Arrays
An array is an ordered sequence of items. Array indexing in MCG is 0-based.
Creating Arrays
The nodes in the Array > Generation category can be used to initialize an array of a given size. Use the "Array of" prefix to search for nodes related to array generation.
Array of Integers: Returns an array of integers from 0 to n-1. For example, a value of n=5 produces the array: [0,1,2,3,4].
Array of Floats Inclusive: Returns an array of n evenly spaced floats between 0.0 (inclusive) and 1.0 (inclusive). For example, a value of n=5 will produce the array: [0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0].
Array of Floats Exclusive: Returns an array of n evenly spaced floats between 0.0 (inclusive) to 1.0 (exclusive). For example, a value of n=5 will produce the array: [0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8].
Array of Value: Returns an array containing n copies of the given value. For example, a value=42 and n=5 will produce the array:
[42, 42, 42, 42, 42].Array 1, Array 2, Array 3, Array 4 can be used to create arrays of length 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
Random Arrays
You can use the "Array of Random ____" nodes from the Random category to generate seeded arrays of random values:
Array of Random Booleans: Returns an array of n random uniformly distributed True or False boolean values.
Array of Random Floats: Returns an array of n random uniformly distributed floats between 0.0 and 1.0, based on the given seed.
Array of Random Integers: Returns an array of n random uniformly distributed integers between -2147483648 and 2147483647.
Array of Random Vectors: Returns an array of n random uniformly distributed vectors between [0,0,0] and [1,1,1], based on the given seed.
Constant Arrays
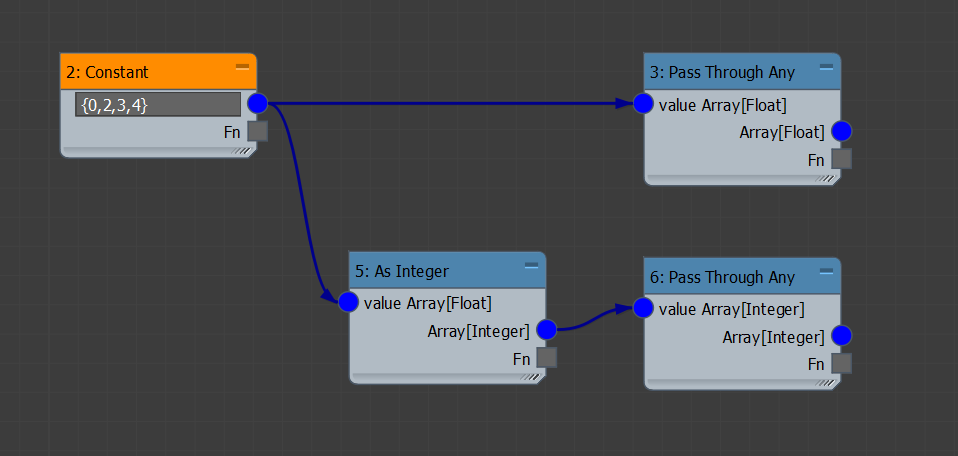
You may also specify hard-coded arrays of floats with the Constant node. The contents of the array are declared as comma-separated numbers inside curly brackets, for example: [0,2,3,4]. The As Integer node can be used to convert this array of floats into an array of integers.
Indexing
Array indexing in MCG is zero-based, compared to MAXScript which is 1-based. The first item in a MCG array is indexed at zero.
Count: Returns the number of items contained in the array. The last item of an array is at Count-1.
Indices: Returns the indices of the array as an array of integers ranging from 0 to Count-1 (inclusively).
At: Returns the item at the given index. This is equivalent to the bracketed subscripting operator in other programming languages:
array[0].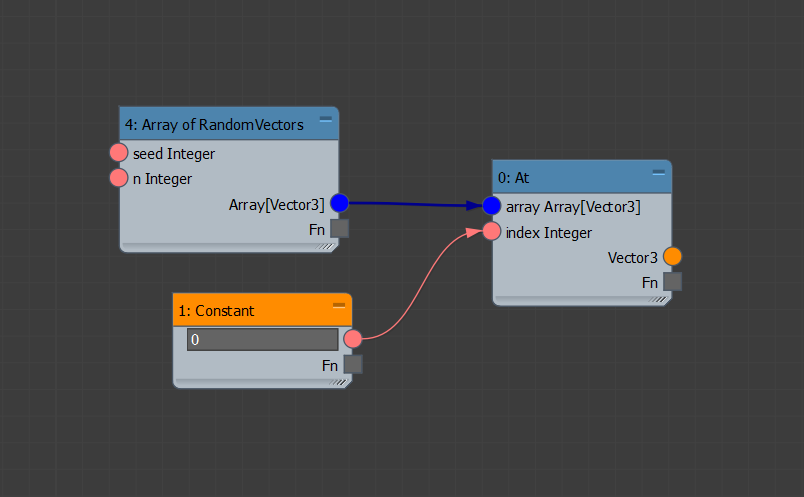 Tip: You may use the At operator in a mapped connection to return the items at the specified indices. In the example below, items at 0, 2, 3, 4 are returned.
