Activity 2: Apply a nonlinear material
A generic steel material was specified in the Design workspace. You need a material from the Fusion Nonlinear Material Library to demonstrate plastic deformation of the beam when the yield stress is exceeded.
In this activity, you
Select the material from the nonlinear material library
Confirm that the material you select shows nonlinear behavior
Determine the pressure at which the material starts to exhibit significant plasticity.
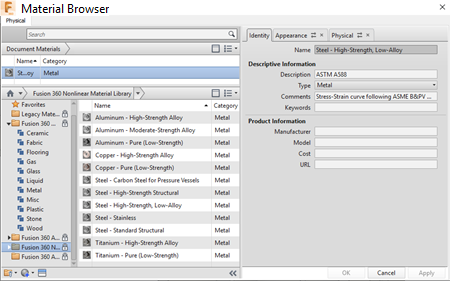
Fusion Material Browser.
Prerequisites
- Activity 1 is complete.
Steps
Select Steel - High-Strength, Low-Alloy from the Fusion Nonlinear Material Library.
- Click
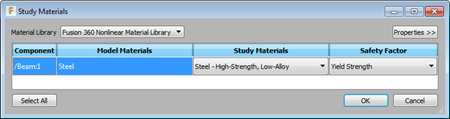
 (Simulation workspace > Setup tab > Materials panel > Study Materials) to open the Study Materials dialog.
(Simulation workspace > Setup tab > Materials panel > Study Materials) to open the Study Materials dialog. - In the Study Materials dialog, select Fusion Nonlinear Material Library from the Material Library drop-down list.
- Select Steel - High-Strength, Low-Alloy as the Study Material.
- Click
Confirm that the material, Steel - High-Strength, Low-Alloy, shows nonlinear behavior.
- While the only row in the Study Materials table is still selected, click Properties in the upper left corner of the dialog.
- In the expanded portion at the right end of the dialog, click View advanced material properties to open the Material Browser dialog.
Note: If you don't see View advanced material properties, confirm that the row on the left of the Study Materials dialog is selected.
- In the Material Browser dialog, hover over the highlighted material near the top of the dialog, and click
 Edit to display the material properties.
Edit to display the material properties. - In the expanded dialog, click the Physical tab to view the Basic Properties.
- Click Advanced Properties to view the nonlinear properties. Be careful not to deactivate the checkbox that enables the advanced properties.
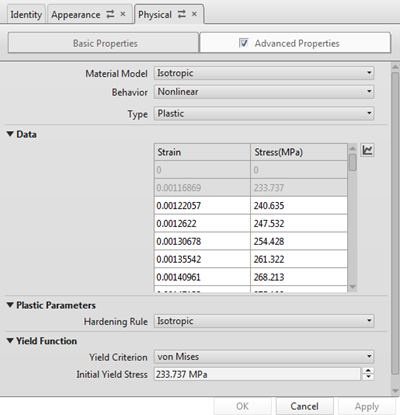
Note: The Material Model is Isotropic, the Behavior is Nonlinear, and the Type is Plastic. This material type is defined by discrete stress-strain values in the data table. Depending on your user preferences, you may see the material represented using different units. The above image is based on the following setting: Preferences > Unit and Value Display > Material Unit Display = Metric Standard (MPa, kg, J).If you change the material unit choice, you must close and reopen the dialog to refresh the displayed units.
Tip: Click
 (Simulation workspace > Setup tab > Materials panel > Manage Physical Materials) to access the Material Browser directly.
(Simulation workspace > Setup tab > Materials panel > Manage Physical Materials) to access the Material Browser directly.
Review the graphic plot of the stress-strain curve to determine the pressure at which the material starts to exhibit significant plasticity.
- In the Material Browser dialog, to the right of the Strain Stress data table, click
 Show Plot, to open the Nonlinear Plastic Plot.
Show Plot, to open the Nonlinear Plastic Plot.Note: You may need to scroll the panel to the side, to see the Show Plot command.
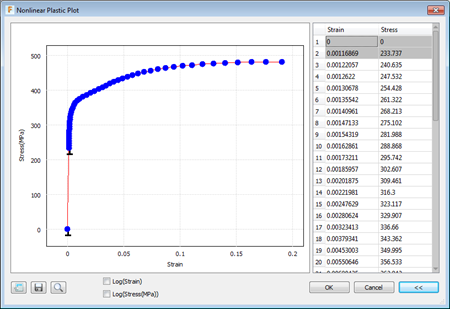
- Notice that slight nonlinear behavior begins at 233.737 MPa (33,900 psi), which agrees with the Initial Yield Stress value displayed in the Yield Function section of the Material Browser dialog. The zero-zero and initial yield data points are added to the table automatically when you define a nonlinear plastic material.
- Notice that the material doesn't exhibit significant plasticity until the stress exceeds about 350 MPa (~50,800 psi). This stress level is comparable to the Yield Strength of 344.738 MPa (50,000 psi) shown under Basic Properties > Strength. The basic yield strength is the stress at which the stiffness of the material deviates 0.2% from the Young's Modulus value. It is not uncommon for a nonlinear material curve to show the small deviations from linear behavior at values less than the basic yield strength.
- Click Cancel to close the Nonlinear Plastic Plot dialog.
- Click Cancel to close the editing panel without changing any of the predefined material properties.
- Click the X in the upper right corner of the Material Browser to close it.
- In the Material Browser dialog, to the right of the Strain Stress data table, click
Activity 2 summary
In this activity, you
- Selected the material from the nonlinear material library
- Confirmed that the material you select shows nonlinear behavior
- Determined the pressure at which the material starts to exhibit significant plasticity.