What's New: 2021
In the Thicken/Offset command, When you select Output, you specify the feature type, depending on your selection:
- Surface creates an offset surface.
- Solid creates a thicken feature.
- New solid creates a body in a multibody part.
You cannot create both thickened faces and offset surfaces in one feature. Offsets are surface features while thicken is a part feature. In the browser, each feature type displays a different icon .
The following images show various thicken or offset solutions.
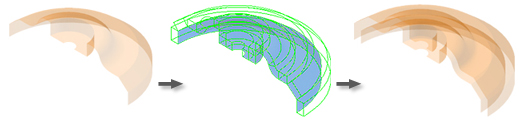
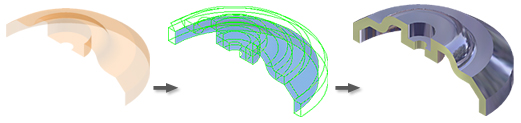
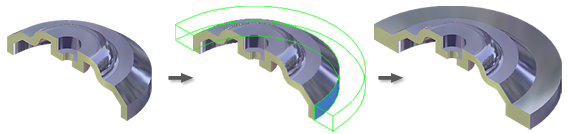

Thicken adds or removes material from the model, changing its mass properties. When you add thickness to a surface, the model adds a solid feature based on the surface.
By default, the software provides a precise offset feature. When a precise solution does not exist, an approximation is attempted.
You can offset one or more faces from a part face or a quilt. Offset surfaces do not add or remove mass.
You can create copies of surfaces with a zero distance offset, but not surfaces with vertical sides. You can make a copy of an entire surface body, or a set of individual faces from any solid model or surface.
Edit Feature vs. Thicken/Offset
You cannot use Edit Feature to change an Offset Surface feature to a Thicken feature or vice versa.
You can, however, thicken an offset surface. This operation adds a solid feature based on the surface and places a thicken icon below the offset surface icon in the browser.
Surfaces for offset operations
You can use surfaces created in Autodesk Inventor or imported surfaces for an offset. Imported surfaces must be promoted to the part environment. You can not perform a thicken or offset operation in the construction environment .
Surfaces must be adjoining to be offset at the same time. The offset result is a copy of the selected geometry (such as face, fillet, adjacent face).
Vertical surfaces can be created from only the internal boundaries of a quilt face.
When importing complex surfaces, you can experiment with the file format. IGES and SAT files are commonly used formats when converting models you receive from a vendor, for example.
Precise and approximate solutions
In a precise solution for Offset, each point of the original surface has a corresponding point on the offset surface. The distance between the two points is equal to the specified distance. An approximate solution enables deviation from the specified distance to find an acceptable solution.
You can control where the deviation can occur, and the accuracy of the approximation. The more accurate the approximation, the longer it takes to compute. When a precise solution does not exist, and if an approximate solution can be found, the approximate solution is provided. If approximate solutions are not acceptable, you can turn off this option.
Each time you use approximation, the tolerance of the deviation is reported.