Tip: You may use the At operator in a mapped connection to return the items at the specified indices. In the example below, items at 0, 2, 3, 4 are returned.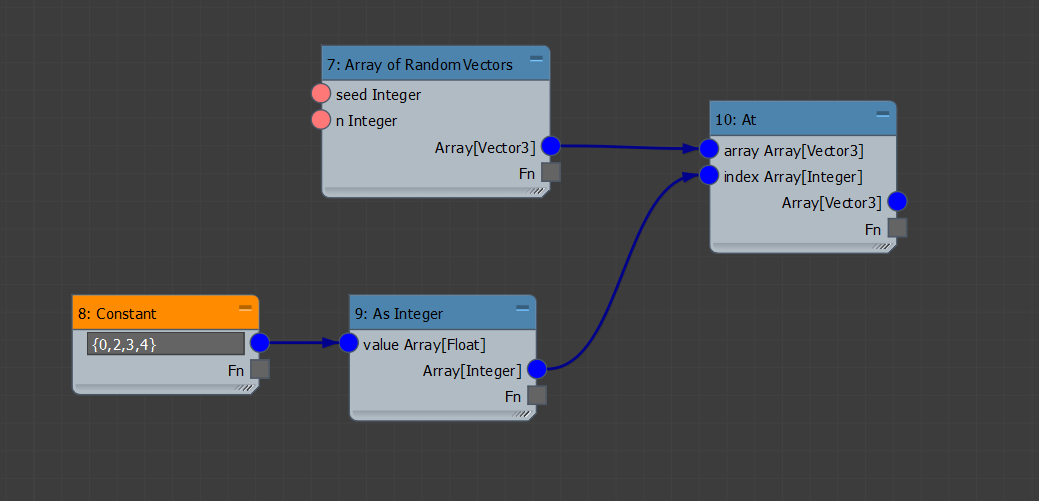
Adding, Setting, and Removing Items
The following operators pertain to growing, shrinking, or setting specific values:
Join Arrays: Returns an array by joining the items of array2 to the end of array1. For example, given array1=
[a,b,c]and array2=[d,e,f], the resulting array will be[a,b,c,d,e,f]. This is also known as array concatenation.Append: Inserts the given item at the end of the array.
Prepend: Inserts the given item at the beginning of the array.
Insert: Inserts the given item in the array before the specified index.
Set Items: Replaces the items in the given array with the specified indexed items. For example, supplying the following indexed items:
[(0,50), (6,29)]replaces the item at index 0 with the value 50, and the item indexed at 6 with the value 29. The pair (0,50) is constructed using the Pair operator.Set Item: Replaces the item at the given index in the array with the specified value. For better performance, consider using Set Items if you want to replace multiple items in the array.
Take: Creates an array composed of the first n items of the given array.
Skip: Creates an array by omitting the first n items in the given array.
Remove Ends: Removes nStart items from the start of the given array, and nEnd items from the end of the array.
Common Operators
The following operators are commonly used to manipulate arrays:
Sort: Sorts the items in the array in ascending order (smallest to largest). The array should contain comparable types such as Boolean, Integer, and Float.
Reverse: Creates an array by reversing the given array. For example, reversing the array
[0,1,2,3]will produce the array:[3,2,1,0].Index of Maximum/Minimum: Returns the index of the maximum/minimum item in an array.
Remove Duplicates: Returns a sorted array in which all the items are unique. The items in the given array must implement the Is Equal operator.
Flatten: Given an array of arrays, returns a new array containing the flattened items. For example, given the array
[[1,2],[3,4]], the flattened array will be:[1,2,3,4].Sliding Window: Returns an array of sub-arrays whose items match a sliding interval of n values across the given array. For example, given the array
[a,b,c,d,e]and n=2, the resulting array will be:[[a,b],[b,c],[c,d],[d,e]].Shuffle Array: Randomly swaps the items of the array. Implements the Fisher-Yates shuffle.
Average Float: Returns the average value of the items in the array.
Average Vector: Returns the average vector among the vectors contained in the given array.
Rescale Array of Floats: Returns an array of rescaled floats in the range 0.0 to 1.0 based on the the minimum and maximum values contained in the given array. The smallest value in the array will map to 0.0, while the largest value will map to 1.0.
Rescale Array of Vectors: Returns an array of rescaled vectors such that the vector with the greatest length has a rescaled length of 1.0, while the smallest vector has a length of 0.0.
Sum: Returns the sum of the items in the array. The items in the array must be addable.
Partial Sums: Returns an array representing the accumulated sum at each item in the original array. For example, the partial sum of
[1, 8, 3, 10, 2, 1]is[1, 9, 12, 22, 24, 25], i.e.:[1, (8+1=9), (9+3=12), (12+10=22), (22+2=24), (24+1=25)].
