Tutorial 1: Creating and Debugging a UI
In this tutorial we will create and debug a small PySide2 tool for 3ds Max
called "pyramid", using Visual Studio Code and the Python module debugpy (A Debugger For Python). This tool shows a Qt dialog with a button. Pressing the
button adds a black pyramid to the current scene.
The code of the completed tutorial can be found at the end of this topic for reference.
Prerequisites
This tutorial series requires that:
- 3ds Max 2021 or later is installed
- 3ds Max 2021 or later is started and using the Python 3 interpreter (the default setting)
- VS Code is installed, and the Python extension is installed
pipis installed for 3ds Max Python (see Using pip with Python 3)
Creating the project
This project will be called pyramid. PEP-8 (the Style Guide for Python) suggests that modules have small lowercase names.
So somewhere in our file system, create a nested set of directories, both with the name 'pyramid':
mkdir -p pyramid/pyramidWe will eventually use this directory structure to add proper pip packaging information to our project. For this tutorial we will just create our program in it.
Starting VS Code
- Start vs code
- Select our top-level
pyramidfolder with File > Open Folder
Creating the source files
Our project is small, but we will separate it in two files to simulate a larger project.
Create a new file named ui.py in the pyramid subdirectory, and then add the following code:
"""
Provide a PySide2 dialog for the pyramid tool.
"""
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QWidget, QDialog, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QPushButton
from pymxs import runtime as rt
from .graphics import make_pyramid_mesh
class PyMaxDialog(QDialog):
"""
Custom dialog attached to the 3ds Max main window
Message label and action push button to create a pyramid in the 3ds
Max scene graph
"""
def __init__(self, parent=QWidget.find(rt.windows.getMAXHWND())):
super(PyMaxDialog, self).__init__(parent)
self.setWindowTitle('Pyside2 Qt Window')
self.init_ui()
def init_ui(self):
""" Prepare Qt UI layout for custom dialog """
main_layout = QVBoxLayout()
label = QLabel("Click button to create a pyramid in the scene")
main_layout.addWidget(label)
btn = QPushButton("Pyramid")
btn.clicked.connect(make_pyramid_mesh)
main_layout.addWidget(btn)
self.setLayout(main_layout)
self.resize(250, 100)- Create another file named graphics.py in the same directory, and add this code:
"""
Provide the graphic functionality for the pryamid tool.
"""
from pymxs import runtime as rt
def make_pyramid_mesh(side=20.0):
'''Construct a pyramid from vertices and faces.'''
halfside = side / 2.0
pyr = rt.mesh(
vertices=[
rt.point3(0.0, 0.0, side),
rt.point3(-halfside, -halfside, 0.0),
rt.point3(-halfside, halfside, 0.0),
rt.point3(halfside, 0.0, 0.0)
],
faces=[
rt.point3(1, 2, 3),
rt.point3(1, 3, 4),
rt.point3(1, 4, 2),
rt.point3(2, 3, 4),
])
rt.redrawViews()
return pyrAt this point you should have this following directory structure:
pyramid/
pyramid/
ui.py
graphics.pyWait, I see problems with my import statements
Visual Studio Code uses a linter to verify imports, and by default it does not know where to find the 3ds Max Python modules. The autocomplete system can also have problems understanding our sources.
To solve this issue, point Visual Studio Code to the 3ds Max Python interpreter:
- Open settings with File > Preferences > Settings
- In the settings page, open Extensions > Python > Auto Complete: Extra Paths > Edit in settings.json. This opens the settings.json file.
- Add:
,
"python.pythonPath": "C:\\Program Files\\Autodesk\\3ds Max 2023\\Python\\python.exe",
"python.autoComplete.extraPaths": [
"C:\\Program Files\\Autodesk\\3ds Max 2023\\Python"
] More information on this can be found here and here.
Running this first version of the project in 3ds Max
Switch to 3ds Max, open the listener window and select the Python tab. At that point we should see that Python 3 is used, from the version string displayed in the listener.
