It is possible to carry out spatial searches as part of the SQL functionality. Spatial searches can either be implicit through the options selected in the SQL dialog, or explicit by using the SPATIAL keyword in a written query.
Implicit Spatial Searches
Implicit spatial searches are defined fully within the SQL dialog, and can be performed between any two network layers, or between a network layer and a GIS layer, as outlined below:
- Choose the
Search Type:
- Cross - Searches for network objects which intersect a layer line or polygon area.
- Inside - Searches for network objects inside a layer polygon.
- Contains - Searches for network polygons with layer objects inside the polygon.
- Distance - Searches for network objects within a search Distance of a layer point, line or polygon.
- Nearest - Searches for nearest network object within a specified Distance. If there is more than one object within the specified distance, the first one found is returned as the result.
- Select
Layer Type:
- Network layer - Object layer in the current network
- GIS layer - GIS background layer displayed behind the network in the GeoPlan
- Select the layer in the
Layer box.
Note: When searching using a GIS layer, the layer must be loaded in the GeoPlan View.Note: The layer is referred to in the query as gislayer (even when using a Network as the Layer Type).
- If appropriate, define a
Distance value.
Important: A distance value is only required/used when using either the Distance or Nearest search types.
To include a field in the spatial layer search, select the field in the Field box, or enter directly into the edit box using the syntax shown below, where the field name is included in the query using the gislayer.<field_name> syntax.
Examples of this type of query are listed below, and can be found in the SQL example: Critical pipes help topic.
Sequence of Operations
When both spatial search select options and object type select options are defined in the query, the spatial search is carried out first. The main query using object type criteria is then carried out on the results of the spatial search. For example:
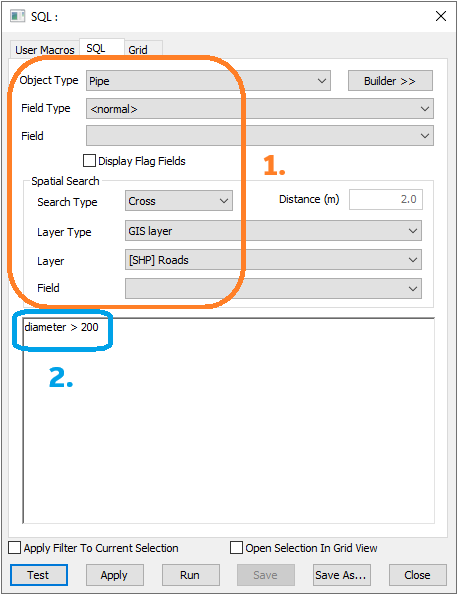
- Object type: Pipe
- [Spatial] Search Type: Cross
- [Spatial] Layer Type: GIS Layer
- [Spatial] Layer: [SHP] Roads
diameter > 200
This query will:
- Search for any pipes crossing roads in the layer '[SHP] Roads'
- Use the pipes found in step 1 to select the pipes that have a diameter greater than 200
Example 1
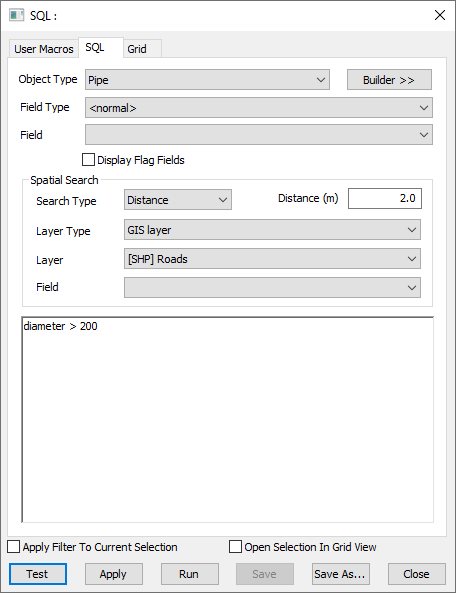
- Object type: Pipe
- [Spatial] Search Type: Distance
- [Spatial] Layer Type: GIS Layer
- [Spatial] Layer: [SHP] Roads
- [Spatial] Distance: 2.0
diameter > 200
uses GIS data to find all pipes with a diameter greater than 200 that lie within 2 metres of a road.
Example 2
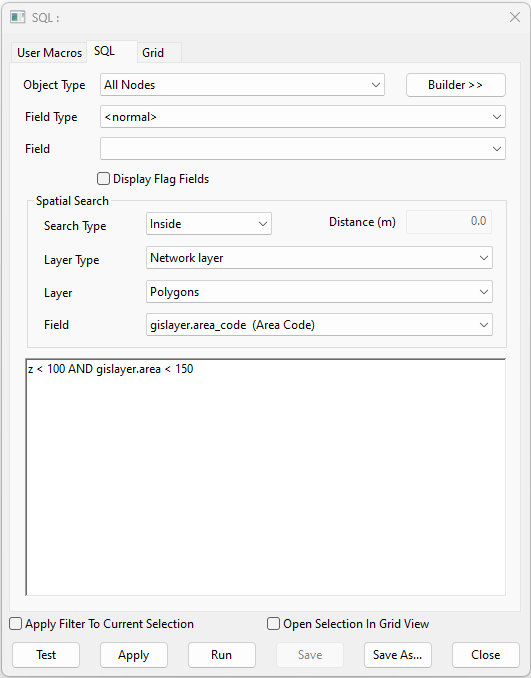
- Object Type: All Nodes
- [Spatial] Search Type: Inside
- [Spatial] Layer Type: Network Layer
- [Spatial] Layer: Polygons
z < 100 AND gislayer.area > 150
selects all nodes that have an elevation less than 100 that are located inside a polygon with an area greater than 150.
