Helical Curve (3D Sketch)
Access
Ribbon:
3D Sketch tab
 Create Panel
Create Panel
 Helical Curve
Helical Curve
![]()
The Helical Curve command creates a helical curve object, consisting of helical curve, a centerline, a diameter dimension, and a height dimension (where applicable).
Specify points in the graphics area within the 3D Sketch environment to define size and placement of the helical curve. Additional aspects of the curve, such as pitch, revolution and taper, are specified in the Helical Curve dialog box.
Once created, add constraints or use the 3D Move/Rotate command to further position the helical curve object.
Helical Shape
The Helical Shape tab specifies how to create the helical curve.
- Type
-
Select a pair of parameters to specify: Pitch and Revolution, Revolution and Height, Pitch and Height, or Spiral. Specify 2 of the 3 parameters. The third parameter is calculated.
Pitch and revolution Create a helical curve by specifying the pitch and the number of revolutions. The Helical Curve is defined by the selection of the following three points in the graphics area:
- Axis Start Point
- Point on Axis (which also specifies direction)
- Point on Diameter (which also specifies the helix start point)
Pick a start point and endpoint in the graphics area. The diameter point is optional and may be specified within the dialog box. The point on diameter is projected into the plane (normal to centerline) of the start point.
Revolution and Height Create a helical curve by specifying the number of revolutions and the height of the helical curve.
Pitch and Height Create a helical curve by specifying the pitch and the height of the helical curve.
Spiral Specifies the number of revolutions for the coil.
The Pitch and Height, Revolution and Height, and the Spiral Helical Curve are defined by the selection of the three following points in the graphics area:
- Axis Start Point
- Axis End Point (which also specifies direction)
- Point on Diameter (which also specifies the helix start point)
Pick a start point and endpoint in the graphics area. The diameter point is optional and can be specified within the dialog box.
Pitch and Height and Revolution and Height options only The point on diameter is projected into the plane (normal to centerline) of the start point.
- Diameter
-
Specifies the diameter of the helical curve.
- Height
-
Specifies the height of the helical curve.
- Pitch
-
Specifies the elevation gain for each revolution.
- Revolutions
-
Specifies the number of revolutions. The number of revolutions must be greater than zero but can include partial revolutions (for example, 1.5 revolutions). The number of revolutions includes the end conditions, if specified.
- Taper
-
Specifies the taper angle, if needed, for all coil types except Spiral.
- Rotation
-
Specifies if the Helical Curve rotates clockwise or counterclockwise.
Helix Ends
Specifies End conditions for the Start and End of the helical curve. Only the helix is flattened, not the profile of the helical curve.
- Natural or Flat
-
Click down arrow to specify Natural or Flat for both ends of the helical curve. Ends can have dissimilar end conditions.
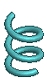 Transition angle
Transition angle -
The distance (in degrees) over which the helical curve achieves the transition (normally less than one revolution). The example shows the top with a natural end and the bottom end with a one-quarter turn transition (90 degrees) and no flat angle.
 Flat angle
Flat angle -
The distance (in degrees) the helical curve extends after transition with no pitch (flat). Provides transition from the end of the revolved helical curve to a flattened end. The example shows the same helical curve as the Transition angle shown previously, but with a half-turn (180 degree) flat angle specified.