设置 BoxObstacle
此页面介绍了如何创建、更新和销毁您游戏中的 BoxObstacle。
有关障碍物管理系统中 BoxObstacle 类的作用的介绍,请参见使用动态障碍物和 TagVolume。
有关 NavTag 系统的背景信息,请参见使用自定义数据进行标记。
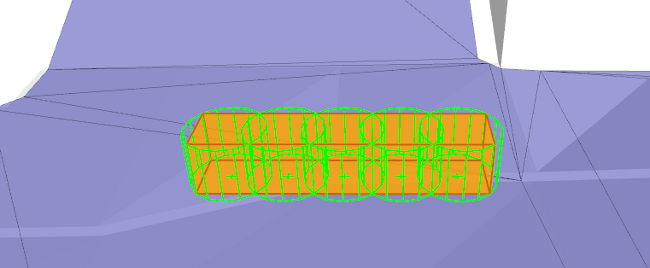
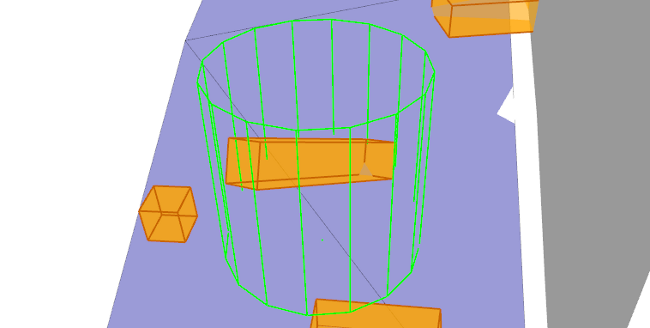
旋转模型
您可以为每个 BoxObstacle 选择两种可能的旋转模型之一。应为您创建的每个 BoxObstacle 选择的模式取决于相应对象将在游戏中显示的预期旋转,所选的模式将影响动态回避系统处理每个障碍物时的精度。
游戏端类
您需要在游戏中创建一个用于管理 BoxObstacle 的初始化和销毁的类。您的游戏中可能已经有一个类在管理 BoxObstacle 计划在 Gameware Navigation 世界中表示的对象或玩家角色的寿命。如果是这样,则可以使用该类。您可能在物理系统中也有类似对象,用于检索对象在每一帧的位置和速度。
例如:[Tutorial_ObstacleIntegration.cpp 中的代码]
class MyGameBoxObstacle
{
public:
MyGameBoxObstacle(): m_navBoxObstacle(KY_NULL) {}
void Initialize(Kaim::World* world, const Kaim::Vec3f& boxHalfExtents, const Kaim::Vec3f& position, const Kaim::Vec3f& linearVelocity, const Kaim::Vec3f& angularVelocity);
void Destroy();
void Update(KyFloat32 simulationStepsInSeconds);
RigidBodyPhysics m_rigidBodyPhysics;
Kaim::Ptr<Kaim::BoxObstacle> m_navBoxObstacle;
};初始化
要初始化 BoxObstacle,您必须提供 BoxObstacleInitConfig 配置类的实例,您可以使用 BoxObstacle 所需的数据进行设置。您必须以最小值设置:
- 体积将添加到的世界。
- 长方体的位置和范围。
- 长方体的旋转模式:BoxObstacleRotation_Yaw 或 BoxObstacleRotation_Free。请参见上面的设置 BoxObstacle。
- 如果要在障碍物变为静止状态时将其集成到 NavMesh,则还必须设置该长方体将用于标记与其体积相交的 NavMesh 的 NavTag。
例如:[Tutorial_ObstacleIntegration.cpp 中的代码]
void MyGameBoxObstacle::Initialize(Kaim::World* world, const Kaim::Vec3f& boxHalfExtents, const Kaim::Vec3f& position, const Kaim::Vec3f& linearVelocity, const Kaim::Vec3f& angularVelocity)
{
// Initialize the object that represents this obstacle in the physics system.
m_rigidBodyPhysics.Initialize(position, linearVelocity, angularVelocity);
// Set up the BoxObstacleInitConfig.
