view the values of program variables). These functions are loaded from AutoLISP source code. The USUBR Inspect window shows the name of the symbol, a list of function parameters (arguments), and a list of local variables declared in the function (listed after the “/” in the defun argument list). The following example shows an Inspect window for a function named YINYANG that does not accept any arguments, but does declare several local variables: 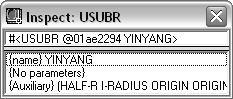 The EXRXSUBR data type represents functions loaded from ObjectARX or .NET applications. The EXRXSUBR Inspect window shows a string containing the function name, as in the following example: 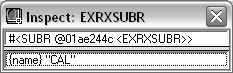 |
|
ENAME (drawing entity) |
The fields in this element list correspond to the AutoCAD DXF object list, as returned by the AutoLISP built-in function. The following example shows an Inspect window for a circle: 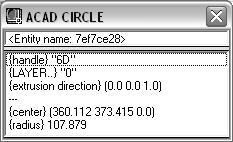 |
|
PICKSET (selection set) |
List of selected AutoCAD objects. 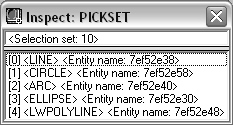 |
|
VARIANT |
The data type and value of the variant. The following example shows an Inspect window for a variant that contains an array of doubles: 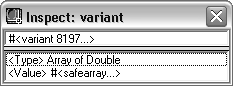 |
|
SAFEARRAY |
The data type, number of dimensions, and value of the safearray. The following example shows a Safearray Inspect window for a single dimension array of doubles: 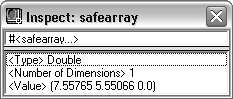 |