In this tutorial, we study the compressible flow in a converging-diverging nozzle. This is a classic case of internal compressible flow, and even though this geometry is simple, the techniques demonstrated are applicable to industrial-level applications of internal compressible flow.
The converging-diverging nozzle has an exit area of 0.008 m2, and a throat area of 0.002 m2, resulting in an area ratio of 4.
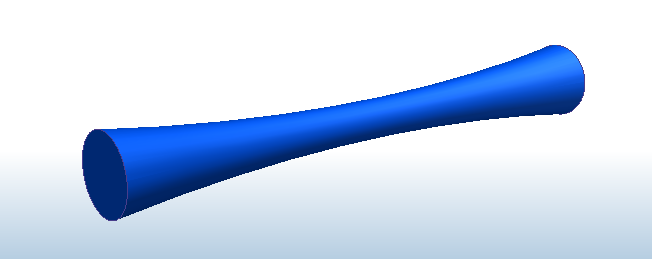
The inlet stagnation temperature is 500K, and the mass flow rate is known to be 3.61 kg/s. We will use this information to determine the exit Mach number and pressure at the inlet and outlet. The outlet of the nozzle cannot be extended, so we will not be able to visualize any shock activity at the outlet.
Key Topics
- Internal Compressible Flow
- Summary Planes
- Critical Values
Goals
- Visualize the flow within the nozzle, and determine the outlet Mach number
- Determine the pressure drop
Reference
1. White, F.M., Viscous Fluid Flow, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1974