Revit uses 2 coordinate systems: a survey coordinate system and a project coordinate system.
 The
survey coordinate system provides a real-world context for the building model. It is intended to describe locations on the surface of the earth.
The
survey coordinate system provides a real-world context for the building model. It is intended to describe locations on the surface of the earth.
 The
project coordinate system describes locations relative to the building model. It uses a selected point within the property boundary or within the extents of the project as a reference for measuring distances and positioning objects in relation to the model.
The
project coordinate system describes locations relative to the building model. It uses a selected point within the property boundary or within the extents of the project as a reference for measuring distances and positioning objects in relation to the model.
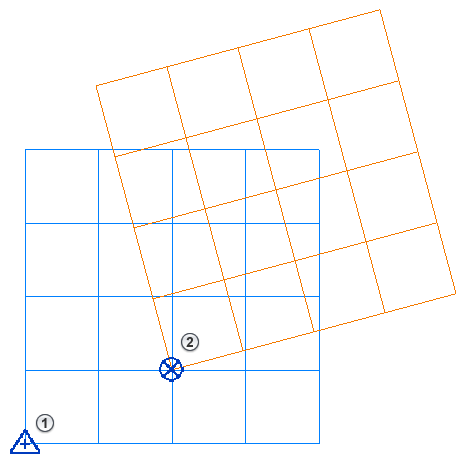
The origin of the internal coordinate system provides the basis for the survey and project coordinate systems. See About the Internal Origin.
You can also use a shared coordinate system to position imported or linked models in relation to a host Revit model. See About Shared Coordinates.
Survey coordinate system
Use the survey coordinate system to identify the specific location on the earth's surface where your Revit model resides. This coordinate system is defined outside the context of a project.
Many survey coordinate systems are standardized. Some systems use latitude and longitude; others use XYZ coordinates. Survey coordinate systems handle significantly larger scales than project coordinate systems and deal with issues such as the curvature of the earth and terrain, which are insignificant to project coordinate systems.
In
Revit, the survey point
 identifies a real-world location near the model. For example, you can place the survey point at a corner of the project site or at the intersection of 2 property lines, and specify its real-world coordinates. (See
identifies a real-world location near the model. For example, you can place the survey point at a corner of the project site or at the intersection of 2 property lines, and specify its real-world coordinates. (See
 in the above image.)
in the above image.)
The survey coordinate system is synonymous with the following terms used by other software applications or in other contexts:
- global coordinates
- GIS coordinates
- grid coordinates
- surveyor coordinates
- projection coordinates
- state plane
- shared coordinates
Project coordinate system
Use the project coordinate system to determine the position of objects relative to a specified point near the model. This coordinate system is specific to the current project.
In
Revit, the origin of the project coordinate system is the project base point
 . Many teams use the project base point as a reference point for measurements across the site. Place it at the corner of a building or another convenient location in the model to simplify on-site measurements. (See
. Many teams use the project base point as a reference point for measurements across the site. Place it at the corner of a building or another convenient location in the model to simplify on-site measurements. (See
 in the above image.)
in the above image.)
Revit's project coordinate system is synonymous with the following terms used by other software applications or in other contexts:
- local coordinates
- World Coordinate System (WCS)
- world coordinates (in a DWG context)
- User Coordinate System (UCS)
- user coordinates
- design coordinates
- model coordinates
- engineering coordinates
- internal coordinates
- CAD coordinates