Dual Domain mesh
A Dual Domain mesh represents a solid CAD model by covering the surface of the model with triangular elements.
 Download the files for this tutorial from Autodesk Knowledge Network - Meshing tutorial.
Download the files for this tutorial from Autodesk Knowledge Network - Meshing tutorial.
The model could be visualized as a hollow body covered with a surface shell made up of triangular elements.
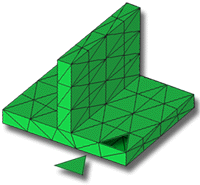
The triangular surface elements are orientated so that the corner nodes of triangles on opposite faces of the part align. The thickness of a given area of the part is then determined by the distance between these nodes.
When analyzing with a Dual Domain mesh, mathematical layers (typically 10 or more layers) through the thickness of the part are used as a frame to simulate the polymer flow. Triangular elements on opposite faces of the part must be matching so these layers can be accurately constructed and to ensure the alignment of the layers through the thickness.
A Dual Domain mesh provides an accurate representation of thin parts, where there is a rapidly changing cross-section profile for parameters such as temperature and flow-front velocity.
In this task, you will:
- Import a Dual Domain model
- Investigate how the mesh is structured
- Ensure the Mesh tutorial project you used in the previous task is active. If it is not, click
 (Start & Learn tab > Launch panel > Open Project) and select Mesh tutorial.
(Start & Learn tab > Launch panel > Open Project) and select Mesh tutorial. - Click
 (Home tab > Import panel > Import).
(Home tab > Import panel > Import). - From the Files of type drop-down list, select Study files (*.sdy).
- Navigate to the where you saved the tutorial files.
- Select dustpan_dual_domain.sdy, then click Open.
- Click
 ( View tab > Navigate panel > Select).
( View tab > Navigate panel > Select). - Click on an element (triangle) in the model and press Delete on your keyboard.
- Click
 Center and click on an element adjacent to the deleted element. This will centralize the area under investigation.
Center and click on an element adjacent to the deleted element. This will centralize the area under investigation. - Rotate and zoom in on the model to understand the way the model has been represented.
- Note that the Dual Domain Mesh type and number of elements in the model are displayed in the Study Tasks pane.
Click the Next topic link below to move on to the next task of the tutorial.
Parent topic: Mesh
Previous topic: Midplane mesh
Next topic: 3D mesh