To complete the design, use a Plane surface to create the front of the casing, and a Surface Fillet to trim and fillet it to the chamfered surfaces.
Use Layer Symmetry and Mirror to create all the surfaces for the front casing.
Finally, duplicate the front casing to create the rear casing, and organize all the geometry onto layers.
Open the tutorial file (optional)
If you successfully completed part 2, proceed to the next step, Create the front surface.
If you were not successful in part 2, open the file called MP3Player_Part2.wire, located in the wire folder of the CourseWare project. This file contains the completed model from part 2.
Create the front surface
First create the front face of the casing, and position it at the correct height for the MP3 Player dimensions.
- Maximize the Top window.
- Choose Surfaces > Primitives > Plane
 . You are prompted to enter the new plane position. Use the
. You are prompted to enter the new plane position. Use the  (Windows) or
(Windows) or  (Mac) key and grid snap the plane to the origin.
(Mac) key and grid snap the plane to the origin. 
- Choose Transform > Scale, type .35 and press Enter to reduce the size of the Plane.
-
Now set the pivot point for the Plane to the lower right-hand corner.
Choose Transform > Local > Set Pivot
 . Use the curve snap (
. Use the curve snap ( +
+  (Windows) or
(Windows) or  +
+  (Mac)) to snap the pivot accurately to the bottom right corner of the plane.
(Mac)) to snap the pivot accurately to the bottom right corner of the plane. 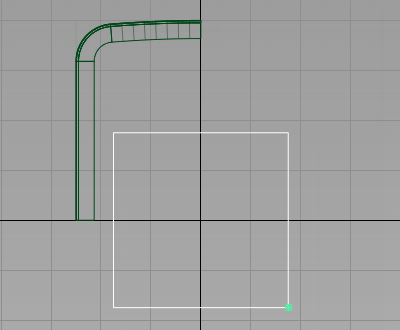
- Now choose Transform > Move
 . Use grid snap (
. Use grid snap ( (Windows) or
(Windows) or  (Mac) key) to position the plane exactly at the origin.
(Mac) key) to position the plane exactly at the origin. 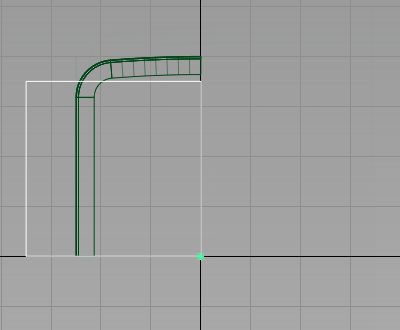
- Use Transform > Non-p Scale
 to size the plane to fit the design approximately. Make sure that the plane overlaps the chamfered edges.
to size the plane to fit the design approximately. Make sure that the plane overlaps the chamfered edges. 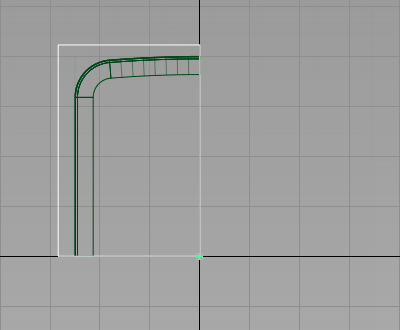
-
Next move the plane up in the z-axis.
Maximize the Left window
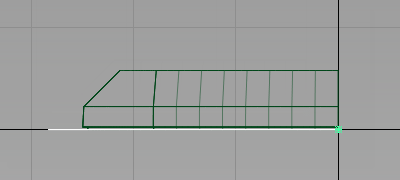
- Choose Transform > Move
 and type 0,0,5.5 to move the plane up 5.5 mm in the z-axis.
and type 0,0,5.5 to move the plane up 5.5 mm in the z-axis. 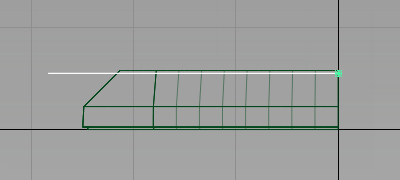
Fillet the plane surface
Now use the Surface Fillet tool to trim the front face and create an edge with a radius in one operation.
- Maximize the Perspective window.
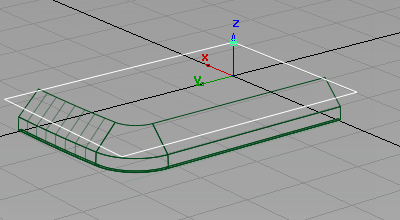
- Choose Surfaces > Surface Fillet
 or Surfaces > Multi-Surface Fillet > Surface Fillet, if you are using Alias Automotive, and double-click the icon to open the option window.
or Surfaces > Multi-Surface Fillet > Surface Fillet, if you are using Alias Automotive, and double-click the icon to open the option window. - Change the Center Radius to 2.
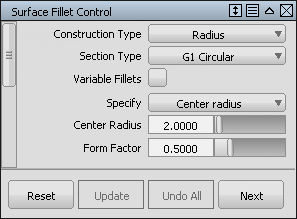
- You are prompted to select input surfaces. Select the plane.
