Use the Macro Manager to manage and run your macros.
Macro Manager is the user interface for:
- Selecting an option that launches a session of Visual Studio Code, where you can add, edit, build and debug your macros.
Note: Visual Studio Code and .NET SDK 8.0 are pre-requisites for creating macros in Revit. When installing Visual Studio code, it is recommended to install with the Add to PATH option selected.
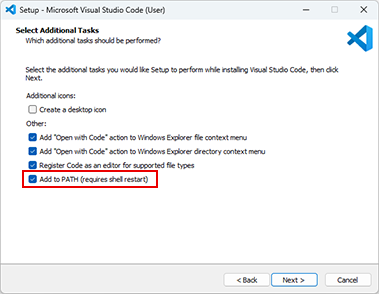 Note: When VSCode is launched you will receive a notification to install the C# extension, it is recommended to install the extension. Without the extension you will be able to use the basic Revit macro functionality, but debugging will not be available.
Note: When VSCode is launched you will receive a notification to install the C# extension, it is recommended to install the extension. Without the extension you will be able to use the basic Revit macro functionality, but debugging will not be available. - Running a previously built macro from a categorized list.
Shown below is the Macro Manager dialog:
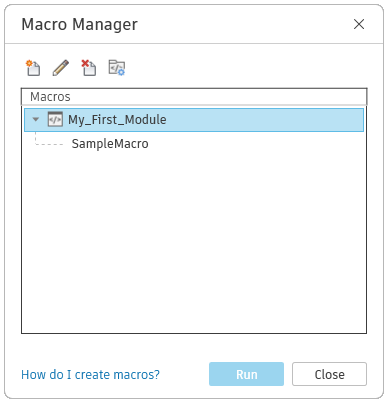
Use the icons located near the top of the dialog to create, edit, and delete modules.
-
Create
 - Create a new module using Visual Studio Code. Name the Module and write macros in the module in C#.
- Create a new module using Visual Studio Code. Name the Module and write macros in the module in C#.
-
Edit
 - Open Visual Studio Code and edit the macros in the selected module.
- Open Visual Studio Code and edit the macros in the selected module.
-
Delete
 - Remove the selected module and its associated macros from
Revit
- Remove the selected module and its associated macros from
Revit
- Configure Path - Configure path will only be shown when multiple versions of Visual Studio Code and .Net SDK are installed. Set the path of the version of the resources you want to use when creating and editing macros.
Macros and Modules
A module is an organizational grouping of macros. Macros can be either independent within a module when they run, or share code or utilities with each other. They are arranged in the Macro Manager as shown in the image above with the macros organized under their parent module.
Macros within a module are seen and built together.
Application-level Modules
Fundamentally, application-level macro tools are written to be useful in any document in nearly any Revit session. Additionally, they do not require a project to be open in Revit to run. This allows you the flexibility to:
- Customize the Revit UI
- Add tools to Revit
- Modify documents on opening
- Batch open documents
- Apply new standards or settings to new documents
Should these uses be implemented, it is good practice to create application-level macros that initiate transactions needed by the macro.
Revit Macro Implementation Language
You create macros in Revit using the implementation language C#.
Now that we have introduced the overall tools and processes, let’s look at the specific tasks.
