Use Uniform Surface Load to define and apply a planar load with the same magnitude to a surface element.
Access
- Click Loads
 Surface
Surface 
 Uniform Surface Load.
Uniform Surface Load.
Parameters of Uniform Surface Load
- Load case
- Use it to select an
active load case.
Click
 to open the Load Cases dialog.
to open the Load Cases dialog.
- Direction
- Select a direction of load: X, Y, or Z direction of the global or local coordinate system.
- P
- Specify magnitude of the load.
- Coordinate system
-
- Global. Select it to specify a load direction in the global coordinate system.
- Global with projected load. It specifies a load direction in the global coordinate system. Use it to apply the load to the surface projected on the plane that is normal to the load direction. Use this option to reduce the load intensity when you apply loads to inclined surfaces. Often used for snow loads.
- Local. Select it to specify a load direction in the local coordinate system of an element to which you apply the load. Used for wind loads or pressure loads.
- Geometrical Limits
- Specify geometrical limits to apply the load to a part of the element surface.
- Plane selection
- Select a cutting plane that limits the load action. You can select:
- A plane parallel to any of the three planes of the global coordinate system:
XY,
YZ, or
ZX
Then specify the point p1 which defines the position of the cutting plane on the element.
-
Arbitrary plane.
Then specify points: p1, p2, and p3 to define the plane.
If you select None, you do not specify geometrical limits.
- A plane parallel to any of the three planes of the global coordinate system:
XY,
YZ, or
ZX
- p4 (direction)
- Enter a point on one side of the cutting plane to specify the direction.
p4 defines a half-plane in which the load act.
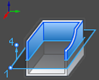
In the image:
1 denotes point p1
4 denotes point p4
- Thickness d
- Specify the thickness of a layer in which loads acts.
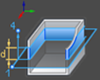
In the image:
1 denotes point p1
4 denotes point p4
- Assignment
- Use Direct or Selection mode to assign a load to model elements.
Example: To Apply a Uniform Surface Load