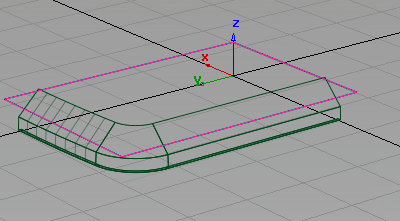
- Next select the second set of surfaces. Click the three chamfered surfaces.
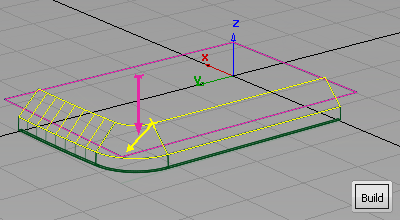
Arrows appear on both surfaces indicating on which side the fillet will be built. In this case, you want the pink arrow to point down, and the yellow arrow to point inwards.
- If necessary, click an arrow to reverse its direction.
- Click Build.
The edge with the specified radius is created and all the surfaces are trimmed.
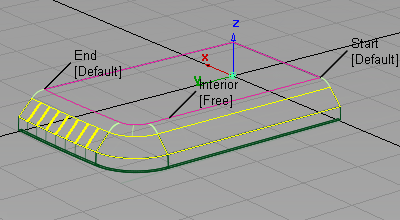
- Choose Pick > Nothing
 to complete the fillet.
to complete the fillet. 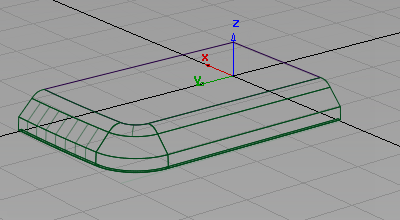
Use round for the remaining edges
Next create a radius on the remaining edges using the Round tool.
You could use either the Round tool or the Surface Fillet tool to create the softened edge. As the surfaces already meet at a sharp edge, the Round tool is quicker to use.
- Choose Surfaces > Round
 . You are prompted to select a pair of edges. Click one of the edges between the chamfer and the side surfaces.
. You are prompted to select a pair of edges. Click one of the edges between the chamfer and the side surfaces. 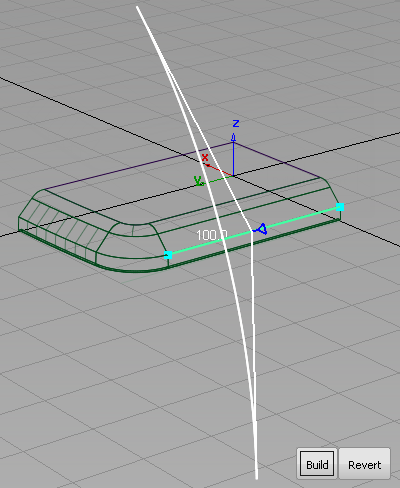
A radius indicator appears and is highlighted in white.
- Type 2 at the prompt line and press Enter to adjust the radius value to 2 mm.
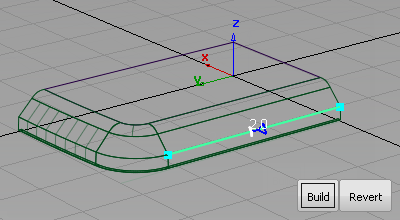
- Click the other edges to complete the round.
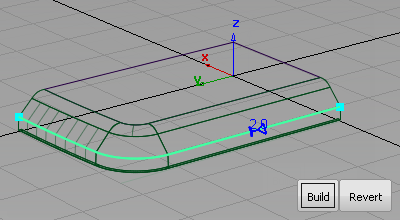
- Click Build to create the round surfaces and trim back the draft surfaces.
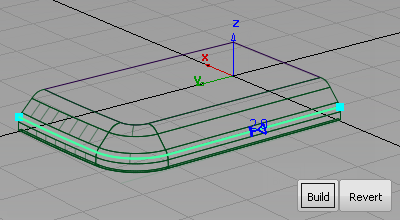
- Choose Pick > Nothing
 to complete the round.
to complete the round. 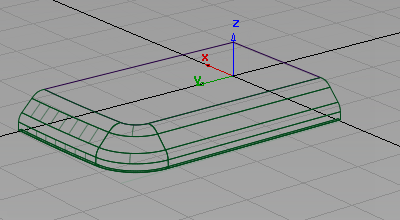
Complete the front casing
The MP3 Player casing is made from two similar components, the front and the back casing. Complete the front and rear casings using the Mirror tool and Layer symmetry.
First create the lower quarter of the front casing.
- Choose Pick > Object
 and drag a selection box over all the surfaces to select them.
and drag a selection box over all the surfaces to select them. 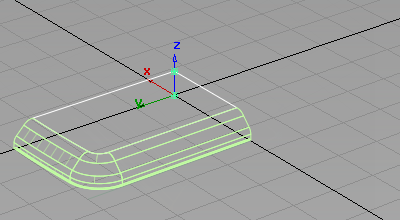
- Choose Edit > Duplicate > Mirror

 to open the mirror option window.
to open the mirror option window. 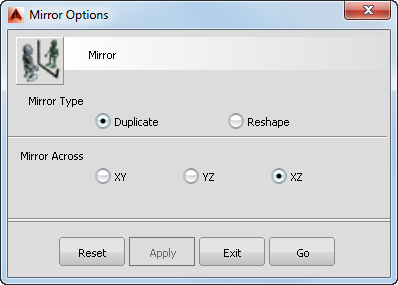
- Choose the XZ plane and click Go.
