When you change the geometry of a space, it can have different results for openings attached to the space surfaces.
Changing the Shape of a 3D Freeform Space
3D freeform spaces have a large number of possible geometries, such as a box, a pyramid, or an irregular freeform shape. Changing the geometry of the space can affect openings in space surfaces in the following ways:
- When a surface is deleted or moved so that it is no longer coplanar to an opening it contains, the opening will be deleted.
- When a surface is edited in a way that does not affect the opening, the opening is retained unchanged.
- When a surface is split and an opening crosses the split line, the opening is split into 2 openings. Note: If the space geometry is changed in any way that changes the total number of surfaces, then openings may be deleted or may occasionally move from one surface to another.
Changing the Geometry Type
You can convert a 3D freeform space to an extruded 3D space, and vice versa. This will affect contained openings in different ways.
- When an extruded 3D space is converted to a 3D freeform space, all openings will be retained with the same location, shape, and area. The opening grips change to the grips of an extruded 3D space surface opening.
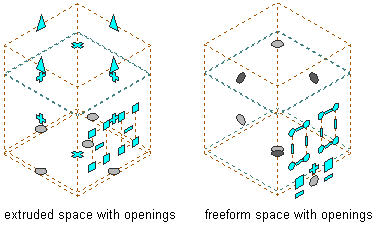
Viewing Extruded and Freeform space surface openings
- When a 3D freeform space is converted to an extruded 3D space, the openings on the horizontal roof or floor surfaces will be kept on the roof or floor of the extruded 3D space. The openings on the surfaces that intersect with the base profile will be retained on the respective edge surfaces. All other openings will be lost. The openings that are retained will change to rectangles, and the area of the opening will remain the same.
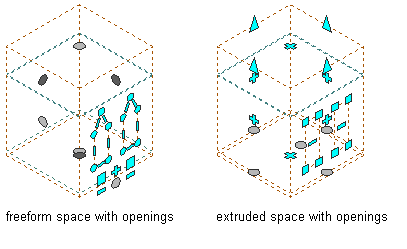
Viewing Freeform and Extruded space surface openings
- When an extruded 3D space or a 3D freeform space is changed to a 2D space, all surface openings are lost.
Changing the Associativity
You can convert associative spaces to non-associative spaces, and vice versa. This will affect contained openings in different ways.
The openings in associative spaces are generated by any openings that are in the boundary walls. For example, if a boundary wall has a window and a door, openings with the shape of the window and door are inserted in the space.
- If an associative extruded 3D space is converted to a non-associative extruded 3D space, all openings will be retained in their original position, but will now have editing grips. If the shape of the original opening is not rectangular, the opening shape will change to a rectangle identical in area to the original shape.
- If an associative 3D freeform space is converted to a non-associative 3D freeform space, all openings will be retained with identical location, size, and shape, and will have editing grips.