You use the Particle Manipulator menu to select the type of manipulator, its speed and position, and the power of its falloff. To access the Particle Manipulator menu, double-click the particle animator node in the schematic, or follow the tab population rules for the Object menu (see Populating Menu Tabs of Selected Objects).
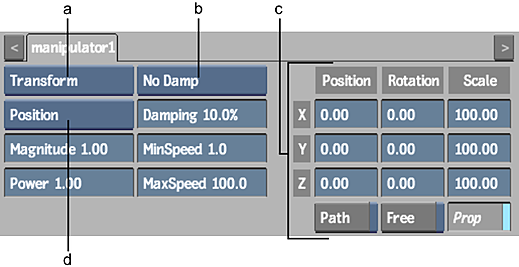
(a) Manipulator Type box (b) Damping box (c) Axis controls (d) Influence box
The particle manipulator controls are described as follows.
- Manipulator Type box
- Select the type of manipulator.
Select: To: Gravity Simulate the effect of gravity. See Simulating Gravity. Transform Apply transformations from the Axis menu to the position or speed of each particle. See Applying Transformations. Vortex Mimic the effect of a vortex. See Creating a Vortex Effect. Acceleration Point Pull particles toward a point. See Using an Acceleration Point Manipulator. Acceleration Line Pull particles toward a line. See Using an Acceleration Line Manipulator. Acceleration Plane Pull particles toward a plane. See Using an Acceleration Plane Manipulator. Path Make the particles follow a path. See Forming a Particle Path. Function Enter a mathematical expression to use as a particle manipulator. See Using a Function as a Manipulator.
- Influence box
- Select whether the manipulator influences each particle's position or speed.
Set the initial speed of each particle using the Speed field in the Surface Particle Generator menu.
By selecting Speed in the Influence box located on the Particle Manipulator menu, each particle's speed is changed with each pass by the selected manipulator.
When you influence by position, the position is applied only once. For example, the following figure uses a gravity manipulator to illustrate the difference between position and speed. The gravity manipulator on the left uses the default gravity manipulator with a magnitude of 4 and with position as the influence. The gravity manipulator on the right uses exactly the same settings except the influence is set to speed.


- Magnitude field
- Displays the unit of measurement specific to each manipulator. Editable.
Magnitude is used by each manipulator for everything from extra scale when using Transform, to a pixel per frame acceleration factor when using AccPoint, AccLine, or AccPlane.
- Power field
- Displays the amount of falloff from the centre of a manipulator. Editable.
If you specify 0 as the power, there is no falloff; the manipulator's influence is universal. This means that a particle is affected no matter where it is located in the scene. A negative value makes particles that are farther away affected by the manipulator.
- Damping box
- Select the type of friction to apply (damping affects the speed of particles by applying friction based on each particle's mass, size, or both).
Select: To: No Damp Turn off damping. Particles have no friction. Damp Mass Activate damping based on mass. The greater a particle's mass, the slower its speed in relation to the manipulator. You set the mass using the Mass channel in the Channel Editor. Damp Size Activate damping based on particle size. The larger the particle, the slower it moves in relation to the manipulator. This corresponds with the Size field in the Surface Particle Generator menu. Damp Both Activate damping based on mass and particle size.
- Damping Percentage field
- Displays the percent value of how much Damping affects the position or speed of the particles. Editable.
- Minimum Speed field
- Displays the minimum speed range for particles affected by Damping. Editable.
- Maximum Speed field
- Displays the maximum speed range for particles affected by Damping. Editable.
- Load button
- Not Shown; available when Function is selected as the Manipulator type. Loads a mathematical expressions to be used as a particle manipulator.
- Save button
- Not Shown; available when Function is selected as the Manipulator type. Saves a mathematical expressions to be used as a particle manipulator.
- Expression field
- Not Shown; available when Function is selected as the Manipulator type. Displays a mathematical expression to be used as a particle manipulator. Editable.
- Axis controls
- Use these controls to animate the position, rotation, and scale of the manipulator.
| Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Position | Use the Position X, Y, and Z fields to displace each particle along the X, Y, and Z axes. |
| Rotation | Use the Rotation X, Y, and Z fields to rotate each particle. Each particle is not the centre of its rotation. Particles rotate around the manipulator's axis. |
| Scale | Use the Scale X, Y, and Z fields to increase or decrease the speed or position of each particle along the X, Y, and Z axes. For example, if speed is the selected influence, a Scale X of 100% has no effect while a Scale X of 105% increases the speed along the X axis by 5% with each pass. Enable Prop to proportionally scale the axes. |
Enable the Path button to animates the position of the axis using a spline drawn in the scene. Disable Path to animate the position of the axis using explicit animation.
- Free button
- Enable to ignore transformations from parent axes.