To understand how individual part sizes relate to the definition files of a part, it is important to understand how the part data is defined in the XML file. Part data stored in the XML definition file consists of 2 types of properties: common parameters and size parameters.
Common parameters remain constant for all part sizes. They are defined once in a part family and are shared by all part sizes. If you change a common parameter, it is updated for all part sizes. Common parameters include domain, type, and subtype. The following examples show common parameters for a mechanical, electrical, and plumbing part size.
- Mechanical: Common parameters for the 6 x 4 inch Rectangular Floor Register part size are as follows:
duct component air terminal rectangular floor register
- Electrical: Common parameters for the 13 Hole Large Outlet Box - 1 inch Conduit part size are as follows:
conduit component junction box square outlet box
- Plumbing: Common parameters for the 5 x 5 inch Rectangular Floor Drain part size are as follows:
pipe component drain plumbing rectangular floor drain
Size parameters include a set of parameter attributes such as name, description, and units; and parameter values such as size dimensions and material type. A size parameter can define one or more part sizes depending on how the size parameter is stored in the part family. Different storage methods enable multiple part sizes to be defined by various combinations of size parameters.
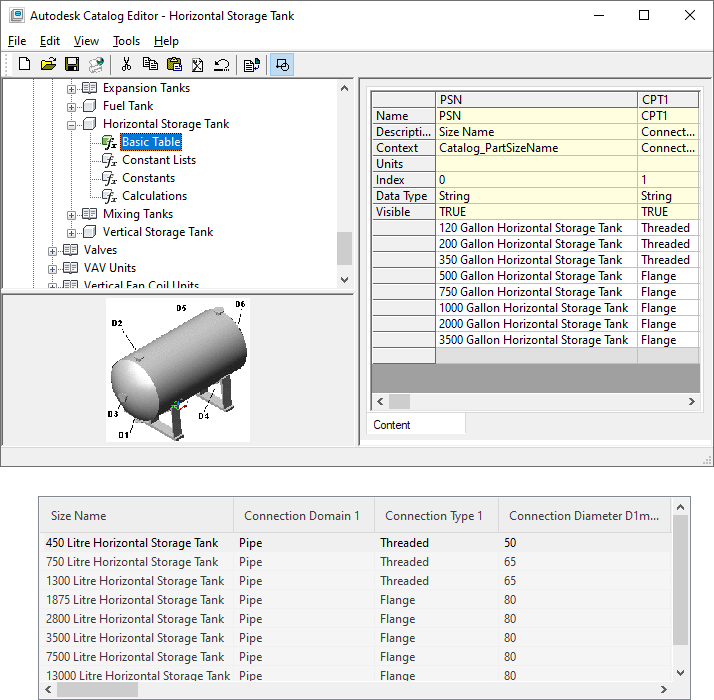
Viewing part sizes in Catalog Editor and in the part size table of the Add dialog box
Size Parameter Attributes
Parameter attributes are defined by both fixed and extensible lists of values. Attribute values are specified by AutoCAD MEP 2026 toolset and cannot be changed; however, attribute values must be specified for custom data parameters that are added. Fixed data values cannot be edited. Extensible data values can be changed based on a list of predefined values, or extended to accommodate user-defined values. The following table shows the parameter attributes used to define size parameters.
| Attribute | Type of Data | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Extensible | D1, A2, user-defined |
| Description | Extensible | Diameter D1, Angle A2, user-defined |
| Context | Fixed | Connection Port Diameter, Path Angle |
| Index | Fixed | 0, 1, 2, 3 |
| Data Type | Fixed | Double, Integer, Boolean, String |
| Visible | Fixed | True, False |
| Units | Extensible | in, ft, mm, m, deg |
Size Parameter Storage Types
Size parameters are separated into 4 types of data, referred to as “storage types.” Each storage type has unique characteristics that determine how the size parameters are used to define the part.
- Basic Tables. Store each parameter as a separate column. An entire row across multiple columns defines related parameters of a specific part size. All parameter columns must have the same number of values.
- Constant Lists. Store each parameter as a separate list and can be used in combination with other lists of values to define multiple part sizes. Each parameter list is independent and can have an infinite number of values.
- Constants. Store each parameter as a separate value that remains the same for all part sizes.
- Calculations. Store each part parameter as a formula. Values are calculated for each parameter based on other values specified for the part size.