The option is used for warping objects according to a given formula. The option is available using either method:
- Click Edit menu > Edit Objects > Space Warping.
- Click
 .
.
The option is available for the following structure types: shell and volumetric structure. The option is available if Solid Modeler is installed.
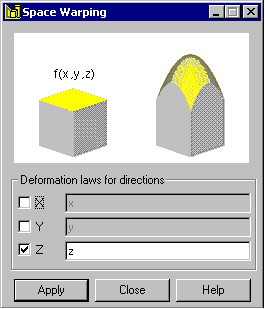
Model warping based on a given arithmetical formula for an axis of the global coordinate system. Such formulas might consist of different types of functions (such as, trigonometric functions) and include references to designations of the global coordinate system (x, y, and z). For example, warping for the global Z axis might be defined as: z+sin(5*x)+2*cos(y).
The list of functions used most frequently for object warping:
- Multiplication, division, addition, subtraction
- Trigonometric functions (sin, cos, arcsin, arccos, tan, cot)
- Maximum and minimum (max, min)
- Square root (sqrt)
- Absolute value (abs)
- Logarithmic functions (log, ln)
- Logical operations (and, or)
- Conditional functions (piecewise), such as, piecewise(x>0,z+x^2,z+abs(x)), therefore, if x > 0, then fz(x,y,z) = z+x^2, if x ≤ 0, then fz(x,y,z) = z+|x|).
The following are several examples of space warping operations. On the left an initial object is shown; whereas, on the right the object is shown after the warping operation:
Example 1
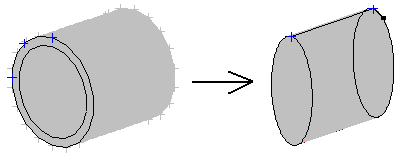
A cylinder with a base radius of 1.0 and height of 1.0, whose base center is positioned at the point of the (0,0,0) coordinates.
Function - Only the X option is selected in the dialog f(x,y,z) = x/2
Example 2
A square located in the XY plane with its diagonal vertices positioned at points of the following coordinates (-1,-1) and (1,1)
Function - Only the Z option is selected in the dialog f(x,y,z) = z+(sin(20*x)+sin20*y))/20
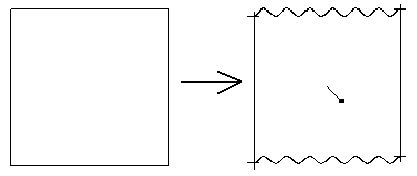
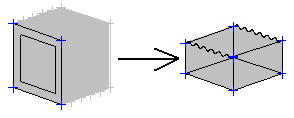
Example 3
A cube with its diagonal vertices positioned at points of the following coordinates (-1,- 1, -1) and (1, 1, 1). The center of the cube is at the origin of the coordinate system (0,0,0).
Function - Only the Z option is selected in the dialog f(x,y,z) = piecewise(z>0,sin(20*x)/20,z)