Example: Temperature Change Material Variation
A heat exchanger device (A) cools the liquid refrigerant in a cold plate (B). The cold plates controls the temperature within an electronics module. We use Temperature Change because the cold plate maintains a known temperature drop within the working fluid.
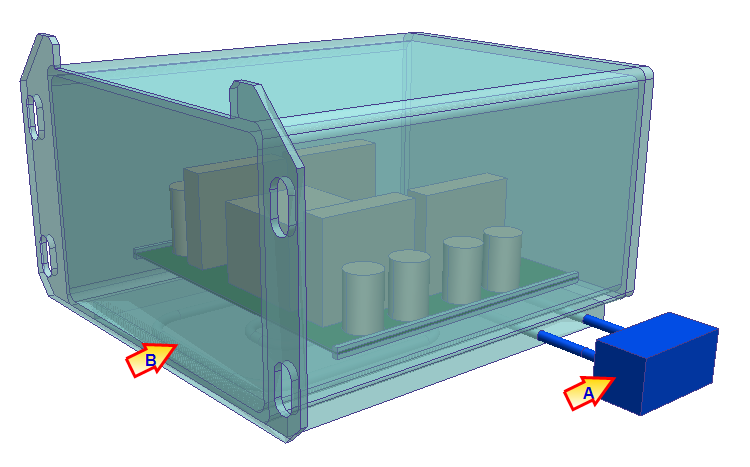
System settings:
- Flow Variation method = Constant. Flow rate = 0.1 gal/min.
- Heat Transfer Variation method = Temperature Change
- Temperature Change = -1**°C** (A negative value means the heat exchanger cools the working fluid.)
The value of Temperature Change came from the manufacturer-supplied thermal characteristics of the cold plate:
- The area of the cold plate surface is 18 in².
- The electronics module dissipates 15 W.
- At a flow rate of 0.1 gal/min, the thermal resistance of the specific cold plate model is approximately 1.24 °C in² / W.
- The heat exchanger device must deliver a temperature change of 1 °C to simulate the effect of the cold plate.
