Get Started with USD in Maya
USD is designed for collaboration
The power of USD lies in its layering system, which facilitates collaboration between different artists and studios via non-destructive editing. For example, if you start with an existing scene and create a new layer containing your edits, these edits won't affect anyone else using the same scene unless they decide to include your new layer. Together, multiple layers provide a complete view of the scene, which is known as the stage.
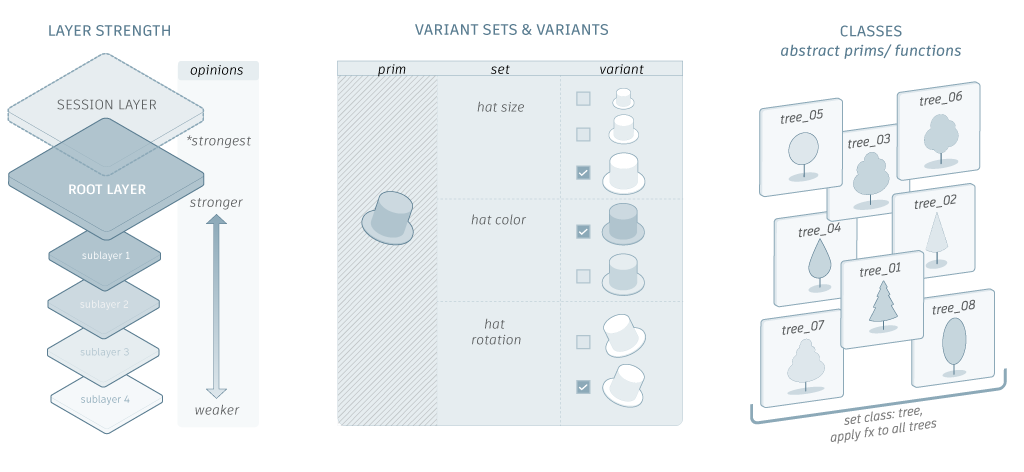
A basic understanding of USD will make it much easier to use and understand Maya's implementation of the USD framework. While the Maya documentation does not include a USD glossary or a complete overview of USD concepts, the following sections provide an overview workflows to showcase what you can do with USD in Maya and where to go to learn more.
For a better understanding of USD concepts, you can watch USD tutorial videos and content on the Maya Learning Channel. View the USD series for real-time explanations of concepts and theory alongside practical workflow showcases.
USD workflows in Maya
Layout and assembly workflows
Create a USD model: Maya's round-trip USD import and export workflow lets artists import USD data as intrinsic Maya data or export intrinsic Maya data as USD data. Artists can use Maya's tools and workflows to create and export models for their USD pipeline and re-import it to make further edits, if necessary. Note: This method converts Maya data and USD data back and forth. This workflow implements:
- USD Import Options and USD Export Options
- Command line support for import (
mayaUSDImport) and export (mayaUSDExport) operations - Exporting USD file types in ascii or binary format
Related Concepts: See variant, variantSet, instancing, metadata in the Pixar USD Glossary.
Create a USD set: A USD set is a single complex asset made from individual USD assets. Artists can take a collection of USD assets on disk and use USD mechanisms like references, variants, and filtering to assemble it in Maya. For example, an artist can create an empty stage in Maya and reference in existing USD assets to create a USD set. This method allows artists to work with USD data intrinsically in Maya. Maya supports the following mechanisms that enable USD set creation:
- Establish parent/child relationships in the Outliner, see Work with USD data in the Outliner
- Create USD prims in the Outliner
- Edit assets in the Outliner and Attribute Editor
- Use references to define your collection of assets in the Outliner
- Activate USD in the Maya Interface and work with USD data intrinsically in Maya
Related Concepts: See prim, stage in the Pixar USD Glossary.
Edit a USD set: Artists can perform in-context editing of existing USD data using the USD Layer Editor.
Editing lets you perform sparse edits on top of an existing USD set. In Maya, the focus of editing with the USD Layer Editor is on managing layers, not creating layer content. For example, the USD Layer Editor provides context, like identifying the target layer, and lets you save your layers to a file on disk. For more information, see USD Layer Editor and Work with USD data in the Outliner.
Related Concepts: See references, variant, kind, purpose, layer, layerStack in the Pixar USD Glossary.
Shot-based animation workflows
Duplicate as Maya/USD: Artists can duplicate USD data created in Maya to Maya data using the ‘Duplicate as Maya Data’ function, and vice versa. This data translation happens in memory and eliminates the need for traditional import/export to disk processes, as an accelerated workflow. For more information see:
- Work with USD data as Maya data
- USD Import Options and USD Export Options
- Command line support for import (
mayaUSDImport) and export (mayaUSDExport) operations - Exporting USD file types in ascii or binary format
Related Concepts: See variant, variantSet, instancing, metadata in the Pixar USD Glossary.
Edit USD as Maya data (Push/Pull Method): When working with USD data in Maya you can edit that data as Maya data. When this occurs, the USD data does an in-memory translation to Maya data, allowing you to use traditional Maya tools and menus. When finished editing the Maya data, you can 'merge' edits back to your USD prim, authoring only the changes made back to USD. For more information see:
Further Reading
- USD Terminology
- USD in the Maya Interface
- USD Layer Editor
- API documentation for Maya 2024 - UFE 4.0, Maya 2023 - UFE 3.2 and Maya 2022 - UFE 2.0 is available. View the respective API documentation to script and develop with Maya USD.