Kaim::BoxObstacleInitConfig boxObstacleInitConfig;
boxObstacleInitConfig.m_world = world;
boxObstacleInitConfig.m_localHalfExtents = boxHalfExtents;
boxObstacleInitConfig.m_startPosition = m_rigidBodyPhysics.GetPosition();
boxObstacleInitConfig.m_rotationMode = Kaim::BoxObstacleRotation_Yaw;
// This sets the NavTag as non-walkable: it will "cut a hole" in the NavMesh.
boxObstacleInitConfig.m_navTag.SetAsExclusive();
// Create and initialize the BoxObstacle, and add it to its World
m_navBoxObstacle = *KY_NEW Kaim::BoxObstacle;
m_navBoxObstacle->Init(boxObstacleInitConfig);
m_navBoxObstacle->AddToWorld();
...
}更新
BoxObstacle 表示的对象每次在游戏中更改其位置、旋转或速度时,您需要更新 BoxObstacle 以反映新的状态。请注意,这包括障碍物在空间中移动时的线性速度,以及旋转时的角速度。您可以使用 BoxObstacle 中的函数反映新的状态。
请注意,此操作不会立即修改 BoxObstacle;更新将推迟到世界的下次更新。
例如:[Tutorial_ObstacleIntegration.cpp 中的代码]
void MyGameBoxObstacle::Update(KyFloat32 simulationStepsInSeconds)
{
...
// Update the object in the physics system.
m_rigidBodyPhysics.Update(simulationStepsInSeconds);
// Update the BoxObstacle.
m_navBoxObstacle->SetTransform(m_rigidBodyPhysics.GetTransform());
m_navBoxObstacle->SetLinearVelocity(m_rigidBodyPhysics.GetLinearVelocity());
m_navBoxObstacle->SetAngularVelocity(m_rigidBodyPhysics.GetAngularVelocity());
}在运动与静止之间切换
如果障碍物停止运动并静止下来,您可能会希望将其集成到 NavMesh,以便游戏中的人物在规划通过地形的路径时可以考虑到它的存在,而不是仅在路径跟随的动态回避阶段对其存在做出反应。
障碍物变为静止状态时,请调用其 BoxObstacle::DoesTriggerTagVolume() 方法,并传递 true。下次更新世界时,障碍物将以相同的位置、尺寸透明地生成 BoxObstacle,并带有初始化 TagVolume 时设置的 NavTag。然后此 TagVolume 会集成到 NavMesh 中,并以自定义数据对区域进行标记或将其标记为“排他”然后从 NavMesh 中移除。集成完成且 NavMesh 更新后,障碍物的体积会自动从所有动态回避计算中移除,因为其存在现在是通过 NavMesh 进行管理。
如果障碍物再次开始移动,请调用 BoxObstacle::DoesTriggerTagVolume() 并传递 false 以反转过程。
例如:[Tutorial_ObstacleIntegration.cpp 中的代码]
void MyGameBoxObstacle::Update(KyFloat32 simulationStepsInSeconds)
{
const bool isStopped = m_rigidBodyPhysics.IsSleeping();
m_navBoxObstacle->SetDoesTriggerTagVolume(isStopped);
if (isStopped)
return;
...
}销毁
销毁 BoxObstacle:
- 调用其 BoxObstacle::RemoveFromWorld() 方法以将其从世界中移除。
- 将您保存到游戏对象中的所有指针设置为 KY_NULL。这会递减引用统计机制,当不剩余任何引用时,将会透明销毁对象。
例如:[Tutorial_ObstacleIntegration.cpp 中的代码]
void MyGameBoxObstacle::Destroy()
{
m_navBoxObstacle->RemoveFromWorld();
m_navBoxObstacle = KY_NULL;
}