The Wave modifier produces a wave effect in an object's geometry. You can use either of two waves, or combine them. Wave uses a standard gizmo and center, which you can transform to increase the possible wave effects.
The Wave space warp has similar features, and is useful for applying effects to a large number of objects.
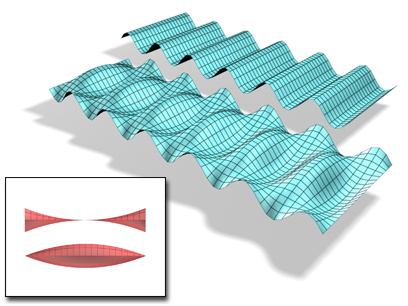
An object with the Wave modifier applied. Amplitude 1 and 2 can be changed, creating different profiles.
Procedures
To make an object wavey:
 Select an object and apply the Wave modifier. Tip: To see the effect clearly, apply Wave to a broad, flat object that has many segments.
Select an object and apply the Wave modifier. Tip: To see the effect clearly, apply Wave to a broad, flat object that has many segments.- Set one or both values for amplitude, or the vertical height of the wave in current units.
Amplitude 1 produces a sine wave from one edge to the other, while Amplitude 2 creates a wave between the opposite edges. Switching a value from positive to negative reverses the position of peaks and troughs.
- Set the length of the wave and the distance in current units between crests of both waves.
The greater the length, the smoother and more shallow the wave for a given amplitude.
To add a phase effect:
- Set a phase value to shift the wave pattern over the object. Positive numbers move the pattern in one direction, while negative numbers move them in the other. This effect is especially clear when animated.
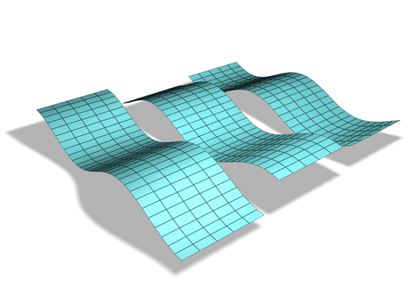
Phase effect on a wave
To add a decay effect:
- Set a decay value to increase or decrease the amplitude.
A decay value decreases the amplitude as the distance from the center increases. As the Decay value increases, the wave is concentrated at the center and flattens until it disappears (completely decays).
Interface
Modifier Stack
- Gizmo
-
At this sub-object level, you can transform and animate the gizmo like any other object, altering the effect of the Wave modifier. Translating the gizmo translates its center an equal distance. Rotating and scaling the gizmo takes place with respect to its center.
- Center
-
At this sub-object level, you can translate and animate the center, altering the Wave gizmo's shape, and thus the shape of the wavy object.
For more information on the stack display, see Modifier Stack.
Parameters rollout
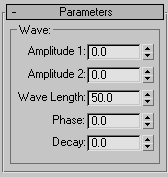
- Amplitude 1/Amplitude 2
-
Amplitude 1 produces a sine wave along the gizmo's Y axis, while Amplitude 2 creates a wave along the X axis (although peaks and troughs appear in the same direction with both). Switching a value from positive to negative reverses the positions of peaks and troughs.
- Wave Length
-
Specifies the distance in current units between the crests of both waves.
- Phase
-
Shifts the wave pattern over the object. Positive numbers move the pattern in one direction, while negative numbers move it in the other. This effect is especially clear when animated.
- Decay
-
Limits the effect of the wave generated from its origin. A decay value decreases the amplitude at increasing distance from the center. As this value increases, the wave is concentrated at the center and flattened until it disappears (completely decays).