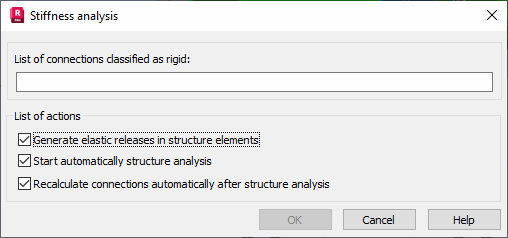
In the Connections layout, select Connections menu > Rigidity Analysis to display the Stiffness analysis dialog.
Currently, stiffness calculations are available for connections with the front plate (such as beam-column and beam-beam) only for Eurocode 3 (2005).
During calculations, a connection type is determined for defined connections and is presented in a calculation note for every connection.
Considering stiffness, connections are defined as:
- nominally pinned
- rigid
- semi-rigid.
Considering resistance, connections are defined as:
- nominally pinned
- connections of full resistance
- connections of partial resistance.
How a connection is classified depends on the global analysis type you perform.
Several types of structure analysis are possible:
- Elastic - a connection is classified due to stiffness
- Rigid-plastic - a connection is classified due to resistance
- Elasto-plastic - a connection is classified due to stiffness and resistance.
In the Stiffness analysis dialog, in the List of connections classified as rigid field, there will be a group of connections that were ascribed the semi-rigid connection type during the connection calculations.
The stiffness analysis and result update consists of several stages:
- Assigning elastic releases to the ends of structure bars corresponding to the bars in the calculated connections; for individual structure bars, appropriate release types are defined automatically. These types will be overwritten when recalculating stiffness for the same nodes.
- Structure recalculation considering the releases assigned.
- Recalculations of all connections considering new values of sectional forces.