By default, the 3ds Max Python interpreter does not know where our sample is, but we want to be able
to make it available through import. So we can type this in the python
listener (substituting your own path for the append function):
import sys
sys.path.append(r'd:\sources\hacking\python\pyramid')Then type:
import pyramid.ui
dialog = pyramid.ui.PyMaxDialog()
dialog.show()this should display our dialog:
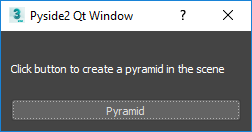
If you press the Pyramid button, you get an exception:
>>> Traceback (most recent call last):
File "d:\sources\hacking\python\pyramid\pyramid\graphics.py", line 11, in make_pyramid_mesh
rt.point3(0.0, 0.0, side),
RuntimeError: MAXScript exception raised.
-- Unable to convert: false to type: FloatNow we need to debug this problem.
Debugging 3ds Max Python code from VS Code
previous versions of this tutorial used ptvsd for debugging, but ptvsd is now deprecated in favor of debugpy. The instructions below will work in previous versions of 3ds Max.
Before we can use the debugger to debug python code in 3ds Max, we need to install the
debugpy (Python Tools for Visual Studio Debug Server):
- In your 3ds Max Python directory, in a command line, type:
.python.exe -m pip install --user debugpyNote:pipshould already be installed, see the prerequisites above.
Enabling the debugger on the 3ds Max side
The debugpy debug server needs to be running in the 3ds Max Python interpreter. In the 3ds Max Scripting Editor window, type or cut and paste the following code:
import sys
import os
import debugpy
def startup():
sysexec = sys.executable
(base, file) = os.path.split(sys.executable)
if file.lower() == "3dsmax.exe":
sys.executable = os.path.join(base, "python", "python.exe")
host = "localhost"
port = 5678
debugpy.listen((host, port))
print(f"-- now ready to receive debugging connections from vscode on (${host}, ${port})")
sys.executable = sysexec
startup()this should display:
('0.0.0.0', 5678)(The previous step will not have to be repeated in our 3ds Max session).
Connecting with VS Code: the first time
3ds Max is now ready to accept a connection from VS Code, but we must still tell VS Code how to connect to 3ds Max. The first time we want to connect to 3ds Max we need to add a configuration for remote debugging in VS Code.
- In VS Code, select Run > Add Configuration.
- From the drop down list, select Remote Attach
- Then hit enter to choose localhost (the default)
- And then hit enter to choose 5678 (the default)
This will add a configuration code that looks like this:
{
"name": "Python: Remote Attach",
"type": "python",
"request": "attach",
"connect": {
"host": "localhost",
"port": 5678
},
"pathMappings": [
{
"localRoot": "${workspaceFolder}",
"remoteRoot": "."
}
]
}We don't need to modify this other than we will want to point the remoteRoot setting
directly at our sources
"remoteRoot": "${workspaceFolder}",This configuration only needs to be set up once.
If we want to debug third party modules as well (for example, put breakpoints in pyside2 code), this is not something we will do in this sample but still a very common debugging task, we will also have to enable it in this json file by adding:
"justMyCode": falseIn the end your configuration should look like this:
{
"name": "Python: Remote Attach",
"type": "python",
"request": "attach",
"justMyCode": false,
"connect": {
"host": "localhost",
"port": 5678
},
"pathMappings": [
{
"localRoot": "${workspaceFolder}",
"remoteRoot": "${workspaceFolder}"
}
]
}Connecting with VS Code
First open the Run and Debug view by selecting View > Open View... and selecting "Run and Debug".
We need to select our Debug Config in VS Code:
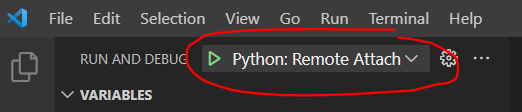
Ensure that our Python: Remote Attach configuration is selected. When this is the case we can connect the debugger to 3ds Max Python by selecting
Debug > Start Debugging from the VS Code menu.
If we go back to 3ds Max, we see that the UI is no longer frozen. However, our program is still not running.
Running the program
To run our script we need to type, in the 3ds Max listener window:
dialog.show()This will run our dialog that does not work the way we want.

