The soil calculator finds the value of equivalent elastic coefficient for a layered soil.
The calculator is installed during the installation of Robot.
Elastic coefficient may be applied while defining the following.
- Elastic support.
- Bar elastic ground.
- Panel elastic ground.
The calculator allows computation of the elastic coefficient directly on the basis of a defined profile of a layered soil and offers the following functions.
- Define a soil profile with the available soil database and its soil characteristics.
- Save and read a complete user defined soil profile.
- Calculate the elastic coefficient for a defined profile.
- Forward a calculated value to the dialogs for support or ground definition.
The calculator operates as an independent tool which enables calculation of the ground reaction coefficient for a defined foundation and soil profile. A saved soil profile may be used in the RC calculator and the continuous footing calculator.
Launch the calculator by doing the following.
- Select Tools > Building Soils - Calculator.
- Click
 (Building Soils) in the Tools toolbar.
(Building Soils) in the Tools toolbar. - Click Elastic coefficient button located in several different contextual dialogs (such as New support definition, New elastic ground, New thickness definition dialog boxes, and others) in Robot.
- Click the desktop icon for the calculator.
- Select Building Soils - calculations of K coefficient from the All Programs group in the Start Menu.
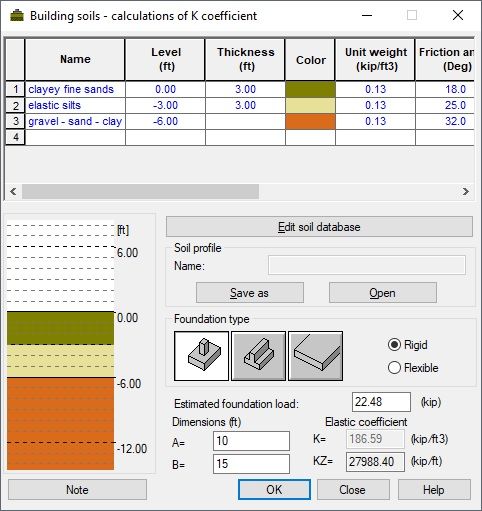
In the calculator, the K coefficient is calculated based on the value of average stresses under the foundation for an area unit. The equivalent KZ coefficient for a foundation with specified dimensions is also computed.
To compute the equivalent K coefficient for a layered soil, do the following.
- Define parameters of the successive soil layers in the table. Consecutive soil layers will be presented schematically in the bottom left part of the dialog. Available soils are from the soil database selected in the Job preferences dialog.
- Select a soil type in the Name column.
- Define the Level or Thickness for level of a given soil layer. Remaining parameters are read from the soil database.
- Choose one of the following foundation types.
-
 Spread footing with dimensions A x B. The KZ coefficient unit is (force/length). A computed value KZ = K * A * B may be applied while defining the elastic coefficient in the support definition dialog.
Spread footing with dimensions A x B. The KZ coefficient unit is (force/length). A computed value KZ = K * A * B may be applied while defining the elastic coefficient in the support definition dialog. -
 Continuous footing with dimensions A (continuous footing length) and B (continuous footing width). The KZ coefficient unit is (force/length^2). A computed value KZ = K * B may be applied while defining the elastic coefficient in the elastic ground type definition dialog.
Continuous footing with dimensions A (continuous footing length) and B (continuous footing width). The KZ coefficient unit is (force/length^2). A computed value KZ = K * B may be applied while defining the elastic coefficient in the elastic ground type definition dialog. -
 Slab foundation with dimensions A x B. The KZ coefficient unit is (force/length^3). A computed value KZ = K may be applied while defining the elastic coefficient in the panel thickness type definition dialog.
Slab foundation with dimensions A x B. The KZ coefficient unit is (force/length^3). A computed value KZ = K may be applied while defining the elastic coefficient in the panel thickness type definition dialog.
-
- Select a rigid or flexible foundation type.
This assumes either an average stress under the foundation from the rigid foundation solution, or from the solution of the elastic semi-space loaded with uniform loads acting on the region defined by the foundation contour. Differences in stress values result in different values of elastic settlement, and in turn, translates into a numerical value of elastic stiffness of the soil. Stress distribution under real structures is closer to the rigid foundation case than to the flexible foundation case.
- Determine an estimated foundation load to limit the scope of calculation of soil stresses (calculating the Value of the K Equivalent Coefficient)
- Determine dimensions of a selected foundation type.
Press Tab key or click OK. A value of the equivalent coefficient for a layered soil will be specified in the K = field.
Clicking OK causes a computed value of the KZ coefficient to be forwarded to the New support definition, New elastic ground or New thickness definition dialogs. This is provided that the relevant dialog is open and the elastic coefficient field is accessible.
Defined soil profiles can be saved on the disk. Click Save as to save a profile to a *.xml (database) file. The File name field displays the current soil profile with a file access path. Click Open to read a file with defined soil profile parameters.
See also:
Description of the Algorithm of Calculating the Value of the K Equivalent Coefficient
