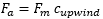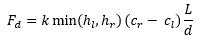Suspended sediment and bed load transport can be modelled in the 2D network by selecting options in the QM Parameters Dialog when scheduling a run in the Schedule Hydraulic Run View:
- Model 2D erosion-deposition - select this option to model suspended sediment transport
- Model 2D bed load - select this option to model bed load transport
Water quality for the 2D parts of the model is set up in much the same way as for the 1D side. See the Water Quality Simulations and Water Quality Model sections for further details.
The 1D and 2D engines first solve advection of the determinants and then perform the diffusion step.
The mass advective flow in each face between elements is given by the following equation:
|
|
where: Fa = mass flow through the face due to advection (kg/s) Fm = volumetric flow through the face (m3/s) c_upwind = cl if volumetric flow goes from left to right element, cr otherwise (kg/m3) where: cl = determinant concentration in left element (kg/m3) cr = determinant concentration in right element (kg/m3) |
The diffusion flow is calculated in each face between elements using the following equation:
|
|
where: Fd = mass flow through the face due to diffusion (kg/s) k = diffusion coefficients (m2/s) hl = water depth in left element (m) hr = water depth in right element (m) cl = determinant concentration in left element (kg/m3) cr = determinant concentration in right element (kg/m3) d = distance between element centroids (m) L = face length (m) |
For details of sediment calculations, see the 2D Sediment Transport Equations topic.
Setting up 2D Water Quality data
The available sources of pollutant in a 2D Zone are:
- River banks
- Manholes
- Point sources
- External boundaries
The steps to setting up a 2D Water Quality model are:
- Set Initial 2D water quality conditions - initial conditions can be set up through 2D IC Zones.
- 2D IC Water Quality Zones are used to define areas in which initial concentration of sediment fractions or determinants apply.
- 2D IC Sediment Zones are used to define areas in which initial sediment layer depths and composition apply.
- The initial concentration values themselves are defined in the Initial Conditions 2D object.
- Initial conditions can be assigned to IC Zones or to 2D Zones.
- Set Pollutograph profiles - time varying profile of determinant concentration is defined in a
Pollutograph object. Profiles for each determinant are associated with a 'node reference'. The node reference can be one of the following objects:
The pollutograph data is combined with the inflow coming from the above objects to set the net mass determinant flow in the 2D engine.
- Set diffusion parameters - diffusion coefficients are set up in the Water Quality and Sediment Parameters dialog.
- To model sediment transport, set sediment parameters - sediment parameters are set up in the Water Quality and Sediment Parameters.
- Set QM parameters on run dialog - to run the water quality simulation set up the following in the water quality module section of the
Schedule Hydraulic Run View:
- Check the Use QM option
- Click the QM parameters button to display the QM Parameters Dialog and select pollutants to be modelled
- Check the Model 2D erosion-deposition option to model sediment transport
- Include the Pollutograph in the schedule
One diffusion coefficient can be set up per sediment fraction and per dissolved determinant.
If no diffusion coefficient is specified for a specific pollutant, the engine will only transport it. There will not be any diffusion.
2D Water Quality Results
Additional results are available when running a water quality simulation:
- In the log file - for each pollutant, a summary is written, with the initial mass, final mass and boundary net inflow.
- Additional results for 2D Zones, network results objects (points, lines and polygons) and Results Analysis Objects - concentration results for each dissolved determinant, attached determinant and sediment fraction