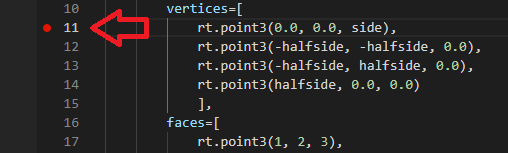
Adding a breakpoint
We know, from a previous run of our program that there is a problem on line 11 of graphics.py. So in VS Code we can add a breakpoint on this line by clicking the margin at the left of the line:
remoteRoot path mapping
is wrong, or that something else in the previous steps did not go well
(for example, your debugger is not running).Triggering the breakpoint
At this point when you click on the Pyramid button of your dialog, your
breakpoint will be reached and you will see it highlighted in VS Code.
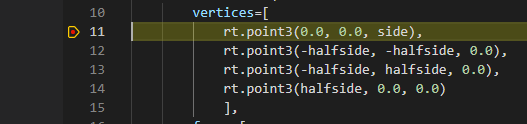
You will be able to inspect the locals and you will see that the side variable is False,
which is not what we want.
Pyramid button on a dialog that
was started before that, it may not work as expected.Fixing the code
What has happened is that side is False. Our code that connects make_pyramid_mesh()
to the dialog button looks like this:
btn.clicked.connect(make_pyramid_mesh)This is wrong because btn.clicked passes us a Bool that tells us whether the button
is checked. Our code receives this bool instead of the default 20.0 value
that we expected.
So we can edit this code to pass a lambda function that sets side to 20.0 instead:
btn.clicked.connect(lambda: make_pyramid_mesh(20.0))And then we save
Making the new code run
To give the control back to max we press F5 (Run -> Continue). We see
that 3ds Max becomes responsive again.
- Close the dialog
- At the listener window's python command prompt type
import importliband then
importlib.reload(pyramid.ui)This displays something like:
<module 'pyramid.ui' from 'd:\\sources\\hacking\\python\\pyramid\\pyramid\\ui.py'>- we must now recreate a brand new version of the dialog by doing:
dialog = pyramid.ui.PyMaxDialog()- and then:
dialog.show()
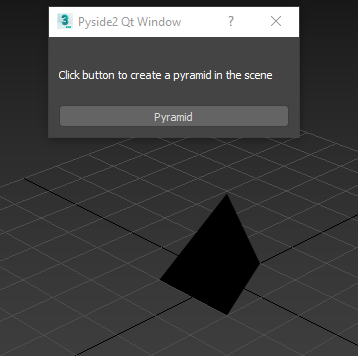
Our breakpoint is reached, but this time side = 20 and halfside = 10 and
if we hit F5 the code will now successfully complete and show our
black pyramid in the viewport.
Full Code
ui.py:
"""
Provide a PySide2 dialog for the pyramid tool.
"""
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QWidget, QDialog, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QPushButton
from pymxs import runtime as rt
from .graphics import make_pyramid_mesh
class PyMaxDialog(QDialog):
"""
Custom dialog attached to the 3ds Max main window
Message label and action push button to create a pyramid in the 3ds
Max scene graph
"""
def __init__(self, parent=QWidget.find(rt.windows.getMAXHWND())):
super(PyMaxDialog, self).__init__(parent)
self.setWindowTitle('Pyside2 Qt Window')
self.init_ui()
def init_ui(self):
""" Prepare Qt UI layout for custom dialog """
main_layout = QVBoxLayout()
label = QLabel("Click button to create a pyramid in the scene")
main_layout.addWidget(label)
btn = QPushButton("Pyramid")
btn.clicked.connect(lambda: make_pyramid_mesh(20.0))
main_layout.addWidget(btn)
self.setLayout(main_layout)
self.resize(250, 100)graphics.py:
"""
Provide the graphic functionality for the pryamid tool.
"""
from pymxs import runtime as rt
def make_pyramid_mesh(side=20.0):
'''Construct a pyramid from vertices and faces.'''
halfside = side / 2.0
pyr = rt.mesh(
vertices=[
rt.point3(0.0, 0.0, side),
rt.point3(-halfside, -halfside, 0.0),
rt.point3(-halfside, halfside, 0.0),
rt.point3(halfside, 0.0, 0.0)
],
faces=[
rt.point3(1, 2, 3),
rt.point3(1, 3, 4),
rt.point3(1, 4, 2),
rt.point3(2, 3, 4),
])
rt.redrawViews()
return pyr