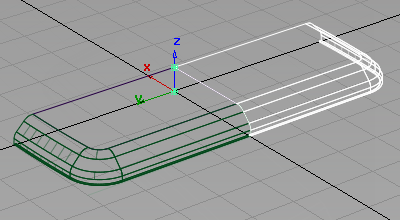
- Choose Pick > Nothing
 to deselect the surfaces.
to deselect the surfaces.
Layer symmetry
You used mirror to create the lower surfaces, so that the top surfaces can be modified by adding a screen, and the lower surfaces can be modified by adding buttons.
For the left and right sides of the design however, you want the geometry to be the same on both sides. So for the left and right sides, use Layer Symmetry to view a mirror image of the geometry, which updates as you continue to build surfaces.
- Choose Layers > New
 to create a layer for the front casing.
to create a layer for the front casing. - Double-click L1 in the layer tab and rename the layer Front Casing.

- Choose Pick > Object
 and drag a pick box over all the surfaces to select them.
and drag a pick box over all the surfaces to select them. - Click the Front Casing layer and select Assign from the drop-down menu.
The new layer is selected and shown in yellow. (If the layer is not selected, click Front Casing on the layer tab).
-
The symmetry on layers is typically used in one of the three axis directions. Set the Symmetry Plane so that your geometry is mirrored left to right.
Choose Layers > Symmetry > Set Plane
 .
. The current symmetry plane is highlighted in yellow. Change the plane so that the geometry is mirrored left and right.
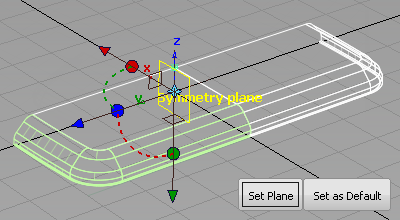
- Click the small brown square that represents the YZ plane.
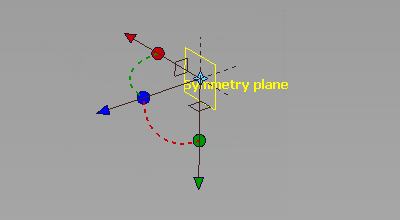
The large yellow plane changes to the right axis for your model.
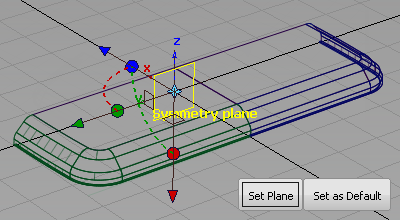
- Click Set as Default to set this axis for all future layers.
- Click Set Plane to set the plane for this layer.
- On the Front Casing layer, choose the symmetry option from the drop-down menu.
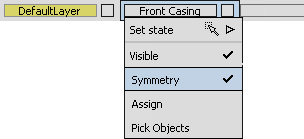
The geometry on the layer is mirrored and shown as dotted lines to indicate that it is only a visualization of the mirrored geometry, not real geometry.
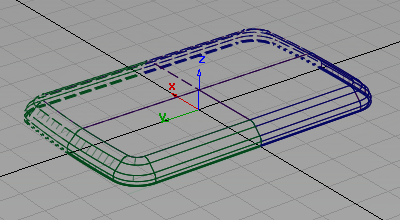
Create the rear casing
Now is a good time to copy the surfaces for the rear casing, before you start to detail the front.
-
First create a layer for the rear.
Choose Layers > New
 and rename the layer Rear Casing.
and rename the layer Rear Casing. 
- Choose Pick > Object
 and drag a pick box over all the geometry to select it.
and drag a pick box over all the geometry to select it. 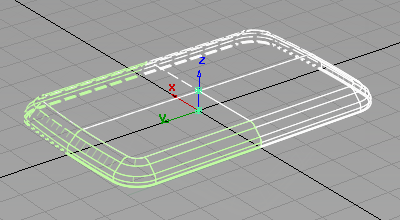
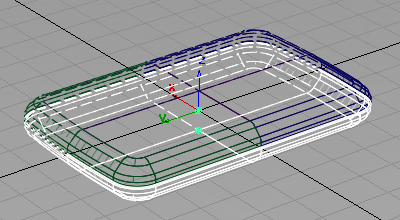
- Choose Edit > Duplicate > Mirror

 to open the option window.
to open the option window. Choose the XY plane and click Go.
The surfaces are mirrored.
- With the surfaces still selected, Assign them to the Rear Casing layer.
- Turn on Symmetry on the Rear Casing layer.
- Turn off Visible on the Rear Casing layer to make it invisible.
Save your work
Save your work in the wire folder of the Lessons project. Name your file myMP3Player3.wire.