Explicit Spatial Searches using the SPATIAL Keyword
The main advantage of using the SPATIAL keyword for spatial searches is that it allows a mixture of lines in the SQL block, some of which use the spatial search and some of which don't.
Performing explicit spatial searches using the SPATIAL keyword also requires defining the object table for the query to perform the search against, which is done through a simple SELECT clause. The order these are written in is:
- SPATIAL query block
- SELECT query block
The syntax for using spatial search in queries is:
SPATIAL <geometry type> <layer type> <layer name>; SELECT FROM <object type>;
SPATIAL <geometry type> <layer type> <layer name> <distance>; SELECT FROM <object type>;
| SPATIAL Syntax Function | Syntax Options | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry Type | Cross | Searches for network objects which intersect a layer line or polygon area. | |
| Inside | Searches for network objects inside a layer polygon. | ||
| Contains | Searches for network polygons with layer objects inside the polygon. | ||
| Distance | Searches for network objects within a search Distance of a layer point, line or polygon. | ||
| Nearest | Searches for nearest network object within a specified Distance. If there is more than one object within the specified distance, the first one found is returned as the result. | ||
| Layer Type | Network | Object layer in the current network | |
| GIS | GIS background layer displayed behind the network in the GeoPlan | ||
| Layer Name | Must be a string in quotes for GIS Layers, and a table name (not in quotes, optionally enclosed by [ ] if it is a single word without spaces, or compulsorily enclosed by [ ] if it isn't) for Network objects. | ||
| Distance |
Important: A
Distance value is only required/used when using either the
Distance or
Nearest geometry types.
Tip: The
Distance field's input value can be a numeric constant or a scalar variable.
|
||
SPATIAL Keyword Usage Rules
- Like standard queries, spatial queries also observe the precedence rules from the SQL dialog i.e. the options specified in the combo boxes and text box serve as the initial spatial configuration until it is changed by a
SPATIAL statement. For example:
SQL query context:
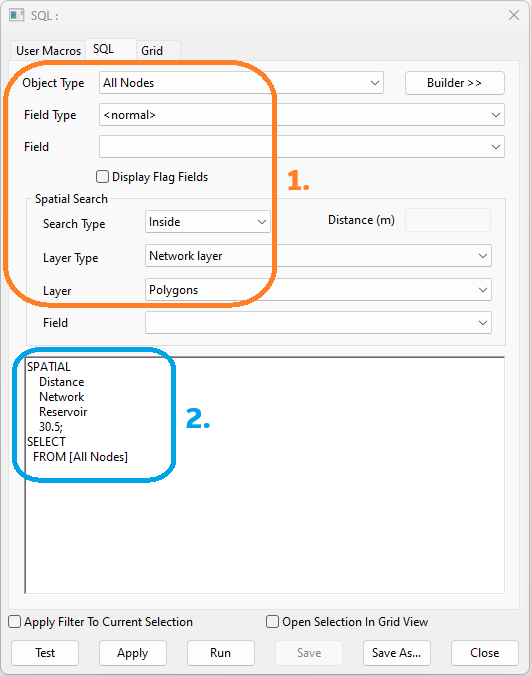
- Object Type: All Nodes
- [Spatial] Search Type: Inside
- [Spatial] Layer Type: Network Layer
- [Spatial] Layer: Polygons
SPATIAL Distance Network Reservoir 30.5; SELECT FROM [All Nodes]
This query will first select all nodes that are located inside a network polygon, and then select all nodes that are within 30.5 units of distance of a reservoir object.
- Any
SPATIAL clause only remains in force until the end of the block containing it i.e.
- If it is within an IF / ELSE / ELSEIF block, then it ceases to have any effect at the end of that block
- If it is in a WHILE block, it ceases to have any effect at the end of that block
- It remains in force in any nested IF / WHILE blocks contained within an existing block
Excluding Spatial Search from Queries
It's also possible to exclude spatial search from segments of queries using the following syntax:
SPATIAL NONE;
When SPATIAL NONE is added as a block to a query, it cancels/nullifies the SPATIAL clause (implicit or explicit) that's in effect for the remainder of the query i.e. the SQL clause has its normal meaning and acts on the data in the network without reference to any spatial search. Additional SPATIAL clauses can be added to a query after a SPATIAL NONE block to introduce new spatial search clauses if desired.
This allows for a mixture of lines in a SQL block, some of which use the spatial search and some of which don't, granting greater flexibility.
Spatial Search Type and Geometry
The table below details the compatible combinations of geometries for each search type.
- For ArcGIS Engine and ArcGIS Desktop GIS layers, the Inside search type finds objects completely inside a polygon.
- For MapXtreme GIS layers, network layers and background network layers, the Inside search type finds objects whose centre is inside a polygon boundary.
- The Cross search type includes all objects Inside a layer polygon and also those which intersect the boundary.
- The Contains search type looks for network polygons with layer objects completely inside the network polygon.
- The Nearest search type looks for the nearest network object within a specified Distance. If there is more than one object within the specified distance, the first one found is returned as the result.
|
Spatial Search Type |
Search Type Description |
Compatible Geometry Combinations |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cross |
Searches for network objects which intersect a layer line or polygon area. |
|
||||||||
|
Inside |
Searches for network objects inside a layer polygon. |
|
||||||||
|
Contains |
Searches for network polygons with layer objects inside the polygon. |
|
||||||||
|
Distance |
Searches for network objects within a search Distance of a layer point, line or polygon. |
|
||||||||
|
Nearest |
Searches for nearest network object within a specified Distance. If there is more than one object within the specified distance, the first one found is returned as the result. |
|
