Learn how Energy Optimization for Revit automatically generates an energy analytical model from the architectural model, and strategies for reducing the processing time.
energy analytical model creation typically requires only a few seconds or minutes. However, the process can be considerably longer, up to an hour or two for very large and detailed models. During this process, Revit is not available to perform other work.
When you click
 (Create Energy Model), the following dialog displays:
(Create Energy Model), the following dialog displays:
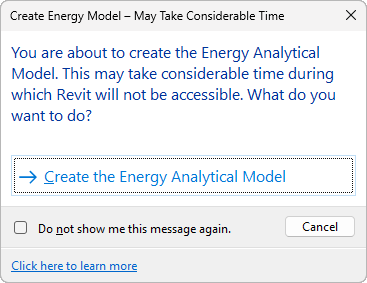
This dialog avoids the accidental initiation of the energy analytical model creation process. To skip this message in the future, select the check box.
Time required to create the energy analytical model
The time required to create the energy analytical model is proportional to both of the following:
- The volumetric space containing all elements used in the energy analytical model creation process
- The Analytical Space Resolution setting
The relationship is cubic. Consider the following examples:
- Model A has a volume that is 3 times larger than Model B, so Model A takes 9 times longer to process than Model B.
- Model C has an Analytical Space Resolution that is 2 times greater than Model D, so Model C takes 8 times longer to process than Model D.
- Model E has a volume that is 3 times larger and a resolution that is 2 times greater than Model F, so Model E takes 72 times longer to process than Model F.
Strategies to reduce processing time
To reduce the amount of time required to create the energy analytical model, use these strategies:
- Minimize the overall volumetric space containing all elements used to create the energy analytical model.
- Don't set the Analytical Space Resolution setting any lower than necessary to capture the main characteristics of the building geometry.
The energy analytical model creation process uses all architectural elements in the model that are room-bounding. Revit models often contain building elements that are outside the main building, such as floors used to represent paths or roads. These elements have no impact on the energy use of the building. Therefore, you should disable the Room Bounding property of each of those elements. This strategy reduces the overall size of the volumetric space that contains the model elements required to create the energy analytical model.
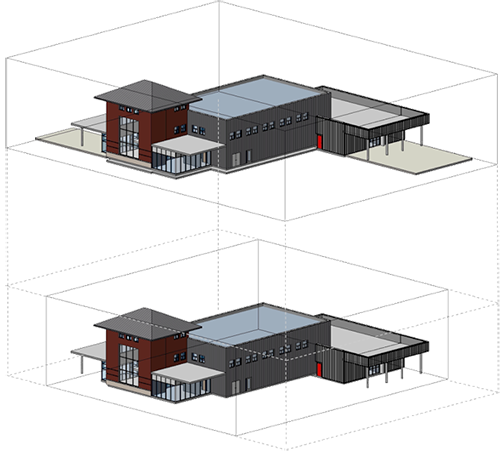
For example, the following illustration demonstrates how, by disabling the Room Bounding property of the outside floor elements, the resulting bounding box is 50% smaller. This change results in an energy analytical model creation process that is 3.4 times faster.